* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Endocrinology - Commons
Survey
Document related concepts
Neuroendocrine tumor wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (female-to-male) wikipedia , lookup
Gynecomastia wikipedia , lookup
Sex reassignment therapy wikipedia , lookup
Hormonal breast enhancement wikipedia , lookup
Bioidentical hormone replacement therapy wikipedia , lookup
Polycystic ovary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (male-to-female) wikipedia , lookup
Hypothalamus wikipedia , lookup
Hyperandrogenism wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (menopause) wikipedia , lookup
Graves' disease wikipedia , lookup
Hyperthyroidism wikipedia , lookup
Hypothyroidism wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
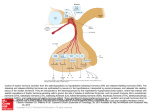
Page 1/1 Get better fidelity in Image View. ENDOCRINOLOGY ASSIGNMENT CLINICAL CHEMISTRY - MLT 233 WENATCHEE VALLEY COLLEGE Directions: (Matching) Match the hormone from the column on the right with the target or source organ, or normal/abnormal function on the left. (An answer from the right column may be used more than once, most are to be used only once – research carefully and choose the best, most typical answer.) Target or Source organ, or Normal or Hormone Abnormal Function 1. ____ Increased water reabsorption A. Thyroxine (T4) 2. ____ Maturation of spermatozoans & ova B. Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH) 3. ____ Hypertension due to cancer of the C. Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH) adrenal medulla (a pheochromocytoma) 4. ____ Induction of labor D. Oxytocin 5. ____ Decreased in hypothyroidism E. Adrenocorticotropic Hormone (ACTH) 6. ____ Large & gross features (acromegaly) F. Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH) 7. ____ Elevated serum [Na] G. Insulin 8. ____ Elevated in hypothyroidism H. Parathormone (Parathyroid Hormone) 9. ____ Increased cortisol (Cushing’s Disease) I. Glucagon 10. ____ Accelerates glyconeogenesis, J. Progesterone inhibits lymphoid development & antibody formation 11. ____ Neuroblastoma K. Aldosterone 12. ____ Primary counterregulatory L. Plasma/Urine catecholamines, or their hormone to insulin metabolites (VMA, HVA, etc.) 13. ____ Maintenance of normal levels of serum M. Growth Hormone (GH or Somatropin) [Ca] and [PO4] 14. ____ beta cells (pancreas) N. Cortisol 15. ____ Suppresses menstruation, ovulation and secretion of LH; stimulates the uterus to prepare it for implantation by the fertilized ovum Find Image View Download a Copy Close