* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Earthquakes and Volcanoes
Survey
Document related concepts
Mount Pinatubo wikipedia , lookup
Mount Garibaldi wikipedia , lookup
Llullaillaco wikipedia , lookup
Mount Meager massif wikipedia , lookup
Mount Pleasant Caldera wikipedia , lookup
Mount Vesuvius wikipedia , lookup
Types of volcanic eruptions wikipedia , lookup
Mount Pelée wikipedia , lookup
Cascade Volcanoes wikipedia , lookup
Mount Edziza volcanic complex wikipedia , lookup
Shield volcano wikipedia , lookup
Cerro Azul (Chile volcano) wikipedia , lookup
Volcano (1997 film) wikipedia , lookup
Wells Gray-Clearwater volcanic field wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
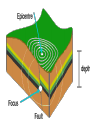
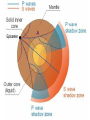
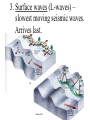
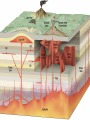
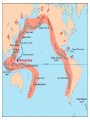
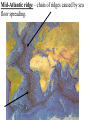
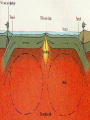
Earthquakes and Volcanoes Earthquakes Earthquake – is the shaking and trembling that results from the sudden movement of part of the Earth’s crust. Tsunamis – A giant sea wave produced by an earthquake. Seismic Waves Focus – The point beneath the Earth’s surface where the rocks break and move, the underground origin of the earthquake. Epicenter – The point directly above the focus, on the earth’s surface where the origin of an earthquake is above ground. Seismic waves – earthquake waves. *Three types. 1. Primary waves (P-waves) – arrive at a given point before any other type of seismic wave. Will pass through solid, liquid and gas.(fastest of the three) 2. Secondary Waves (S-waves) – arrive at a given point after the P wave. (second fastest) Will only travel thru solids. Will NOT pass through liquids and gases thus creating a shadow zone. 3. Surface waves (L-waves) – slowest moving seismic waves. Arrives last. Seismograph – is an instrument that detects and measures seismic waves. Seismogram – is the record of waves. (paper record) Seismologists – scientists who study earthquakes. Richter scale – calculation of the strength or magnitude of an earthquake. For every 1 point rise 30 times the energy is released. Magnitude - Height of a line traced on a seismogram. Liquefaction – Shaking up of wet soil making it unstable. This causes surface object to sink. Earthquake preparedness – Tie down heavy objects, take objects off of high shelves. Build on an earthquake proof foundation. Have a plan and emergency items. Volcanoes Volcano – the place in the Earth’s surface through which magma and other materials reach the surface. Magma – rock that exists as a hot liquid deep within the earth. Lava – is magma that reaches the Earth’s surface. Vent – an opening from which lava erupts. Crater – Steep walled depression around a volcano’s vent. Hot Spot – Hot rock that is a result of unusually hot areas in the mantle and core where volcanoes form on the Earth’s surface. Hawaii is the result of a hot spot. Lava flows • Basaltic – Is lava that contains a lot of water and rich in iron and magnesium. Thin and quiet eruptions. • Granitic - this lava contains very little water and is rich in silicon and aluminum. Thick heavy lava causing gases to trap underneath producing large violent eruptions. Andesitic - is a combination of both granitic and basaltic lava flows (quieter than granitic but more violent than basaltic). Gas filled lava – This lava cools to form hole filled rock that has the appearance of a sponge or loaf of bread. This rock type is typically light in weight. Pumice and scoria are examples of this type of igneous rock. Tephra – bits of rock or solidified lava dropped from the air. Volcanic Dust – Is fragments of rock that are blown into the air during a volcanic eruption. (very small particles) Volcanic Ash – Is particles blown into the air from a volcano that are bigger than volcanic dust yet smaller than anything else. • Volcanic Bombs – Are large rock particles that are blown out during a volcanic eruption. • Volcanic cinders – are smaller volcanic bombs. • Cinder cone volcano – Volcanoes made mostly of cinders and other rock particles that have been blown into the air. Narrow bases with steep sides due to loosely arranged cinder type eruptions. Shield volcano – Volcanoes composed of quiet lava flows. Gently sloping sides with very wide base. Composite Volcanoes – are made of alternating layers of rock particles and lava. Violent eruptions followed by quiet lava flows are the reasoning for the alternating layers. Caldera – A roughly circular, steep-sided pit at the top of a volcanic cone whose diameter is at least three times its depth. Dike – Batholith – Sill - Dormant – (sleeping) has erupted but not in modern time. Extinct – Not known to have erupted in recorded time. Usually weathered down to base. Active – well, it is active in modern time. ZONES Ring of fire – is the zone of active earthquakes and volcanoes due to very active tectonic plate movement. Mid-Atlantic ridge – chain of ridges caused by sea floor spreading.