* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 2 – Chemistry of Life and the Cell
Survey
Document related concepts
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
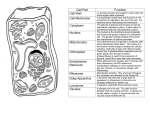
Chapter 2 – Chemistry of Life and the Cell Attributes of a living organism include: growth, movement, reproduction, response to stimuli, and metabolism. All living things are able to maintain homeostasis. Living organisms are made up of molecules based on the element carbon and combined with many other elements. All elements are made of atoms. All atoms are made of: 1. Protons 2. Neutrons 3. Electrons Atoms can bind together to form molecules such as glucose C6H12O6. The three types of chemical bonds are: 1. Covalent bonding 2. Ionic bonding 3. Hydrogen bonding Water (H2O) is one of the most important molecules to life on this planet. 1. Water is a good solvent 2. Water is polar 3. Water is Cohesive Molecules that are hydrophobic do not mix with water i.e. oil and fats. Those that are hydrophilic mix well with water. The pH scale indicates the concentration of H+ or OH-. 1. Low pH is acidic and has more H+ 2. High pH is basic and has more OHProkaryotic organisms are one celled and have no nucleus, bacteria is an example of this kind of cell. Eukaryotic organisms are made up of one or more nucleated cells that contain organelles that perform specific functions. An example of a eukaryote is the human. The Cell is the basic unit of life. The eukaryotic cell is made up of the following structures: Plasma membrane – Membrane that surrounds the cell. Nucleus – Spherical structure in eukaryotic cells that contains chromatin Lysosome – Membrane-enclosed sac that contains digestive enzymes Ribosomes – Two piece structure which aids in translation of DNA Endoplasmic reticulum(ER) – folded membranes coming off of the nucleus which have sections called rough ER and smooth ER. Golgi apparatus – Stacks of membranes in the cytosol. Mitochondria – A membrane folded within a membrane, location of most of cell respiration.