* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Prokaryotes
Survey
Document related concepts
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
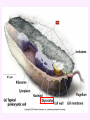
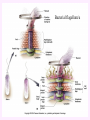
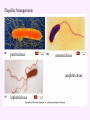
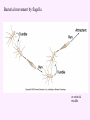
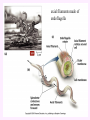
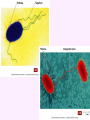
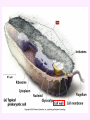
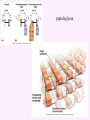
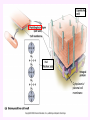
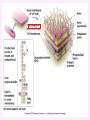
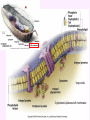
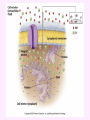
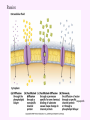
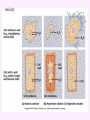
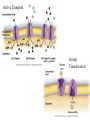
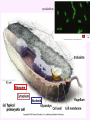
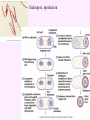
3a - Prokaryotic Cells What is it to be alive? 1) growth What is it to be alive? 1) growth 2) capable of reproduction What is it to be alive? 1) growth 2) capable of reproduction 3) responsiveness/irritability What is it to be alive? 1) growth 2) capable of reproduction 3) responsiveness/irritability 4) perform metabolism What is it to be alive? 1) growth 2) capable of reproduction 3) responsiveness/irritability 4) perform metabolism 5) made of cells What is it to be alive? 1) growth 2) capable of reproduction 3) responsiveness/irritability 4) perform metabolism 5) made of cells 6) involved in evolution Prokaryotes vs. Eukaryotes size organelles (including nucleus) DNA ribosomes Sizes Very large bacteria Thiomargarita namibiensis Common prokaryotic cell shapes Fig. 11.1 Bacterial flagellum/a Flagellar Arrangements peritrichous monotrichous amphitrichous lophotrichous Bacterial movement by flagella or swim & twiddle axial filaments made of endoflagella sheath stalk prostheca peptidoglycan Wall Cytoplasmic/ plasma/cell membrane Why organisms make cells walls hopanoids Cytoplasmic/plasma/cell membrane Nitrosomonas: folded membrane for respiration Rhodospirillum: folded membrane for photosynthesis Passive aquaporin tonicity Active Transport Group Translocation cytoskeleton Other prokaryotic internal structures (inclusions) lipid “Bt” toxin carboxysomes sulfur magnetite aka. gas vacuoles Endospore: sporulation