* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download BIO Ch 4 NOTES Abbreviated
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Causes of transsexuality wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Blood–brain barrier wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Hypothalamus wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
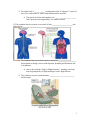
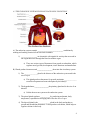
Name________________________________ CHAPTER 4 NOTES PACKET Date______________ 4.1 THE NERVOUS SYSTEM RESPONDS AND CONTROLS A) Our _____________________ help monitor the environment to maintain homeostasis. 1) Our eyes collect, bend and ____________________ light into an image. a) Light is bent onto the _______________ and passes through the pupil. b) Light then enters the lens, which is connected by _______________ so it can move to focus on an image. c) The light forms an upside down image on the _________________ and nerves send the image to the brain, which turns it right side up! i. Within the retina are ___________, which detect grey and dark for night vision and cones, which detect bright light and color for daytime. 2) Ears perceive sound waves, which are produced by _____________________. a) Sound vibrates through the ______________. b) The vibrations are sent through bones called the hammer, anvil and stirrup to the inner ear. c) Cells in the cochlea detect the vibrations and send the message to the brain. 1 3) Sensory receptors in the skin detect pressure, texture, ________________ and temperature. 4) Your nose processes _______________________ information in the back of your nose with hair like fibers, which are covered in mucus. 5) Taste buds on the tongue perceive chemicals in food. B) The brain and ____________________________________ make up the central nervous system, which controls functions. 1) Electrical signals are sent from 100 billion nerve cells called ______________ and travel as fast as 90 meters/second. 2) Every area of the brain has a specific function, which is a ________________ of involuntary response. 2 3) The spinal cord is ____________ cm long and weighs 35-40grams; 31 pairs of nerves are connected to it, which sends information to the brain. a) The spinal cord is the main pathway for ________________________ and is protected and supported by our vertebra column. C) The peripheral nervous system is a network of both _______________________ and motor nerves. 1) The autonomic nervous system conserves and stores ____________________ and responds to change, such as with digestion, breathing and heartbeats and is involuntary. a) Also works with the “Fight or Flight Response,” meaning your body must respond quickly to fight the danger or take flight and run. 2) The voluntary nervous system monitors ____________________________ and functions 3 4.2 THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM HELPS REGULATE BODY CONDITIONS A) The endocrine system controls _____________________________ conditions by making and sending chemicals from one area to another. 1) __________________ are chemicals with signals for activity that are made in one organ that travel through the blood to another organ. a) There are various types of hormones from growth to adrenaline, which regulate mood, growth, development, tissue functions and metabolism. B) Glands produce hormones and _________________ them into the circulatory system. 1) The _______________gland is the director of the endocrine system and is the size of a pea. a) This gland produces hormones for growth, maintains ______________ sexual development and water absorption by the kidneys 2) The hypothalamus ________________the pituitary gland and is the size of an almond. a) It links the nervous system to the endocrine system. 3) The pineal gland regulates ___________ by producing melatonin, body temperature, reproduction and aging and is also the size of a pea. 4) The thyroid gland is the _____________ gland in the body and produces growth and metabolism hormones. It also produces calcitonin, which helps to regulate calcium in the body. 4 5) The __________________ helps the body fight disease, by controlling production of white blood cells or T-Cells. 6) The adrenal glands, located at the top of the _________________, produce about 30 hormones that regulate metabolism, water/salt levels, immunity fight infection or allergies and response to stress. 7) The pancreas produces _______________, which regulates glucose levels in the blood. 5