* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Small Amplitude Short Period Crystal Undulators
Interpretations of quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Particle in a box wikipedia , lookup
Hawking radiation wikipedia , lookup
Quantum group wikipedia , lookup
EPR paradox wikipedia , lookup
Quantum key distribution wikipedia , lookup
Quantum machine learning wikipedia , lookup
Scalar field theory wikipedia , lookup
Quantum state wikipedia , lookup
Atomic theory wikipedia , lookup
Symmetry in quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Bremsstrahlung wikipedia , lookup
Hidden variable theory wikipedia , lookup
Wave–particle duality wikipedia , lookup
Quantum electrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
Planck's law wikipedia , lookup
History of quantum field theory wikipedia , lookup
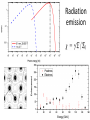
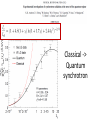
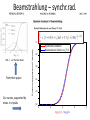
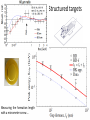
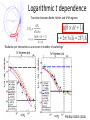
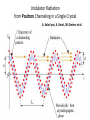
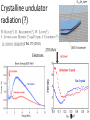
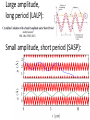
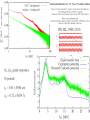
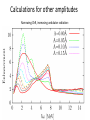
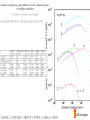
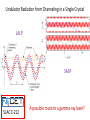
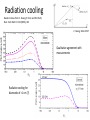
Small Amplitude Short Period Crystal Undulators - a New Type of Gamma-Ray Source Ulrik I. Uggerhøj Department of Physics and Astronomy Aarhus University, Denmark On behalf of the collaborations CERN NA63 and SLAC E-212 Strong field effects - crystalline targets Strong fields •Strong – compared to what? • The critical field: Relativistic invariant: Radiation emission Classical -> Quantum synchrotron Beamstrahlung – synchr.rad. From their paper Our curves, supported by meas. in crystals Quantum suppression of intensity 1.0 Synchrotron radiation Blankenbecler & Drell, eq. (7.5) 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.0 -4 -2 0 log10(1/), log10(C) 2 4 Formation length effects - amorphous targets Structured targets Measuring the formation length with a micrometer screw.... Logarithmic t dependence Transition between Bethe-Heitler and LPM regimes: ’Radiation per interaction as a function of number of scatterings’ PRD 81, 052003 (2010) Crystalline undulators Undulator Radiation from Positron Channeling in a Single Crystal A. Solov’yov, A. Korol, W. Greiner et al. Crystalline undulator radiation (?) C 34, 175 (2011) Electrons Large amplitude, long period (LALP): Small amplitude, short period (SASP): Calculations for other amplitudes Narrowing ChR, increasing undulator radiation: Electrons Positrons 10 GeV, 12 μm Si, a=0.4 Å _____ incl. Quantum corr. -------- excl. Quantum corr. Next step, SLAC E-212 20 GeV electrons and positrons, strong fields, quantum regime undulator GDR energies Undulator Radiation from Channeling in a Single Crystal LALP SASP SLAC E-212 A possible route to a gamma-ray laser? Thank you! Transverse energy states Harmonic potential for positrons equidistant transverse energy states ‘Population inversion’ from high-lying transverse energy states Lorentz boost => a factor γ Doppler-shift back to the lab => another factor 2γ Measurements in Si (1980’s), event-based Enhancements of 80-100... (110) (110) Radiation cooling Based on ideas from: Z. Huang, P. Chen and R.D. Ruth, Nucl. Instr. Meth. B 119 (1996), 192 Z. Huang, SLAC-R-527 Qualitative agreement with measurements Radiation cooling for diamonds of >1 cm (?)