* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Evolution T/F
Sociocultural evolution wikipedia , lookup
Sexual selection wikipedia , lookup
Unilineal evolution wikipedia , lookup
Creation and evolution in public education wikipedia , lookup
Paleontology wikipedia , lookup
Acceptance of evolution by religious groups wikipedia , lookup
Sociobiology wikipedia , lookup
Natural selection wikipedia , lookup
Evolving digital ecological networks wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Catholic Church and evolution wikipedia , lookup
Inclusive fitness wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary mismatch wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
The Descent of Man, and Selection in Relation to Sex wikipedia , lookup
Genetics and the Origin of Species wikipedia , lookup
Theistic evolution wikipedia , lookup
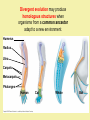
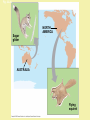
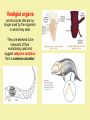
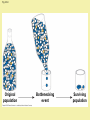
Evolution T/F … _____ explains how organisms change over time _____ is a theory that has been proven to be true _____ assumes that all living organisms are somehow connected to each other _____ is no longer occurring in humans _____ produces organisms that are bigger, stronger, faster, and/or smarter _____ could be occurring with people in this room right now _____ happens when organisms want (or need) to change … be prepared to justify your groups response Evolution – The process by which modern organisms have descended from ancient organisms. Evolution – The process by which modern organisms have descended from ancient organisms. Adaptation – A trait that helps an organism be better suited to its environment. ex) a ducks webbed feet Another Adaptation!!! Fitness – The physical traits and behaviours that better enable organisms to survive and reproduce in their own environment. Fitness … can take many forms. It’s not always the biggest, strongest, & fastest. EXPLANATIONS FOR EVOLUTION Around 1800, scientists began to realize that living things changed over time. Charles Darwin (1809-1882) • English naturalist • travelled around the world on the H.M.S. Beagle observing plant and animal life • the trip took over 5 years Darwin’s time on the Galapagos Islands had a big impact on him developing his theory of evolution. marine iguana flightless cormorant Galapagos penguin Sally Lightfoot crab frigate bird Galapagos Finches The 13 species of Galapagos Finches were also important to Darwin developing his Theory of Evolution. Observation Extraordinaire Finches from different islands with different sources of food (nuts, berries, nectar, insects, etc) had different beaks! Adaptations develop through natural selection. How do adaptations evolve through natural selection? Within a species there is Speckled moths may be variation for all traits. more white or black in Organisms that have certain varieties of a trait will have a slightly better chance of surviving and reproducing. color Moths born with more black pigment are better likely to blend into the dark background of tree bark and therefore are less likely to be eaten. How do adaptations evolve through natural selection? Traits are inherited from parents. Those that will survive may pass on their beneficial traits to their offspring. The cycle continues and the population changes … ADAPTIVE RADIATION leads to EVOLUTION through NATURAL SELECTION. Surviving moths will reproduce and pass on their traits to their offspring. Over many generations the population of moths evolves to become darker. Making it better adapted to its environment. • Darwin decided that species change over time • in 1859, he published his famous book that describes his theory of evolution • a key part of the theory was the idea of Common Descent. It argued all species have evolved from one common ancestor. an evolutionary tree, from one of Darwin’s notebooks Further Influences on Darwin: Charles Lyell (a rock star - geologist) • he argued the Earth was very old while most believed earth to be a few thousand years old • this meant common descent could have had enough time to occur Further Influences on Darwin: Farmers • Darwin knew farmers altered their stocks with breeding programs (artificial selection) • with a.s. humans ensure only animals with desirable traits are allowed to breed • Darwin felt nature must have a similar process only allowing the best suited to the environment to survive Further Influences on Darwin: Thomas Malthus • he realized babies were being born faster than people were dying • he felt only famine, disease and war would prevent endless human population growth • Darwin extended this to plants & animals as he realized many individuals of each species die and few raise offspring. The question was what determined who survived and reproduced? • In 1858 Alfred Wallace wrote to Charles Darwin about his ideas of evolution. • His work also describes the theory of natural selection. • Wallace and Darwin copublished a paper on evolutionary theory and are considered the co-discoverers of the Theory of Evolution. • Each man gave the other as much credit as possible. Traits are inherited from parents to offspring Spore cloud Reproduction creates offspring that have variations from their parents … and each other! Organisms vary within a species as no two individuals are exactly alike! This leads to a great deal of diversity of characteristics within a population. Members of a population often vary greatly in their traits Some traits make an organism more likely to survive in their environment. … others … not so much!. Fig. 22-12 A flower mantid in Malaysia A stick mantid in Africa Offspring with traits that are most “fit” for their environment will outcompete others and pass these traits on. Evolution by natural selection results in a population that is better adapted (suited) to its environment. Evolution at its best? Divergent Evolution - an ancestral species gives rise to a number of new species. This is also known as adaptive radiation! Darwin’s finches likely developed different beaks through divergent evolution due to natural selection. Diverge you finches! Diverge you bear (–like creatures)! Divergent evolution may produce homologous structures when organisms from a common ancestor adapt to a new environment. Humerus Radius Ulna Carpals Metacarpals Phalanges Human Cat Whale Bat Convergent Evolution - similar structures develop from separate ancestors because the organisms occupy a similar niche. These are analogous structures Nature selects a similar outcome! Similar environment selects for similar trait Converge you web-footed creatures! Converge you swimmy marine creatures! Converge you … wacky looking insect eaters! Animals in Australia are weird because they have been separated from the rest of the world for a long time and evolved separately. They still developed analogous structures to animals elsewhere due to having similar niches. Converge you crazy aussies! Fig. 22-20 Sugar glider NORTH AMERICA AUSTRALIA Flying squirrel Vestigial organs are structures that are no longer used by the organism in which they exist They are believed to be remnants of their evolutionary past and suggest adaptive radiation from a common ancestor Genetic Drift • Occurs more frequently in smaller populations • Genetic drift tends to reduce genetic variation through losses of alleles Animation: Causes of Evolutionary Change The rest of the population dies randomly (is eaten) Remaining population is different due to the Bottleneck Effect Some brave Smarties relocate to a new area Population is different due to the FounderEffect Fig. 24-6 A. harrisi A. leucurus If organisms are well suited to their environment … evolution can be very minimal! The tuatara is thought to have evolved little in the last 200 to 250 million years. The photo shows Henry. He is 111 and is the father of babies that hatched in January, 2009. Crocodiles are thought to have evolved little in the last 200 million years. Mountain Goats near Mt. St. Helens show little variation caused by a genetic drift Horseshoe Crabs were present around 230 million years ago with very similar species existing over 400 million years ago. Darwin’s Theory of Natural Selection states: • survival of the fittest organisms with favourable variations survive and reproduce the individuals with characteristics not well suited to their environment either die or leave fewer offspring in this way, favourable variations are passed from generation to generation Evolution by Natural Selection – Key Points • Note that individuals do not evolve; populations evolve over time • Natural selection can only increase or decrease heritable traits in a population • Adaptations vary with different environments Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings Natural Selection Lamarck believed in the inheritance of acquired characteristics. Consider the ears and tails of Doberman Pinschers. Fig. 23-9 Original population Bottlenecking event Surviving population