* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CR 10: Myocarditis mimicking an acute coronary syndrome
Survey
Document related concepts
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Remote ischemic conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
Cardiothoracic surgery wikipedia , lookup
Drug-eluting stent wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
History of invasive and interventional cardiology wikipedia , lookup
Echocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac arrest wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
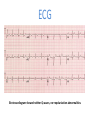
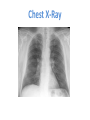
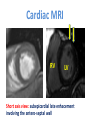
CR 10: Myocarditis mimicking an acute coronary syndrome. Contribution of cardiac MRI Sdiri W., Mbarek D., Tlili R., Ben Ameur Y., Boujnah M. R. Cardiology Departement – Mongi Slim University Hospital La Marsa – TUNISIA Background • Myocarditis is an inflammation of myocardium usually due to a viral infection. • Clinical presentation: Heart failure + Fever • Rarely: chest pain mimicking acute coronary syndromes. Case report • • • • A 42 years-old man. CV risk factors: smoking Admitted to our CCU for prolonged chest pain. Physical exam: Temperature:37.2°C Blood pressure: 14/9 Cardiac auscultation: nomal No cardiac failure. ECG Electrocardiogram showed neither Q waves, nor repolarization abnormalities. Chest X-Ray Biology • White blood cells=11.000el/mm3 • Hb= 16.4g/dl • Creatinin=63µmol/l • Troponin=1.44ng/l • CPK=348UI/l Positive Echocardiography • • • • LVd=48mm LVs=30mm EF=61% No abnormal wall motion • The diagnosis of Non ST Segment Elevation acute coronary syndrome was considered. • The patient received anti-ischemic treatment. • Coronary angiogram: normal. An acute myocarditis was suspected. Cardiac MRI RV LV Short axis view: subepicardial late enhacement involving the antero-septal wall • The diagnosis of myocarditis was finally retained. • The anti-ischemic treatment was stopped. • After 6-month follow-up, the patient is still asymptomatic. Conclusion: • Cardiac MRI is the gold standard for detecting myocardial infarction (subendocardial or transmural enhacement). • It also allows easily the diagnosis of myocarditis (subepicardial late enhacement). • In a context of acute chest pain, Cardiac MRI should be performed if ECG, echocardiogram or coronary angiogram are not conclusive.