* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 20-1: The Heart - Jordan High School
Remote ischemic conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Saturated fat and cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
History of invasive and interventional cardiology wikipedia , lookup
Echocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Cardiothoracic surgery wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
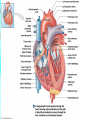
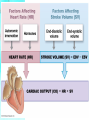
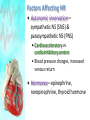
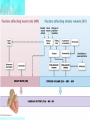
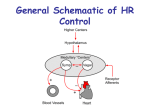
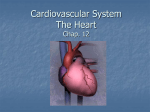
CHAPTER 20 The Heart 20-1: The Heart • Know chambers & where each pumps to • Apex vs. base vs. mediastinum The Pericardium • Pericardial sac vs. visceral pericardium vs. parietal pericardium • Pericardial fluid Superficial Anatomy of Heart • Auricle, coronary sulcus The Heart Wall • Epicardium vs. myocardium vs. endocardium • Cardiac cells joined by intercalated discs Internal Anatomy • See Cardiovascular Hotlist for structures to know, including functions Blood Supply to the Heart • Purpose of coronary circulation • Coronary arteries vs. coronary veins (functions, not names) • Read Spotlight Figure 20-10 (pg 682 – 683) on heart disease & heart attacks 20-2: Conducting System Cardiac Physiology • Conducting system vs. contractile cells The Conducting System • Initiate & distribute electric impulses • SA node vs. AV node vs. AV bundle/bundle branches/Purkinje fibers • Tachycardia vs. bradycardia Electrocardiogram (ECG) • Records heart’s electrical events • P wave vs. QRS complex vs. T wave • What is happening electrically & physically during each wave • Arrhythmias • Premature beats, fibrillation, asystole Contractile Cells • Bulk of atria & ventricular walls • Action potential causes rapid depolarization, then plateau period, then repolarization • Energy for cardiac contractions from mitochondria & glucose 20-3: Cardiac Cycle • Cardiac cycle: systole & diastole Phases of the Cardiac Cycle • Know Figure 20-16 (pg 692) Pressure & Volume Changes in Cardiac Cycle • Use Cardiophysiology Worksheet to help learn this section • Heart sounds—valves closing 20-4: Cardiac Output • Understand EDV, ESV, SV, EF, CO & how to calculate (Cardiophysiology Worksheet) • Factors affecting CO: • Automatic innervation, hormones (affect HR) • EDV, ESV (affect SV) Factors Affecting HR • Autonomic innervation— sympathetic NS (SNS) & parasympathetic NS (PNS) • Cardioacceleratory vs. cardioinhibitory centers • Blood pressure changes, increased venous return • Hormones—epinephrine, norepinephrine, thyroid hormone Factors Affecting SV • EDV—filling time, preload • Greater EVD = greater SV • Frank-Starling principle • ESV • Contractility—positive/negative inotropic affects (SNS causes positive; PNS causes negative) • Afterload—increase causes decrease in SV