* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download WorthamSemester2LS-1st4.5 Study Guide
Survey
Document related concepts
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
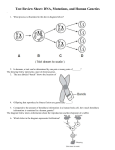
S2- Life Science 4.5 Assessment Study Guide Vandiver/Wortham Directions: Use the pedigree below to answer the following questions. 1. Which shape represents an affected male? Shaded square 2. Which shape represents an unaffected female? Unshaded circle 3. How many males are there in all generations? 8 4. How many generations are represented on the pedigree? 3 5. How many females are affected with the disorder? 4 6. How many marriages are there? 4 7. How many children did the couple in row one have? 5 8. How many children did the couple in row one have? 5 9. In a living thing, a characteristic such as eye color is a _trait________. 10. _Down Syndrome is a genetic disorder where a person’s cells have an extra copy of chromosome. It results in some degree of mental retardation and possible heart defects. 11. One advantage to asexual reproduction is _it happens faster________. 12. One advantage to sexual reproduction is __there is more genetic variety________. 13. The passing of characteristics from parents to offspring is called _heredity_______________. 14. The joining of egg and sperm is called __fertilization________________________________. 15. An organism with two different alleles for a trait called a _heterozygous or hybrid__. 16. What is the genetic code for a female? _XX____ 17. What is the genetic code for a male? _XY_____ 18. An allele whose trait is masked in the presence of a dominant allele is a _recessive_________. 19. An allele whose trait always shows up or is expressed in the organism is a _dominate_______. 20. Segments of chromosomes that control a specific trait of an organism are called __gene_____. 21. The visible traits and behavior of an organism is called _phenotype__________________. 22. What is the shape of DNA? __double helix______. 23. What is the function of a chromosome? _it carries a cell’s genetic material to new cells____ 24. On which pair of chromosomes can the code for the organism’s sex be found? _#23_ 25. _Sickle Cell Anemia____ is a genetic disorder that is codominant, affects hemoglobin, and causes the red blood cells to have a sickle shape. 26. A permanent change in a gene or chromosome of a cell that can be helpful, harmful, or have no effect at all on an organism is a __mutation_______. 27. _Environment______ mainly determines if a mutation is helpful, harmful, or has no effect. 28. The nitrogen base that pairs with adenine is _thymine____. 29. The nitrogen base that pairs with guanine is _cytosine____. Punnett Squares: Complete the Punnett Square. Then answer questions related to the Punnett Square. What are the results when a heterozygous male mates with a female who has a red hair? Brown hair is dominant to red hair. B b b Bb bb b Bb Bb bb 30. What is the genotype of the male? Bb 31. What is the genotype of the female? bb 32. What percentage of the offspring will have brown hair? 50% 33. What percentage of the offspring will have red hair? 50% 34. The sides of DNA are made of _deoxyribose___ and _phosphates____ 35. The “rungs” or steps of DNA are made of _nitrogen bases_____________________. 36. The process that is used to make new body cells is _mitosis____________. 37. The code for making proteins is carried to the ribosome by __messenger RNA______. 38. Proteins are made of units called, _amino acid__ which are linked together in a specific order. 39. __Fertilization____________ is the process of joining egg and sperm to form a zygote. 40. What is the job of a ribosome? Make protein 41. The three stages of the cell cycle are _interphase_, __mitosis___, and _cytokinesis____. 42. Which of the forms of reproduction involves sperm and egg? sexual 43. How many chromosomes are found in the body cells of a human being? 46 44. If a grasshopper has 24 chromosomes it its body cells, how many chromosomes will be in its sex cells? _12___________ 45. Mendel called plants that received different alleles for a trait from each parent _hybrid______. Directions: Identify #37 – 40 as one of the following: a. homozygous dominant b. homozygous recessive 46. Aa __C_______ 47. BB ___A______ c. heterozygous 48. PP __A_______ 49. tt ___B____ Directions: Identify the phenotype for the following genotypes: B = blue b= white a. blue b. white 50. Bb __A_________ 51. BB ___A______ 52. bb ___B_________ Directions: Identify the genotype for the following phenotype. a. Bb b. bb c. WW d. ww 53. Blue flowers _A______ 54. White flowers __B_____ 55. Gregor Mendel experimented with pea plants. What did he discover through his experimentation in the F1 generation when he crossed a dominant trait (tall) with a recessive trait (short)? 100% of the offspring were dominant.