* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download LHC sensitivity to almost all SM Higgs masses 2011-12
Renormalization wikipedia , lookup
History of quantum field theory wikipedia , lookup
Weakly-interacting massive particles wikipedia , lookup
Higgs boson wikipedia , lookup
Grand Unified Theory wikipedia , lookup
Mathematical formulation of the Standard Model wikipedia , lookup
Theory of everything wikipedia , lookup
Elementary particle wikipedia , lookup
Higgs mechanism wikipedia , lookup
Technicolor (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Supersymmetry wikipedia , lookup
Search for the Higgs boson wikipedia , lookup
Minimal Supersymmetric Standard Model wikipedia , lookup
Renormalization group wikipedia , lookup
Peter Kalmus wikipedia , lookup
ALICE experiment wikipedia , lookup
Standard Model wikipedia , lookup
ATLAS experiment wikipedia , lookup
Compact Muon Solenoid wikipedia , lookup
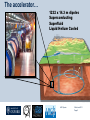
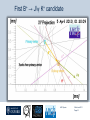
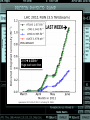
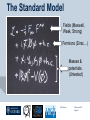
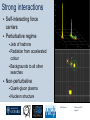
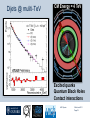
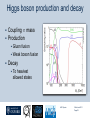
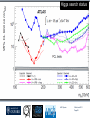
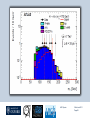
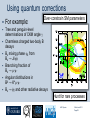
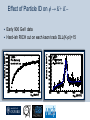
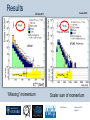
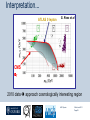
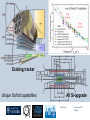
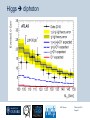
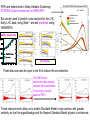
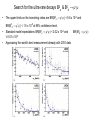
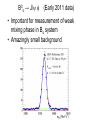
Department of Physics LHC physics Dr Alan J Barr For the TeV-scale physics group Oxford: Synonymous with subatomic physics Frederic Soddy (1877–1956) Dick Dalitz (1925-2006) “I used to know all the data; at one time I knew every event…” Denys Wilkinson (1922-) Transmutation: “The interpretation of Radium” Creation of the Nuclear physics laboratory 1964 International cadre of Oxford-trained physicists LHC Physics 22nd June 2011 Page 2 Oxford’s international standing Global experimental leadership in: Detectors Tracker R&D Construction & upgrade Monte Carlo Simulation Triggering / selection algorithms Calibration Exploitation / analysis Stellar international reputation (Even before talking about accelerators & theory…) LHC Physics 22nd June 2011 Page 3 Large Hadron Collider LEP [ CERN ] Geneva HERA [ DESY ] Hamburg TEVATRON [ FermiLab ] Chicago LHC [ CERN ] Geneva Particles: Electron Positron ElectronProton ProtonAnti-proton ProtonProton Beam energy/TeV 0.105 e: 0.030 p: 0.92 0.980 7.0 (current 3.5) 75 402 10,000 Luminsoity 100 (1030 cm-2 s-1) Stored energy (magnets) ~ GJ 1 MJ melts 1.5 kg Cu Stored energy (beam) ~ 100 MJ LHC Physics 22nd June 2011 Page 4 The accelerator… 1232 x 14.3 m dipoles Superconducting Superfluid Liquid Helium Cooled LHC Physics 22nd June 2011 Page 5 ATLAS Segment of 4π detector LHC Physics 22nd June 2011 Page 6 Semiconductor Tracker… Robotic assembly of precision silicon tracker 2004 2005 LHC Physics 22nd June 2011 Page 7 LHC Physics 22nd June 2011 8 The LHCb spectrometer 4Tm Dipole Vertex Locator (Silicon) RICH detectors Tracking Calorimeters LHC Physics Muon System 22nd June 2011 Page 9 RICH1 Front-end electronics Johan Fopma, Phil Sullivan & the electronics workshop team PIXEL anodes Kaptons Level-0 board LHC Physics 22nd June 2011 Page 10 RICH1 Mechanics Mike Tacon & the workshop team Design and constructed the lower HPD mounting system Designed the upper system Designed the RICH gas enclosure 2009: Cosmic rays Precision alignment Calibrations Data acquisition Combined tests LHC Physics 22nd June 2011 Page 12 March 2010: first collisions LHC Physics 22nd June 2011 13 First B+ → J/ K+ candidate 5 April 2010, 01:30:09 LHC Physics 22nd June 2011 Page 14 LAST WEEK 2010 0.035 fb-1 Huge reach even then LHC Physics 22nd June 2011 Page 15 The Standard Model Fields (Maxwell, Weak, Strong) Fermions (Dirac…) Masses & potentials. (Untested) LHC Physics 22nd June 2011 Page 16 Sure things Strong interaction Weak interaction Higgs Sector or other EWSB Flavours 3rd generation quarks (t and b) CP violation 45 physics publications from ATLAS on last year’s beam data LHC Physics 22nd June 2011 Page 17 Strong interactions Self-interacting force carriers Perturbative regime Jets of hadrons Radiation from accelerated colour Backgrounds to all other searches Non-perturbative Quark-gluon plasma Nucleon structure LHC Physics 22nd June 2011 Page 18 Dijets @ muliti-TeV CM Energy = 4 TeV Excited quarks Quantum Black Holes Contact interactions LHC Physics 22nd June 2011 Page 19 Weak interactions Masses and couplings well known Self-interactions under study Cross-sections diverge without new physics WW ZZ LHC Physics 22nd June 2011 Page 20 W charge asymmetry Vector – Axial couplings (Chiral couplings) Probe proton structure (Parton distributions) Cancellation of systematic uncertainties LHC Physics 22nd June 2011 Page 21 Higgs sector – the model Field couples to mass Scalar potential Vacuum expectation value W, Z masses via Higgs/gauge interactions Fermion masses via Higgs/Yukawa coupling Field excitation = Higgs boson(s) LHC sensitivity to almost all SM Higgs masses 2011-12 LHC Physics 22nd June 2011 Page 22 Higgs boson production and decay Coupling mass Production Gluon fusion Weak boson fusion Decay To heaviest allowed states LHC Physics 22nd June 2011 Page 23 Last week: full ATLAS search Higgs analysis of 2010 data LHC Physics 22nd June 2011 Page 24 Higgs search status LHC Physics 22nd June 2011 Page 25 LHC Physics 22nd June 2011 Page 26 3rd Generation: t and b Three generations needed for CP violation Nearly decoupled from first two generations Long lived b-quark hadrons Standard Model: top Higgs coupling ~unity Radiative corrections from top on mH Role in electroweak symmetry breaking? LHC Physics 22nd June 2011 Page 27 LHC Physics 22nd June 2011 Page 28 Using quantum corrections Over-constrain SM parameters For example: Tree and penguin-level determinations of CKM angle Charmless charged two-body B decays Bs mixing phase s from Bs → J/ Branching fraction of Bs → +Angular distributions in B0 → K*+Bs → and other radiative decays Hunt for rare processes LHC Physics 22nd June 2011 Page 29 Effect of Particle ID on → K+ K Early 900 GeV data Hard-ish RICH cut on each kaon track DLL(K-pi)>15 Example of CP violation measurement 2010 data Separate samples into B0 and B0 using particle ID Raw asymmetries clearly visible in data: direct CP Violation > 3s Central values consistent with expectations and previous measurements NB: corrections from production and detector asymmetry not yet corrected for CP violation Bd0 Bs0 More speculative (perhaps?)… Further generations Unification of forces Supersymmetry WIMPs Compositeness / substructure New gauge forces / particles Strong gravity Extra dimensions Something else? LHC Physics 22nd June 2011 Page 32 Supersymmetry Partner particles Spin differ by ½ Stabilise mH Dark Matter candidates “Missing” momentum Huge reach at LHC LHC Physics 22nd June 2011 Page 33 Results 3 June 2011 25 Feb 2011 “Missing” momentum Scalar sum of momentum LHC Physics 22nd June 2011 Page 34 Interpretation... ATLAS 0 lepton G. Ross et al CMS T 2010 data approach cosmologically interesting region LHC Physics 22nd June 2011 Page 35 LHC and ATLAS upgrade schedules LHC Phase-0 Shutdown: End 2012-mid 2013 Physics resumes 2014 ATLAS Phase-0 IBL installation Repairs/consolidation Phase-I shutdown End of 2017 Physics resumes end of of 2018 Phase-II End of 2021 Phase-I shut down Muon small wheels Mini-FCAL L1 calo topological trigger Calorimeter readout NewPix Phase-II Tracker ready on surface end of 2020 TDAQ LHC Physics 22nd June 2011 Page 36 Existing tracker Unique Oxford capabilities All Si-upgrade LHC Physics 22nd June 2011 Page 37 Software Operations Hardware Grid Computing Detector & Upgrade LHC Physics 22nd June 2011 Page 38 AJB EXTRA SLIDES LHC Physics 22nd June 2011 Page 39 Semiconductor Tracker close-up LHC Physics 22nd June 2011 Page 40 LHC Physics 22nd June 2011 Page 41 Four Detectors <10> inelastic collisions @ 20 MHz crossing rate Record ~100 events/s 1 MB per event Micron-scale precision LHCb ATLAS ALICE CMS LHC Physics 22nd June 2011 42 Higgs diphoton LHC Physics 22nd June 2011 Page 43 December 2008 LHC Physics 22nd June 2011 Page 44 PDFs are determined in Deep Inelastic ScatteringSTRONG Oxford involvement in HERAPDFBut can be used to predict cross sections for the LHC. Early LHC data, using 36pb-1, are well predicted using HERAPDFs CMS μ asymmetry ATLAS jets These data can also be input to the fit to reduce the uncertainties The CMS muon asymmetry data already reduces the uncertainties on the low-x u and dvalence PDFs These improvements allow us to predict Standard Model cross sections with greater certainty so that the signal/background for Beyond Standard Model physics is enhanced Search for the ultra-rare decays B0s & B0d → +• The upper limits on the branching ratios are BR(B0s → +-) < 5.6 x 10-8 and BR(B0d → +-) < 1.5 x 10-8 at 95% confidence level. • • Standard model expectations BR(B0s → +-) < 0.32 x 10-8 and BR(B0d → +-) < 0.01 x 10-8 Approacing the world’s best measurement already with 2010 data B0s → J/ (Early 2011 data) • Important for measurement of weak mixing phase in Bs system • Amazingly small background