* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ATLAS experiment at the CERN Large Hadron Collider
Eigenstate thermalization hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Casimir effect wikipedia , lookup
History of quantum field theory wikipedia , lookup
Scalar field theory wikipedia , lookup
Renormalization wikipedia , lookup
Quantum chromodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Canonical quantization wikipedia , lookup
Peter Kalmus wikipedia , lookup
Double-slit experiment wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Atomic nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear structure wikipedia , lookup
Supersymmetry wikipedia , lookup
Identical particles wikipedia , lookup
Technicolor (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Weakly-interacting massive particles wikipedia , lookup
Strangeness production wikipedia , lookup
Electron scattering wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
Grand Unified Theory wikipedia , lookup
Higgs boson wikipedia , lookup
Mathematical formulation of the Standard Model wikipedia , lookup
Minimal Supersymmetric Standard Model wikipedia , lookup
Higgs mechanism wikipedia , lookup
Search for the Higgs boson wikipedia , lookup
Elementary particle wikipedia , lookup
ALICE experiment wikipedia , lookup
Standard Model wikipedia , lookup
ATLAS experiment wikipedia , lookup
Future Circular Collider wikipedia , lookup
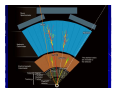
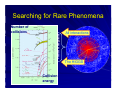
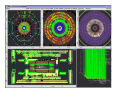
ATLAS experiment at the CERN Large Hadron Collider Peter Watkins, Head of Particle Physics Group, University of Birmingham, UK [email protected] Large Hadron Collider (LHC) Point 1 activities and perspectives Marzio Nessi plenary ATLAS d Outline of talk • • • • • Building blocks of the universe Why do experiments at the LHC ? LHC, ATLAS and collaboration Searching for a new particle Recent LHC news Acknowledgements – Many slides from LHC colleagues 4 The very small electron nucleus 10-10 m (thickness of human hair ~ 10-5 m) 10-14 m proton neutron 10-15 m up quark down quark < 10-18 m Fundamental Forces All forces are carried by particles ! Gravity – solar system, galaxies …- extremely weak force Electromagnetic – atoms, electricity ….. - carried by photons Weak force – beta decay and how stars generate energy - carried by massive W and Z bosons Strong – binds quarks inside proton carried by gluons Higgs boson? The Higgs Boson One key objective of the LHC is to understand the origin of mass – is it due to a universal Higgs field? (A Higgs field everywhere with the Higgs boson as the force carrier?). Massless particles are not impeded by the Higgs field and, thus, travel at the speed of light. Analogy: Downhill skier experiences no drag by the snow field. Light particles interact weakly with the Higgs field and travel slower. Analogy: Snowshoes on the top of the snow field experience some drag. Heavy particles interact strongly with the Higgs field and travel very slowly. Analogy: Wading through the snow field is a big drag! We call this drag “Mass”. What else is out there? • Various ideas considered… • Dark matter • • Extra dimensions of space • Suggested by superstring theory • Microscopic black holes The The LHC LHC experiments experiments can can look look for for all all of of these these.. Also Alsosensitive sensitiveto tosomething something“completely “completelydifferent” different” The Large Hadron Collider (LHC) Mont Blanc Geneva Airport The LHC is a 27km accelerator that collides counter-rotating beams of protons of up to 7 TeV. (Tev = million million eV) Energy densities similar to billionths of a second after the big-bang will be recreated at collision points CERN laboratory on Swiss – French border Building the LHC In the main ring: 1746 superconducting magnets … including 1232 15m SC dipoles … weighing 27 tonnes each … producing 8.36 Tesla … and running at –270c … needs 700,000 litres liquid He … and 12 million litres liquid N2 The fastest racetrack on the planet The protons will reach 99.9999991% speed of light, and go round the 27km ring 11,000 times per second Collision points At four places the beams intersect Hot spots too ! When the two beams of protons collide, they will generate temperatures 1000 million times hotter than the heart of the sun, but in a minuscule space ATLAS Detector 7,000 tonnes 42m long 22m wide 22m high (About the height of a 5 storey building) 2,800 Physicists 169 Institutes 37 Countries Electromagnetic Calorimeter A basic calorimeter Basics The past Challenges Where to start? Detector Design Tracker Calorimetry Particle ID LHC detectors “Events” Final thoughts Total # of particles is proportional to energy of incoming particle Active detector slices produce a signal proportional to the number of charged particles traversing Muon Detectors E2 = p2c2+ m2c4 Discovering a new particle The collision rate challenge • Proton bunches collide 40 million times a second • ~25 proton-proton collisions occur each time • 1000000000 collisions per sec – 200 per second limit for recording • Select the most ‘interesting’ collisions in few microseconds Searching for Rare Phenomena 9 orders of magnitude Number of collisions All interactions The HIGGS Collision energy 50 magnets repaired 3 km of beam pipe cleaned LHC status and plans • Large Hadron Collider restarted in Nov 2009 and is working well • World record was set for collision energy in December 2009 • On March 30th 2010 the collision energy was increased to 7 TeV • Some early measurements already published • Search for Higgs boson needs more collisions Z boson candidate Summary • Many people are interested in the LHC and the key ideas are widely accessible • The searches for new particles are only just beginning and will last for a decade • We work on sharing the excitement of the project with the widest possible audience • We need your help to do this to an even wider audience! Thanks for listening