* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slide ()
Survey
Document related concepts
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
G protein–coupled receptor wikipedia , lookup
Purinergic signalling wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
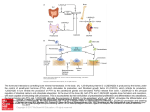
PTH effects on bone. PTH binds to osteoblast parathyroid hormone receptor 1 (PTHR1), stimulating the cell surface expression of RANKL, which binds to RANK, a cell surface protein on osteoclast precursors. Binding of RANKL to RANK activates osteoclast gene transcription and the differentiation into a mature osteoclast, characterized by the ruffled membrane under which bone resorption occurs. Osteoclasts attach to the bone surface through β-integrins generating an isolated extracellular microenvironment. Acidic intracellular vesicles fuse to the cell membrane facing the bone matrix forming the scalloped or ruffled border. Hydrogen ions generated by carbonic anhydrase II are delivered across the plasma membrane by H+-ATPases recruited into the cell’s ruffled membrane. The acidification of this isolated extracellular microenvironment to a pH of approximately 4 favors the dissolving of hydroxyapatite and Source: Chapter 5. Parathyroid Gland and Ca2+ and PO - Regulation, Endocrine Physiology, 4e provides optimal conditions for the action of the lysosomal proteases4including collagenase and cathepsins to dissolve bone mineral. The products of bone Molina PE. Physiology, 4e; 2013 Available at: http://mhmedical.com/ Accessed:surface August providing 09, 2017 ionized Ca++, inorganic degradation Citation: are endocytosed byEndocrine the osteoclast and transported to and released at the cell’s antiresorptive Copyright © 2017 McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved phosphate, and alkaline phosphatases, into circulation. Osteoprotegerin, secreted by osteoblasts serves as a decoy ligand for RANKL, preventing binding of RANKL to RANK, thereby inhibiting the process of osteoclastic bone resorption. Production of osteoprotegerin is increased by estrogen and decreased by glucocorticoids and PTH. ATPase, adenosine triphosphatase; PTH, parathyroid hormone; RANK, receptor activator of nuclear factor-κB; RANKL,