* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download RAP80
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcriptional regulation wikipedia , lookup
Comparative genomic hybridization wikipedia , lookup
Community fingerprinting wikipedia , lookup
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
Maurice Wilkins wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
DNA repair protein XRCC4 wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Transformation (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
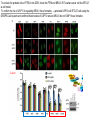
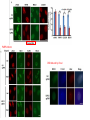
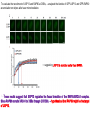
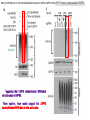
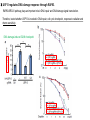
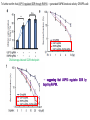
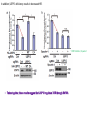
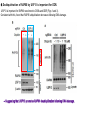
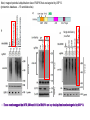
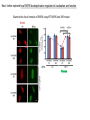
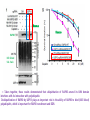
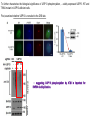
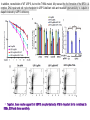
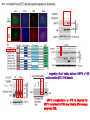
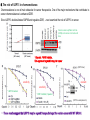
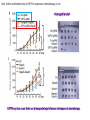
2017. 06. 08 Jin-Sun Ryu Introduction BRCA1 functions in a number of cellular pathways that maintain genomic stability including DNA damage-induced cell cycle checkpoint activation, DNA repair (HR), protein ubiquitination, chromatin remodelling, transcriptional regulation and apoptosis. [Her J et al., Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2016] * RAP80 ; ubiquitin-interacting motifs (UIMs) [Yan J, Jetten AM., Cancer Lett. 2008] RAP80 is important for BRCA1 recruitment to the DSBs and RAP80 depletion results in loss of BRCA1 focus formation, induces genomic instability and impairs HR. RAP80 fine tunes BRCA1 activity and prevents excessive HR by blocking DSB end resection. [Coleman KA, Greenberg RA., J Biol Chem. 2011] * BRCA1-RAP80 → prevents excessive recruitment of the MRN/CtIP and formation of the BRCA1-CtIP-MRN complex → limiting end resection and maintaining an appropriate balance between HR DSB repair and NHEJ in S and G2 cell cycle phases [Kim H et al., Science. 2007] DSB-induced BRCA1 focus formation is essential for proper BRCA1 function in DDR. To further study the regulation of BRCA1 focus formation, → performed a targeted shRNA library screen of the USP subfamily of deubiquitinases for their role in regulating BRCA1 focus formation. Results 1. USP13 regulates RAP80-BRCA1 complex foci formation. DSB-induced BRCA1 focus formation is one of the key signatures for proper BRCA1 function in the DDR. → performed a targeted shRNA library screen of USP family of deubiquitinases for their role in regulating BRCA1 focus formation. USP13 is a deubiquitination enzyme that has been implicated in melanocyte development, hypoxia signalling, tumorigenesis and the endoplasmic reticulum stress pathway. A previous publication reported that USP13 regulates PTEN (tumour suppressor). To exclude the probable role of PTEN in the DDR, chose the PTEN-null BRCA1 WT ovarian cancer cell line EFO-27 as cell model. To confirm the role of USP13 in regulating BRCA1 focus formation, → generated USP13-null EFO-27 cells using the CRISPR-Cas9 system and confirmed that knockout of USP13 reduces BRCA1 but not 53BP1 focus formation. Cisplatin PARP inhibitor DSB induced by I-SceI To evaluate the recruitment of USP13 and RAP80 at DSBs, → analysed the kinetics of GFP-USP13 and GFP-RAP80 accumulation on stripes after laser microirradiation. → suggesting USP13 is recruited earlier than RAP80. ∴ These results suggest that USP13 regulates the focus formation of the RAP80-BRCA1 complex. Since RAP80 recruits BRCA1 to DSBs through CCDC98, → hypothesized that RAP80 might be the target of USP13. 2. USP13 interacts with and deubiquitinates RAP80. Hypothesis ; RAP80 might be the target of USP13. To test hypothesis, first examined whether USP13 interacts with RAP80. Since USP13 is an ubiquitin-specific protease that functions to remove ubiquitin chains from its substrate proteins, → analysed the effect of USP13 expression on RAP80 ubiquitination (in vivo). * USP13- catalytically inactive (CA) mutant * USP13 specific inhibitor, Spautin-1 ∴ These results suggest that USP13 regulates RAP80 ubiquitination and foci formation through its deubiquitinase activity. Next, performed an in vitro deubiquitination assay to further confirm that USP13 directly deubiquitinates RAP80. Ubiquitin ∴ Suggesting that USP13 deubiquitinates K63-linked ubiquitin chain of RAP80. Taken together, these results suggest that USP13 deubiquitinates RAP80 both in vitro and in vivo. 3. USP13 regulates DNA damage response through RAP80. RAP80-BRCA1 pathway plays an important role in DNA repair and DNA damage signal transduction. Therefore, tested whether USP13 is involved in DNA repair, cell cycle checkpoint, response to radiation and chemo sensitivity. DNA damage-induced G2/M checkpoint To further confirm that USP13 regulated DDR through RAP80, → generated RAP80 knockout cells by CRISPR-cas9. DNA damage-induced G2/M checkpoint → suggesting that USP13 regulates DDR by targeting RAP80. In addition, USP13 deficiency results in decreased HR. * USP13 inhibitor ; Spautin-1 → Taken together, these results suggest that USP13 regulates DDR through RAP80. 4. Deubiquitination of RAP80 by USP13 is important for DDR. USP13 is important for RAP80 recruitment to DSBs and DDR (Figs 1 and 3). Consistent with this, found that RAP80 ubiquitination decreases following DNA damage. → Suggesting that USP13 promotes RAP80 deubiquitination following DNA damage. Together with results showing USP13 is important for DDR and RAP80 localization at the sites of DNA damage, → Hypothesized that RAP80 ubiquitination is inhibitory of its (RAP80) function, and deubiquitination of RAP80 by USP13 following DNA damage promotes RAP80 function in the DDR pathway. The UIM domains of RAP80 bind with polyubiquitin K63 linkage following DNA damage, which is critical for the recruitment of RAP80 to the DNA damage sites. Hypothesized that USP13 may regulate RAP80 binding with polyubiquitin K63-linkage following DNA damage through deubiquitinating RAP80. [Troy E. Messick and Roger A. Greenberg, J Cell Biol. 2009] → These results suggest that deubiquitination of RAP80 by USP13 following DNA damage facilitates the binding between RAP80 and K63- linked polyubiquitin chain. Next, mapped potential ubiquitination sites of RAP80 that are targeted by USP13. (proteomics database → 15 candidate sites) 3KR Single deficiency ; no effect → These results suggest that K75, K90 and K112 of RAP80 are key deubiquitination sites targeted by USP13. Next, further explored how RAP80 deubiquitination regulates its localization and function. Examined the focus formation of RAP80 using WT RAP80 and 3KR mutant. RAP80 Rescue Rescue RAP80 Rescue K63 linked Ub. chain → Taken together, these results demonstrated that ubiquitination of RAP80 around its UIM domain interferes with its interaction with polyubiquitin. Deubiquitination of RAP80 by USP13 plays an important role in the ability of RAP80 to bind (K63 linked) polyubiquitin, which is important for RAP80 recruitment and DDR. 5. USP13 is phosphorylated by ATM following DNA damage. USP13 deubiquitinates RAP80 following DNA damage, which in turn facilitates RAP80 recruitment to DSBs. However, how USP13 is regulated in response to DNA damage is unclear. → This result suggests that USP13 may be phosphorylated by ATM following DNA damage. Next analysed the USP13 protein sequence and found three threonine sites fitting the ATM consensus phosphorylation motif (SQ/TQ motif): T196, T380 and T385. → further examined the phosphorylation of these candidate sites. • SQ/TQ motifs, which are consensus ATM or ATR phosphorylation sites • Ku55933 ; ATM inhibitor To further confirm these results, generated site-specific antibody against p-Thr196 and examined the USP13 phosphorylation following DNA damage. ATM-proficient cells ATM-deficient cells → Suggesting ATM phosphorylates USP13 on T196 following DNA damage. To further characterize the biological significance of USP13 phosphorylation, → stably expressed USP13 WT and T196A mutant in USP13-deficient cells. First, examined whether USP13 is recruited to the DSB site. → suggesting USP13 phosphorylation by ATM is important for RAP80 deubiquitination. In addition, reconstitution of WT USP13, but not the T196A mutant, fully rescued the foci formation of the BRCA1-A complex, DNA repair and cell cycle checkpoint in USP13-deficient cells and reversed hypersensitivity to cisplatin or olaparib induced by USP13 deficiency. → Together, these results suggest that USP13 phosphorylation by ATM is important for its recruitment to DSBs, DDR and chemo sensitivity. Next, investigated how USP13 phosphorylation regulates its localization. → suggesting direct binding between USP13 p-T196 residue and the MDC1 FHA domain. USP13 ∴ USP13 phosphorylation by ATM is important for USP13 recruitment to DSB sites following DNA damage and proper DDR. 6. The role of USP13 in chemoresistance. Chemoresistance is one of main obstacles for cancer therapeutics. One of the major mechanisms that contributes to cancer chemoresistance is enhanced DDR. Since USP13 deubiquitinates RAP80 and regulates DDR, → next examined the role of USP13 in cancer. human ovarian epithelial cell line (HOSE) and ovarian carcinoma cell lines. • Olaparib : PARP inhibitor, FDA-approved targeted therapy for cancer (USP13-low) sensitivity resistant sensitivity * USP13 knockout * USP13 inhibitor ; Spautin-1 (USP13-overexpression) → These results suggest that USP13 may be a good therapeutic target for ovarian cancer with WT BRCA1. Next, further confirmed the role of USP13 in response to chemotherapy in vivo. <Xenograft model> ∴ USP13 may be a causal factor and a therapeutic target of cancer cell response to chemotherapy. Discussion USP13 plays an important role in DNA repair and one of the components of the BRCA1 complex, RAP80, is a target of USP13. In response to DNA damage, USP13 is phosphorylated by ATM, which in turn facilitates USP13 recruitment to DSBs, RAP80 deubiquitination, and triggers DDR signalling. Importantly, depleting or inhibiting USP13 sensitizes ovarian cancer cells to cisplatin and Poly (ADPribose) polymerase (PARP) inhibitor (olaparib) suggesting USP13 is a potential novel therapeutic target for ovarian cancer. DSB P Ub Ub ATM MRN RAP80 (no damage) P RNF168 ATM RNF8 /UBC13 MRN Me P P (1) MRN MDC1 53BP1 MDC1 MDC1 Me P MRN MDC1 K63 Ub P USP13 (3) Me Ub Ub Ub Ub 53BP1 P RAP80 USP13 BRCA1 Ub Ub (2) Me 53BP1