* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Monoclonal Antibodies
Survey
Document related concepts
Lymphopoiesis wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Immunocontraception wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Innate immune system wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Anti-nuclear antibody wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
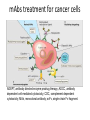
Monoclonal Antibodies Monoclonal antibodies (mAb) are antibodies that are identical because they were produced by one type of immune cell, all clones of a single parent cell. Polyclonal antibodies are antibodies that are derived from different cell lines. • Antibodies have important uses beyond fighting infections in the body. • Production of long-lasting monoclonal antibodies is a recent invention and it is used in both medicine and research. • Monoclonal Antibody: a stable antibody which can be used over a period of time Producing Monoclonal Antibodies 1. Inject a mouse with a specific antigen to stimulate its immune system to produce necessary antibodies. 2. Extract mouse spleen cells (containing Blymphocytes) and culture them in the lab. 3. Extract mouse tumour cells, which grow continuously, and culture them in the lab. 4. Mix spleen cells and tumour cells on the same plate and culture. Producing Monoclonal Antibodies 5. Add polyethylene glycol – this causes some Blymphocytes to fuse with tumour cells to produce a hybrid cell called a hybridoma. 6. Grow the cells under conditions that allow only hybridoma cells to survive. 7. Extract the cells, culture them separately and test the medium around each cell for the specific antibody of interest. 8. Culture the cells making the desired antibody and use as needed. The types of mAb designed A. Murine source mAbs: rodent mAbs with excellent affinities and specificities, generated using conventional hydrioma technology. Clinical efficacy compromised by HAMA(human anti murine antibody) response, which lead to allergic or immune complex herpersensitivities. B. Chimeric mAbs: chimers combine the human constant regions with the intact rodent variable regions. Affinity and specificity unchanged. Also cause human antichimeric antibody response (30% murine resource) C. Humanized mAbs: contained only the small part the rodent variable region grafted onto human variable region framework Evolution of Therapeutic Antibodies Treatment of Cancer • Cancer cells carry specific tumour-associated antigens (TAA) on their plasma membrane. • Monoclonal anti-TAA antibodies have been produced. • Drugs which kill tumour cells or inhibit key proteins in tumour cells are attached to monoclonal anti-TAA antibodies. • Cancer cells are specifically targeted, avoiding damage to healthy host cells. Three mechanisms that could be responsible for the cancer treatment. A. mAbs act directly when binding to a cancer specific antigens and induce immunological response to cancer cells. Such as inducing cancer cell apoptosis, inhibiting growth, or interfering with a key function. B. mAbs was modified for delivery of a toxin, radioisotope, cytokine or other active conjugates. C. it is also possible to design bispecific antibodies that can bind with their Fab regions both to target mAbs treatment for cancer cells ADEPT, antibody directed enzyme prodrug therapy; ADCC, antibody dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity; CDC, complement dependent cytotoxicity; MAb, monoclonal antibody; scFv, single-chain Fv fragment. Problems… • Many patients develop immune response to monoclonal antibodies produced in mice, as these are foreign proteins. • Genetically engineered antibodies are being perfected to avoid triggering immune response.