* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The pH Scale…
Survey
Document related concepts
Water splitting wikipedia , lookup
Water pollution wikipedia , lookup
Nucleophilic acyl substitution wikipedia , lookup
Nanofluidic circuitry wikipedia , lookup
Rutherford backscattering spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Sodium hydroxide wikipedia , lookup
Freshwater environmental quality parameters wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Debye–Hückel equation wikipedia , lookup
Stability constants of complexes wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Acid dissociation constant wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Electrolysis of water wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
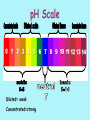
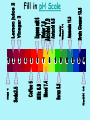
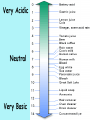
pH What is pH? pH is the scale that tells you whether a substance is acidic, basic, or neutral. pH=“p” stands for power and “H” stands for hydrogen. The values correspond to the concentration of the hydronium ions. What is an acid? An acid is a substance that donates hydrogen ions (H+) to form additional hydronium ions when dissolved in water. Therefore, there is a larger concentration of hydronium ions versus hydroxide ions. What is the formula for a Hydronium ion? Just add an H+ to water (H2O) = H3O+ (hydronium ion) What is a base? A base is a substance that either contains hydroxide ions or reacts with water to form additional hydroxide ions. Therefore, there is a larger concentration of hydroxide ions versus hydronium ions. What is the formula for a Hydroxide ion? Just take an H+ from water (H2O) - = OH There’s no HO’s in science! Do you remember any compounds that had an OH? NaOH Sodium Hydroxide from the Penny Lab! Properties: ACIDS BASES • Sour taste • Can burn skin • Contains more H3O+ than OH- • Bitter taste • Can burn skin • Contains more OHthan H3O+ • Feels slippery/soapy What is a common property of Acids and Bases? They both can burn! The pH Scale… The pH scale ranges from 0-14. 0 = most acidic 7 = neutral (Distilled H2O) 14 = most basic But you can also have… Diluted acids= 3,4,5,6 on the pH scale and Diluted bases = 8,9,10,11 on the pH scale! Diluted vs. Concentrated • Diluted means to weaken with the addition of water. • Concentrated means to strengthen with the absence of water. • Think about when you made Kool-Aid and added too much water and what it tasted like. • Too much water = it was too diluted = Does not taste good! Copy pH scale in Notebook pH Scale Diluted= weak Concentrated=strong During the Lab… You will find the pH level using the pH probe. (take one place after the decimal point) Remember to dip the probe into the clean water BEFORE you dip it into the chemical! You will dip it in the substance for about 30 seconds and record the reading. You will Clean up any spills. Do not waste time talking. You will Hold on to the probe when it is in the beaker. You will Leave the pH probe at the table in the beaker of water! You will Move clockwise after 2 minutes / table. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Post-Lab Questions Which items were the is most acidic? Which items were the most basic? Which items on your scale were neutral? Which items on your scale were weakest acids? Which items on your scale were the weakest bases? 6. Why would you take an antacid if your stomach was upset? 12 7. Label your pH scale with the different substances, according to the pH you found! Copy pH scale in Notebook Fill in pH Scale Acids and Bases • We can have weak acids and bases. Likewise, we can have strong acids and bases. • Neutralize- to add an acid to a basic solution or a base to an acidic solution until it is chemically neutral or safe. (pH = 7). • So…how would you neutralize a strong base like a laundry detergent spill on your skin? Pour large amounts of a weak acid on your skin like vinegar Very Acidic Neutral Very Basic So what’s wrong with Soda? • Prolonged exposure to soft drinks can lead to significant enamel loss (tooth decay)! • The erosive potential of colas is 10 times that of fruit juices in just the first three minutes of drinking!!!