* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download These mountains are formed by compression Fault structures is a
Mount Meager massif wikipedia , lookup
Olympus Mons wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Level Mountain wikipedia , lookup
Craters of the Moon National Monument and Preserve wikipedia , lookup
Mount Pleasant Caldera wikipedia , lookup
Nevado del Ruiz wikipedia , lookup
Mount St. Helens wikipedia , lookup
Cascade Volcanoes wikipedia , lookup
Shield volcano wikipedia , lookup
Mount Edziza volcanic complex wikipedia , lookup
Mount Vesuvius wikipedia , lookup
Mount Pelée wikipedia , lookup
Volcanology of Io wikipedia , lookup
Wells Gray-Clearwater volcanic field wikipedia , lookup
Silverthrone Caldera wikipedia , lookup
Potrillo volcanic field wikipedia , lookup
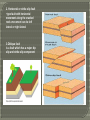
Mountain formation How Are Formed •Convergence due to converging plates can be either continental-oceanic convergence, oceanic-oceanic convergence or continental-continental convergence. •deformation folding and faulting of layers Types of mountains Volcanic mountains Fold- Block mountains Erosional mountains Folded Mountains Volcano -Natural vent or opening in the earth’s crust that is connect by a pipe, or conduit , to a chamber at a depth that contains magma Volcanoes may be: • active •Extinct •Dormant Type of eruption •Hawaiian-out pouring of fluid lava and little explosive activity. •Peleean-violent eruption with viscous lava “ nuees ardentes ’’. •Strombolian-moderate eruptions , small explosions and lava of average viscosity. •Vesuvian-very explosive after a dormant period with ash/gas clouds and gas-filled lava. •Plinian-very explosive with pyroclastics ejected in a column up to 50kg high producing thick air fall deposits Volcanic mountains •found in association with mid ocean ridge systems , plate tectonics , along convergent boundaries. •also known as a composite volcano, tall, conical volcano built up by many layers (strata) of hardened lava, tephra, pumice, and volcanic ash. •built almost entirely of highly fluid basaltic lava, which travel farther than those erupted from more explosive volcanoes Fault-block mountains •are formed when large areas of bedrock are widely broken up by faults creating large vertical displacements of continental crust. Grand Tetons from Jackson Lake Lodge (WY) Erosional mountains •formed by wind or water wearing down weak spots in land and carrying it away. Non-resistant material is washed away, whereas the stronger material remains Rocky mountains(north America) Folded mountain created when two tectonic plates come together . This causes them to rise out of the earth. These mountains are formed by compression •is a structure with major displacement of rock material along a crack in a rock Types of faults • are based on relative movement along the cracked rock and include horizontal, vertical, or a combination of movements 1. Vertical or dip slip fault •type of fault with movement along the dip of the fault--the concepts of hanging wall and footwall are important in defining the different types of vertical faults Normal fault--hanging wall moves down in respect to footwall Reverse fault--hanging wall moves up in respect to footwall--a low angled reverse fault is called a thrust fault •Horst and graben--a wedge of land which moves up (horst) or down (graben) between 2 normal faults 2. Horizontal or strike slip fault •type fault with horizontal movement along the cracked rock--movement can be left lateral or right lateral 3.Oblique fault is a fault which has a major dip slip and strike slip component •Slickenside- a polish and striated rock surface that results from friction along a fault plane. •Striations- means linear furrows generated from fault movement. striation slickenslide grooves Fault breccia, or tectonic breccia, is a breccia (a rock type consisting of angular clasts) that was formed tectonic forces. Fault breccia of the Keystone Thrust, Red Rock Canyon National Conservation Area, Nevada. Fault gouge is an unconsolidated tectonite(a rock formed by tectonic forces) with a very small grain size Salmon-colored fault gouge and associated fault separates two different rock types on the left (dark grey) and right (light grey). From the Gobi of Mongolia.