* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download **** 1
Survey
Document related concepts
Investment fund wikipedia , lookup
Moral hazard wikipedia , lookup
Federal takeover of Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac wikipedia , lookup
Investment management wikipedia , lookup
Pensions crisis wikipedia , lookup
Financial economics wikipedia , lookup
Merchant account wikipedia , lookup
Systemic risk wikipedia , lookup
Financialization wikipedia , lookup
Credit card interest wikipedia , lookup
Syndicated loan wikipedia , lookup
Shadow banking system wikipedia , lookup
Interbank lending market wikipedia , lookup
Credit bureau wikipedia , lookup
Securitization wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
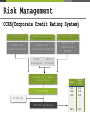
The Role of Credit Guarantee In Capital Relief under New Basel Accords Korea Credit Guarantee Fund (KODIT) 11 May 2016 Contents PowerPoint is a complete presentation graphic package it gives you everything you need to produce a professionallooking presentation 01. Credit Risk Mitigation 02. Prime Operational Factors 01 : Credit Risk Mitigation About us As of the end of Yr 2015 Basel Ⅲ Basel Ⅲ Key principles • Capital requirements requirements • • 𝐶𝑜𝑚𝑚𝑜𝑛 𝑒𝑞𝑢𝑖𝑡𝑦 𝑡𝑖𝑒𝑟 1 𝑅𝑖𝑠𝑘−𝑤𝑒𝑖𝑔ℎ𝑡𝑒𝑑 𝑎𝑠𝑠𝑒𝑡𝑠 𝑇𝑖𝑒𝑟 1 𝐶𝑎𝑝𝑖𝑡𝑎𝑙 𝑅𝑖𝑠𝑘−𝑤𝑒𝑖𝑔ℎ𝑡𝑒𝑑 𝑎𝑠𝑠𝑒𝑡𝑠 𝑇𝑜𝑡𝑎𝑙 𝐶𝑎𝑝𝑖𝑡𝑎𝑙 𝑅𝑖𝑠𝑘−𝑤𝑒𝑖𝑔ℎ𝑡𝑒𝑑 𝑎𝑠𝑠𝑒𝑡𝑠 𝑇𝑖𝑒𝑟 1 𝐶𝑎𝑝𝑖𝑡𝑎𝑙 𝑇𝑜𝑡𝑎𝑙 𝑒𝑥𝑝𝑜𝑠𝑢𝑟𝑒 ≥ 4.5% ≥ 6% ≥ 8% Leverage ratio • Liquidity requirements requirements • 𝐿𝑖𝑞𝑢𝑖𝑑𝑖𝑡𝑦 𝐶𝑜𝑣𝑒𝑟𝑎𝑔𝑒 𝑅𝑎𝑡𝑖𝑜 = ≥ 3% 𝐻𝑖𝑔ℎ 𝑞𝑢𝑖𝑎𝑙𝑖𝑡𝑦 𝑙𝑖𝑞𝑢𝑖𝑑 𝑎𝑠𝑠𝑒𝑡𝑠 𝑇𝑜𝑡𝑎𝑙 𝑛𝑒𝑡 𝑙𝑖𝑞𝑢𝑖𝑑𝑖𝑡𝑦 𝑜𝑢𝑡𝑓𝑙𝑜𝑤𝑠 𝑜𝑣𝑒𝑟 30 𝑑𝑎𝑦𝑠 • 𝑁𝑒𝑡 𝑆𝑡𝑎𝑏𝑙𝑒 𝐹𝑢𝑛𝑑𝑖𝑛𝑔 𝑅𝑎𝑖𝑜 ≥ 100% ≥ 100% Risk Weight The key risk weight Type • Sovereigns Risk Weight (Basel Ⅱ standardized approach) − 0 ~ 150% (differentiated by credit rate) * Republic of Korea : 0% − Equals to that of the government (if the loss is covered) 20 ~ 150% (if the loss is not covered by the government) • Public Institutions • • Banks − Securities Companies 20 ~ 150% (differentiated by credit rate) • Corporates − 20 ~ 150% (differentiated by credit rate) • Cash − 0% − • Secured by commercial real − estate 100% Legal Support Legal support for coverage of loss Korea Credit Guarantee Fund Act Article 41 (Coverage of Loss) ① In case where any profits are made in the closing, those profits shall be reserved in full. ② In case where any losses are incurred in the closing, they shall be covered by the reserve under Paragragh ①, and if the reserves are insufficient, the Government may cover them. Risk Weight Conditions of guarantee to fulfill Basel requirement Irrevocabl e payment Unconditio nal payment Explicit & documented obligation Effect of Credit Guarantee Effect on capital adequacy ratio Direct Effect Loan to SMEs which would not be eligible without CG Credit Supply Increase Indirect Effect Supplying additional credit by Improving capital adequacy ratio Effect of Credit Guarantee Path of indirect effect Step 1 Reducing risk weight of the loan secured by credit guarantee Increasing Capital adequacy ratio of banks Step 2 Step 3 Banks get the effect of increase in equity without actual input of capital Supply additional credit to the market up to 12.5x of the increased capital Step 4 Effect of Credit Guarantee Empirical research result Outstanding guarantee Average coverage ratio 1 USD = 1,140 KRW Loan secured by guarantee $ 26.3 B 87.0 % $ 30.3 B Equity increase effect Minimum CAR Available amount of additional credit $ 2.4 B 8 % $ 30.6 B Direct effect Indirect effect Total amount of additional credit supply $ 60.9 B 02 : Prime Operational Factors to ensure commitment of its liabilities Integrated System for Soundness Four major criteria Legal Support & Supervision Legal support Korea Credit Guarantee Fund Act Legal Basis Mandate Credit guarantee and relevant services Fund(no shareholder or ownership) Type of Entity Government Support Liquidity risk is covered by the government(by law) Legal Support & Supervision Sound governance Budget planning The Board of Policy Operation supervision The Board of Directors Capital contribution Financial Stability Sources of fund Government (irregular) Subject to yearly budget of the government Banks (regular) Mandatory donation in proportion to monthly balance of outstanding corporate loans of commercial banks Others (irregular) Occasional contributions from banks or large enterprises Guarantee Fee SMEs pay 0.5 ~ 3.0% of annual guarantee fee (upfront) Average fee rate : 1.27%(as of 2014) Financial Stability Sources of fund Government (irregular) Subject to yearly budget of the government Banks (regular) Mandatory donation in proportion to monthly balance of outstanding corporate loans of commercial banks Korea Credit Guarantee Fund Act Article 6 ①The equity fund of KODIT shall be built up with resources falling under the followings: 1.Contributions from the government; 2.Contributions from financial institutions; 3.Contributions from enterprises; ③Financial institutions shall make contributions to KODIT such amount by the rate as prescribed in the Ordinance of the Prime Ministry, within the scope of not exceeding 3/1000 per annum of their loans. Financial Stability Source of fund Government (irregular) Subject to yearly budget of the government Banks (regular) Mandatory donation in proportion to monthly balance of outstanding corporate loans of commercial banks Others (irregular) Occasional contributions from banks or large enterprises Guarantee Fee SMEs pay 0.5 ~ 3.0% of annual guarantee fee (upfront) Average fee rate : 1.27%(as of 2014) Operational Mechanism Guarantee procedure Step 01 Step 02 Step 03 Step 04 Apply & Interview Credit Analysis & On-site Visit Evaluation & Approval Issuance of Guarantee Letter • SME’s application • Eligibility check-up by interview with owner • Document submitted & reviewed • Credit rating & Evaluation • Contract & Paying fee • Analyst’s on-site visit • Guarantee approval • Issue of guarantee Operational Mechanism Eligibility, ceiling & coverage Risk Management Optimal enterprise risk management system Credit Risk Liquidity Risk Operational Risk Exposure Default rate Internal audit Risk taking ratio Leverage ratio Monitoring Portfolio management system Risk Management CCRS(Corporate Credit Rating System) Financial Model Scores from Financial Factors Quantitative Model Scores from Quantitative Factors Credit Investigation Qualitative Model Scores from Qualitative Factors Owner’s CB rating Combination of Model (Combined Score) Pre-Rating Filtering CCRS Rating (Final) Rating Median PD(%) KR1 KR2 KR3 • • • KR15 0.10 0.30 0.60 • • • 30.0 Leverage Ratio Outstanding guarantees & Leverage ratio 50.0 45.0 10.0 41.5 39.9 39.9 41.6 42.5 9.0 40.0 9.0 35.0 8.5 8.0 8.0 30.0 25.0 43.1 7.3 20.0 6.9 7.0 7.2 6.0 15.0 10.0 5.0 5.0 0.0 4.0 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014 2015 (1 USD = 1,140KRW) Default Rate Consistent Default Rate 8.0 7.2 7.0 6.2 6.4 6.7 6.2 6.0 5.2 5.1 5.0 4.0 4.9 4.7 5.0 4.6 4.2 4.8 4.2 4.7 4.1 4.0 2.9 2.8 4.0 4.0 3.6 3.0 2.0 4.8 2.3 3.3 2.6 2.3 1.0 0.3 0.0 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014 2015 Thank you