* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Key Terms:
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrion wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (H+-translocating) wikipedia , lookup
Butyric acid wikipedia , lookup
Glyceroneogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Lactate dehydrogenase wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
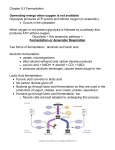
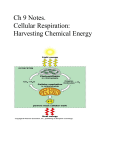
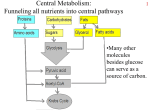
Bio102: Introduction to Cell Biology and Genetics Anaerobic Respiration Key Terms: Anaerobic Respiration Lactate Fermentation Alcoholic Fermentation Phosphofructokinase Feedback Inhibition Key Questions: How are all the parts of aerobic respiration connected together? What is the key problem that must be solved for a cell to survive anaerobically? How is respiration commonly regulated? Why might a cell want to slow down respiration? Lecture Outline: Anaerobic Metabolism recall that in glycolysis no oxygen required 2 ATP generated (net) per glucose but there's an NAD+/NADH problem! continuous running of glycolysis will use up all of your NAD+ need a means to NADH NAD+ Fermentation Purpose is to get rid of NADH to allow glycolysis to continue 1) alcoholic fermentation pyruvate ethanol & CO2 in plants and fungi (like yeasts) both ethanol and CO2 are useful byproducts 2) lactate fermentation pyruvate lactate in animals (like people) waste product: lactate (lactic acid) or ethanol (alcohol) Aerobic metabolism = glycolysis + citric acid cycle + electron transport + oxidative phosphorylation Anaerobic metabolism = glycolysis + fermentation (lactate or alcoholic) Regulation of Metabolism Allosteric regulation of phosphofructokinase by ATP -- feedback regulation Regulation by substrate concentration Alternative energy sources carbohydrates other than glucose lipids proteins



![fermentation[1].](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008290469_1-3a25eae6a4ca657233c4e21cf2e1a1bb-150x150.png)