* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Standard 3
Survey
Document related concepts
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Biosequestration wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
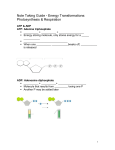
Standard 3 Vocabulary Review Name __________________________________ Match the term on the left with its definition on the right: ____ ADP A. Most important and main compound cells use to store and release ENERGY. ____ Aerobic B. This is a compound made up of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms (1:2:1); it is used by cells for short-term energy. Examples: sugars and starches. ____ Amino Acids C. These are LARGE chemical compounds, primarily consisting of carbon and hydrogen, that exist in living organisms. Examples: carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids. ____ Anaerobic D. This is the circulation of water between land, air and surface. Processes included evaporation, transpiration, condensation, and precipitation. ____ ATP E. This is a macromolecule that holds cell information in a coded form. Made of sugar, phosphate and nitrogen-containing bases. Two types DNA and RNA. ____ ATP Cycle F. This is a simple biological process not requiring oxygen. ____ Autotroph G. Organisms that make their own food, also known as an autotroph. ____ Macromolecule H. The cycling of carbon through the biosphere, geosphere, hydrosphere, and atmosphere. Process include photosynthesis, respiration, decomposition, combustion, and weathering. ____ Carbohydrate I. This is a molecule that contains both amino group, carboxyl group, H atom, and a variable R-group. They are the building blocks of protein. ____ Carbon J. This is short for adenosine diphosphate. An organic compound that contains energy and is composed of adenine and two phosphate groups. ____ Carbon Cycle K. This is a biological process that requires oxygen. ____ Carbon Dioxide L. An organelle found in most eukaryotic cells described as "cellular power plants", because their primary function is to convert organic materials into energy in the form of ATP. ____ Cellular Respiration M. This is the name applied to the cycle by which ATP is broken down to ADP with the release of energy, and the regeneration of ATP from ADP through the process of phosphorylation. ____ DNA N. This is a green pigment in chloroplasts that traps light energy from the sun. ____ Chlorophyll O. 6CO2 + 6H2O + sun 6O2 + C6H12O6 ____ Fermentation P. Another name for a producer. ____ Glucose Q. 6O2 + C6H12O6 6CO2 + 6H2O + energy ____ Heterotroph R. C6H12O6 Sugar produced by producers during the process of photosynthesis. ____ Lipid S. This is the gas produced as a result of respiration. ____ Mitochondria T. This is an organism that obtains energy by consuming food. ____ Monosaccharide U. This is the simplest type of carbohydrate, commonly known as a SIMPLE SUGAR, which acts as a building block for larger carbohydrates such as starches. Example: GLUCOSE ____ Nucleic Acid V. Genetic code that contains an organism’s hereditary information. ____ Photosynthesis W. The process by which cells release energy in the absence of oxygen. Not efficient produces less ATP ____ Producer X. A macromolecule made up of mainly carbon and hydrogen atoms that is primarily used for long-term energy storage and in cell membranes. ____ RNA Y. A single stranded nucleic acid that plays a role in protein synthesis. ____ Water Cycle Z. This is an element in the periodic table that is the basis for all ORGANIC molecules.