* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Evolution Packet Name
Survey
Document related concepts
Natural selection wikipedia , lookup
Unilineal evolution wikipedia , lookup
Acceptance of evolution by religious groups wikipedia , lookup
Evidence of common descent wikipedia , lookup
Punctuated equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
Paleontology wikipedia , lookup
Catholic Church and evolution wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Acquired characteristic wikipedia , lookup
Genetics and the Origin of Species wikipedia , lookup
Saltation (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
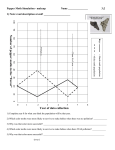
Evolution Packet Components: 8.7.3, 8.7.4, 8.7.5., 8.7.6 and 8.7.8 Agenda □ Evidence of Evolution Notes- Page 2 Watch the video and take notes. □ Evolution Webquest Pages 3-4 □ Evidence of Evolution Stations- Pages 5- 8 □ Evidence of Evolution Quiz→ 10 Minutes Ask any questions you might have and study your notes page Take the Types of Resources Quiz TOMORROW You cannot take the quiz the same day you finish the activity. STUDY!!! o Give your Science teacher your score and percent 70% or Above 69% or Under (Pick one of the following) Continue working on the packet STUDY!!! Retake the quiz TOMORROW o o □ Natural Selection Notes- Page 9 Watch the video and take notes. □ Peppered Moth Activity – Pages 10-12 Use the simulation on my page to answer the questions. □ Natural Selection Application Questions- Page 13-15 □ Natural Selection Quiz → 10 Minutes Ask any questions you might have and study your notes page Take the Types of Resources Quiz TOMORROW You cannot take the quiz the same day you finish the activity. STUDY!!! o Give your Science teacher your score and percent 70% or Above 69% or Under (Pick one of the following) Continue working on the packet STUDY!!! Retake the quiz TOMORROW o o THE EVOLTION OF MARIO Name:______________________ Period: ____ 1 Evidence of Evolution Evolution Definition: The gradual change in a species over time Takes a Looooong time Results from a change in the _________ material of an organism Not acted on at the individual level Passed on from one generation to the next Evidence for Evolution Similarities of structures in living things _______________________ Structures Common function Ex. Used to fly Different structure Ex. Different arrangement of bones Different origins Do not have a common ancestor ______________________ Structures Similar structure Same basic arrangement of bones Different function Adapted to different purposes Humans arm is used differently than a whales fin Same origin Common ancestor Embryo development (early stages) Embryos develop similarly in many vertebrates ____________________l Organs Inherited structures that no longer serve a function for the organism Examples Hipbone in dolphin/whale Our appendix Our wisdom teeth Shared Ancestry The fossil record Found fossils that show slow progression of change Biogeography Found animals in isolated islands or environments that ended up being perfect for that area after generations Where they are now compared to then Patterns in different places tell how organisms __________________ Populations on different islands all look different… Originate from a mainland Ex: Galapagos________________________ Change over time… Depending on the food source and environment, different birds survived and changed to best fit each island 2 Evidence of Evolution Web quest Use the following website (on my page), to answer the following questions http://evolution.berkeley.edu/evolibrary/article/similarity_ms_01 Similarities and Differences 1. What is the difference between homology and analogy? 2. What is a common ancestor? (click on the word to find out the definition) Click next. Tale of the Limb 3. What were the similarities between the limbs that are alike? Make sure to find all four limbs that are alike before you click next. The tetrapod limb Definition of a tetrapod: four-limbed vertebrates and their descendants 4. Click on all the limbs. Click next. Inheriting homologies 5. What are homologous structures? 6. Why do the different species share a similar structure or homology? Click next. Not all similarity is homology 7. Why were the octopus and tetrapod limbs different from each other? 8. What is the definition of analogous structures? Click next. 3 Analogies 9. Describe the similarities between the two skulls of the extinct animals. 10. Why is it that the saber teeth of the Thylacosmilus and the Smilodon not homologous structures? Click next. How do analogies evolve? 11. Why do two species that come from different ancestors share similar characteristics? Click next. Test your understanding 12. Why do scientists believe that the sugar gliders and flying squirrels do not share a common ancestor? 13. What type of structure is their “wings”? Submit your answer. 4 Evolution Stations Station 1: Analogous A B Use the image above to answer the following questions. 1. What function does each of the structures in image A perform? 2. What similarities do you observe in imagine A? 3. What differences do you observe in image A? 4. Taking a closer look into the wing with image B, what differences do you observe? 5. Do you think the 4 different wings in image B came from related organisms? Why or why not? 6. How can this evidence be used to support the theory of evolution? Station 2: Homologous Use the image above to answer the following questions. 1. What function do each of the structures perform? 2. What similarities do you observe? 3. What differences do you observe? 4. Do you think the 4 different images came from related organisms? Why or why not? 5. How can this evidence be used to support the theory of evolution? 5 Station 3: Embryology Use the image above to answer the following questions. 1. What similarities do you observe in the first stage of each development? 2. What differences do you observe in the first stage of each development? 3. What similarities do you observe in the third stage of each development? 4. What differences do you observe in the third stage of each development? 5. Do you think the 4 different images came from related organisms? Why or why not? 6. How can this evidence be used to support the theory of evolution? Station 4: Vestigial Structures Use the images above to answer the following questions. 1. Why might a whale have a hipbone if it doesn’t walk or use it for any purpose? 2. A friend or family member goes into surgery and has their appendix removed. Why are they able to live a long healthy life? 6 3. As you get older the last teeth that come into your mouth are your wisdom teeth. Many people often have their wisdom teeth removed. Explain why you don’t need them to help you eat? 4. Why do you think we have wisdom teeth if we don’t need them? 5. When you see a video of an ostrich they are often running at high speeds. Even though they have wings they are never seen flying. Why don’t these use their wings even though they have them? 6. Explain why the star nosed mole doesn’t have functional eyes. (They cannot see but still survive) Station 5: Fossil Evidence Using the image on the right, answer the following questions 1. What similarities do you observe in each of the horses? 2. What differences do you observe in each of the horses? 3. Do you think the 4 different images came from related organisms? Why or why not? 4. What could have caused the horses to change? 5. How can this evidence be used to support the theory of evolution? 7 Station 6: Fossil Evidence Continued Use the image above to answer the following questions 1. What is the biggest habitat difference between the left and right organism? 2. Do you think all of the organisms are related? Why or why not? 3. How can this evidence be used to support the theory of evolution? Station 7: Biogeography a. How can being located in a different area change a species? b. How might a species change over time if it moves to a colder climate? c. How might a species change over time if it moves to a habitat that is a different color? d. How might a species change over time if a new predator moves into the area? 8 Natural Selection Notes What is evolution? Definition: The gradual change in a species over time Takes a Looooong time Results from a change in the __________________ material of an organism Not acted on at the individual level Passed on from one generation to the next Darwin vs. Lamarck Lamarck Darwin Developed 1st idea about how organisms get their traits Developed current idea about how organisms get their traits When an individual organism acquires a new trait IN ITS LIFETIME it passes that trait to its offspring All organisms are born with different traits and when that organism reproduces the traits get passed on to its offspring Ex. A giraffe wanted to reach a higher tree so it stretched its neck. This longer neck was passed onto the next generation Ex. Giraffes were all born with different heights. The ones with longer necks were more “fit” and they were able to get additional food, survive, and pass on those traits. NO EVIDENCE!!!!!!! __________________of evidence! What is natural selection? Darwins idea! The process through which members of a species are best suited to their environment survive and reproduce at a higher rate than other less suited members of the species Survival of the fittest The most “fit” animals will be selected for and will survive. Species adapt to their environment ____________________________: A characteristic, a behavior, or an inherited trait ____________________________: How well you are equipped to survive the environment you live in Natural Selection Overproduction Variation When a plant or an animal reproduces it usually creates more offspring than the environment can support Ex. Salmon lay 100’s of eggs but only a few will survive Within a species there are natural differences in traits due to mutations (change in DNA) Genetic variations are passed from one generation to the next Adaptation Selection Mutation that makes an individual better able to survive Individual organisms with a particular adaptation will survive long enough to reproduce Gives organism an advantage Adaptation becomes more common in next generation New Species Evolve from Earlier Species Speciation: Evolution of a new species from an existing species May occur when the environment changes dramatically or gradually Species can also be isolated if they feed on different things or reproduce at different times of year 9 Peppered Moth Simulation Introduction: Charles Darwin accumulated a tremendous collection of facts to support the theory of evolution by natural selection. One of his difficulties in demonstrating the theory, however, was the lack of an example of evolution over a short period of time, which could be observed as it was taking place in nature. Although Darwin was unaware of it, remarkable examples of evolution, which might have helped to persuade people of his theory, were in the countryside of his native England. One such example is the evolution of the peppered moth. The economic changes known as the industrial revolution began in the middle of the eighteenth century. Since then, tons of soot had been deposited on the country side around industrial areas. The soot discolored and generally darkened the surfaces of trees and rocks. In 1848, a dark-colored moth was first recorded. Today, in some areas, 90% or more of the-peppered moths are dark in color. More than 70 species of moth in England have undergone a change from light to dark. Similar observations have been made in other industrial nations, including the United States. Procedure: Click on the Natural Selection simulation on your teacher’s page. At the end, you will run two simulations for 5 minutes each, during this time you will play the part of a blue jay that eats moths. After 5 minutes record the % of dark moths and light moths - you will need this information later. Read the background information and answer the questions as you go. Life Cycle of the Peppered Moth 1. Why are these moths called "peppered moths?" 2. What animals eat the peppered moth? 3. How do peppered moths spend the winter? 4. Moths that have more dark spots than the average moth are called what? Impact of Pollution 5. Where was the first black form of the moth found? 6. What was the Industrial Revolution? 10 7. What was causing the different colors in the moths? 8. What is natural selection? Kettlewell's Experiments 9. How do scientists test theories? 10. Write down TWO of Kettlewell's predictions. 11. Dark moths were found in what parts of the country? 12. Why did dark moths have a survival advantage? 13. When Kettlewell recaptured the marked moths, what did he find? Birdseye View 14. Open the simulation and play the role of the bird in both the dark and the light forest. Try to behave as a bird would behave, choosing the moths that are the most obvious. At the end of each simulation, record the percent of moths captured in the table below. Final Analysis 15. Explain how the color of the moths increases or decreases their chances of survival. 11 16. Explain the concept of "natural selection" using your moths as an example. 17. What would happen if there were no predators in the forest? 18. Would the colors of the moths change over time? WHY? 19. Imagine an organism that isn’t the most fit for its environment, in addition to dying, what can happen to that organism? 12 Natural Selection Application Questions 1. A species of bird is found on an island and all the birds vary in beak size. A drought hits the island for a few years and most seeds for the birds dry up. The only seeds remaining that grow on the island are the large hard ones. Predict what bird beak size (A-D) will be selected for starting after the drought. A Explain why. C 2. A lot of research has gone into the idea that birds are descendants of dinosaurs. At some point, a mutation occurred that made feathers pop up. Why do you think feathers stayed around and wasn’t one of the mutations that just disappeared after a generation or two? 3. Often when you are sick a doctor will prescribe an antibiotic to fight off the bad bacteria in your body. Why do we need to create new antibiotics all the time? 4. If you get a flu shot one year why would you need to get it the next year? Why you aren’t still protected from the flu? 5. There are two types of polar bears: ones with thick coats and ones with thin coats. It is fall, soon to be winter. The temperatures are dropping rapidly and the bears must keep warm or they will freeze to death. Many of the bears have 2 cubs but due to the extreme cold, they lose one. a. Which type of bear is fittest for the environment? b. Which type will be more present in the next few years? c. As global warming impacts more of our polar regions, what may happen to the type of polar bears as the temperatures increase? 13 B D 6. Can human beings make an impact on natural selection? How? Give at least one example. 7. Below is a series of pictures representing changes in a population of cacti over many generations. a. Why would a deer be more likely to eat the left cactus than the right cactus? b. In figure 3, the right cactus has flowers, but the cactus that has been eaten by the deer is too damaged to make flowers. Figure 4 shows the situation several months later. What has happened? c. What adaptation seems to increase the fitness of the cacti on the right? How do you think this adaptation increases the ability of cacti on the right to survive and reproduce? 8. Examine the picture below. Figure 1 through 3 shows you a change in the population of mice in a given area over time. a. Which adaptation is the fittest for the area? b. What will happen to the unfit adaptation? c. What would happen if the winter season comes and snow covers the area? 14 9. The table below gives descriptions of four female mice that live in a beach area which is mostly tan sand with scattered plants. According to the definition given for fitness, which mouse would biologists consider the fittest? Explain why by USING 2 pieces of DATA from the table. 15