* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Marine Ecology 1a
Physical oceanography wikipedia , lookup
Abyssal plain wikipedia , lookup
Pacific Ocean wikipedia , lookup
Sea in culture wikipedia , lookup
Arctic Ocean wikipedia , lookup
Raised beach wikipedia , lookup
Critical Depth wikipedia , lookup
Anoxic event wikipedia , lookup
Marine microorganism wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on oceans wikipedia , lookup
Marine debris wikipedia , lookup
Demersal fish wikipedia , lookup
Marine life wikipedia , lookup
Marine pollution wikipedia , lookup
Marine biology wikipedia , lookup
The Marine Mammal Center wikipedia , lookup
Marine habitats wikipedia , lookup
Deep sea fish wikipedia , lookup
Ecosystem of the North Pacific Subtropical Gyre wikipedia , lookup
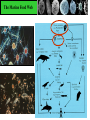
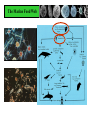
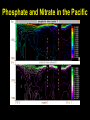
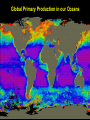
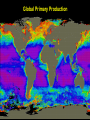
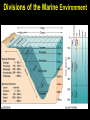
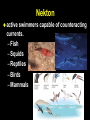
From Friday’s The Blue Planet PREDATOR PREY Sardines Flying fish Surgeonfish eggs Yellowfin tuna eggs PLANKTON NUTRIENTS Striped tuna, Bluefin tuna Marlin Sei whale Manta ray, Ray Pacific Mackeral Spotted Dolphin Sailfish Blue Shark Deepwater crab • Sunfish with half-moon fish and seagull Wahoo • Fish with flotsam The Marine Food Web Biological Productivity Conditions for Life in the Sea Consider the main biochemical reaction for life in the sea, and on earth in general: 6H2O + 6CO2 + energy = C6H12O6 + 6O2 Focus on left side of equation What is in short supply in the sea and thus limits the amount of life in the ocean?? 6H2O + 6CO2 + energy = C6H12O6 +6O2 Phytoplankton are base of the food chain Most important primary producers of complex sugars and oxygen 80% of the world’s photosynthesis occurs in the sea. Lauderia sp. The Marine Food Web Gasses & Water are absorbed through diffusion across a semipermeable membrane Lauderia sp. Diffusion: molecules move from high to low concentrations Which Elements are in Short Supply? Nitrogen (N) as Nitrate NO3 (-2) Phosphorus (P) as Phosphate PO4 (-2) Silicon (Si) as Silicate SiO4 (-2) Phosphate and Nitrate in the Pacific Silicate in the Pacific Biolimiting Nutrients N, P, and Si are exhausted first in Eq. surface waters during photosynthesis Essential to the growth of phytoplankton Nutrients increase … life increases Nutrients decrease … life decreases Where would you expect to find the highest biomass in the Pacific?? Global Primary Production in our Oceans Dissolved O2 Reverse of Nutrients O2 is high in the surface mixed layer O2 decreases to a minimum at base of thermocline O2 then steadily increases with depth – Why? Why is the Concentration of Oxygen High in the Mixed Layer?? Hint #1: How and where is oxygen produced in the sea??? 6H2O + 6CO2 + energy + nutrients = C6H12O6 + 6O2 Hint #2: How can oxygen be mixed downward from the atmosphere into the ocean? Global Primary Production Marine Ecology Basic Ecology physical and chemical parameters affecting distribution and abundance An ecosystem includes both the living (biotic) and non-living (abiotic) portions of the environment. – Examples include: salt marshes, estuaries, coral reefs, the North Pacific Gyre. Classification of Organisms by Environment horizontal: neritic | oceanic vertical: – epipelagic (top) / euphotic (good) – mesopelagic (middle) / disphotic (low) – bathypelagic (deep) / aphotic (without) – abyssopelagic (“bottomless”) Divisions of the Marine Environment Classification of Organisms by Lifestyle Scientists have established another classification scheme to categorize biota on the basis of lifestyle. The major groups are: – plankton (floaters) – nekton (swimmers) – benthos (bottom dwellers) Plankton weak swimmers, drifters, unable to counteract currents. – Phytoplankton (plants) – Zooplankton (animals) Nekton active swimmers capable of counteracting currents. – Fish – Squids – Reptiles – Birds – Mammals Distribution of Marine Lifestyles 16.7% of Earth’s animals are marine 2% inhabit pelagic environment (most of the oceans are cold and dark) 98% are benthic! Benthos Epiflora or epifauna live on the sea bottom. Infauna live in the sea bottom. Benthic plants - restricted to shallow waters (light) Benthic animals occur everywhere from shallow depths to the deep sea. Hydrostatic Pressure Pressure caused by the height of water. Function of water height and water density Pressure generally increases at a rate of 1 atm per 10 m of water. (or 16 psi per 10 m depth) Hydrostatic Pressure (Cont.) enormous in the deep sea yet animals live there. Animals do not contain gases. However, mesopelagic fish which have gasfilled swim bladders to help maintain neutral buoyancy – unable to move rapidly between depths – pressure change could cause bladder to explode.