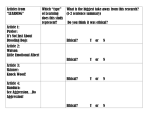
* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Key Terms
Symbolic behavior wikipedia , lookup
Behavioral modernity wikipedia , lookup
Prosocial behavior wikipedia , lookup
Observational methods in psychology wikipedia , lookup
Insufficient justification wikipedia , lookup
Abnormal psychology wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Thin-slicing wikipedia , lookup
Theory of planned behavior wikipedia , lookup
Attribution (psychology) wikipedia , lookup
Theory of reasoned action wikipedia , lookup
Social perception wikipedia , lookup
Descriptive psychology wikipedia , lookup
Counterproductive work behavior wikipedia , lookup
Sociobiology wikipedia , lookup
Applied behavior analysis wikipedia , lookup
Verbal Behavior wikipedia , lookup
Adherence management coaching wikipedia , lookup
Behavior analysis of child development wikipedia , lookup
Psychological behaviorism wikipedia , lookup
Psychophysics wikipedia , lookup
Classical conditioning wikipedia , lookup
adjunctive behaviors acquisition behavior-systems analysis conditioned reinforcer discrimination discriminative stimulus extinction free-operant procedure generalization generalized reinforcer instinctive drift interim behavior Law of Effect percentile schedule of reinforcement positive reinforcement primary reinforcer prompt puzzle box reinforcer response chain shaping spontaneous recovery stimulus control stop-action principle superstition experiment superstitious behavior terminal behavior three-term contingency adjunctive behaviors Stereotyped behaviors that arise when food or some other reinforcer is delivered at regular intervals. acquisition The learning of a new behavior or skill, or the time period over which this learning occurs. behavior-systems analysis The view that different reinforcers evoke different systems or collections of species-typical behaviors, which can account for the types of behaviors seen in autoshaping, classical conditioning, and some operant conditioning situations. conditioned reinforcer A previously neutral stimulus that has acquired the capacity to strengthen responses because it has been repeatedly paired with a primary reinforcer. discrimination In either classical or operant conditioning, learning to respond to one stimulus but not to another, similar stimulus. discriminative stimulus In operant conditioning, a stimulus that indicates whether or not responding will lead to reinforcement. extinction In classical conditioning, presenting the conditioned stimulus without the unconditioned stimulus. In operant conditioning, no longer presenting the reinforcer when the operant response is made. In both cases, responding decreases and eventually disappears. free-operant procedure A procedure developed by Skinner in which, unlike a discrete trial procedure, the operant response can occur at any time and can occur repeatedly for as long as the subject remains in the experimental chamber. generalization The transfer of a learned response from one stimulus to another, similar stimulus. generalized reinforcer A conditioned reinforcer that has been associated with a large number of different primary reinforcers. instinctive drift In operant conditioning, innate behaviors that are related to the type of reinforcer being used that cause an animal’s performance to drift away from the reinforced behavior and toward instinctive behaviors. interim behavior A behavior pattern that occurs in the early parts of each interval when food or some other primary reinforce is delivered at regular intervals. Law of Effect Thorndike’s version of the principle of reinforcement, which states that responses that are followed by pleasant or satisfying stimuli will be strengthened and will occur more often in the future. percentile schedule of reinforcement A reinforcement schedule in which a given response is reinforced if it is better than a certain percentage of the last several responses the learner has made. positive reinforcement A behavior-strengthening procedure in which the occurrence of a behavior is followed by a desired stimulus, or reinforcer. primary reinforcer A stimulus that naturally strengthens any response it follows (e.g., food, water, sexual pleasure, and comfort). prompt In behavior modification, a stimulus that makes a desired response very likely to occur, and is gradually removed (faded out) as training proceeds. puzzle box A type of experimental chamber used by Thorndike in which an animal had to make a certain response in order to open the door and obtain food that was available outside. reinforcer A stimulus that strengthens behavior if it is delivered after the behavior occurs. response chain A sequence of learned behaviors that must occur in a specific order, with a primary reinforcer delivered only after the final response. shaping (or method of successive approximations) A procedure for teaching a new behavior in which closer and closer approximations to the desired behavior are reinforced. In classical or operant conditioning, the reappearance of a response that spontaneous recovery has undergone extinction after a passage of time without further conditioning trials. stimulus control The general topic of how behaviors can be controlled by the stimuli that precede them. stop-action principle A principle of reinforcement that states that the precise movements being performed at the moment of reinforcer delivery will be strengthened and be more likely to occur in the future. superstition experiment Skinner’s classic experiment in which food was delivered to pigeons every 15 seconds no matter what they were doing, and most pigeons developed distinctive behaviors that they performed repeatedly between food presentations. superstitious behavior A behavior that occurs because, by accident or coincidence, it has previously been followed by a reinforcer. terminal behavior A behavior pattern that occurs near the end of each interval when food or some other primary reinforce is delivered at regular intervals. three-term contingency A contingency involving a discriminative stimulus, a response, and a reinforcer or punisher. The contingency states that in the presence of a specific discriminative stimulus, a specific response will lead to specific consequences.