* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download SOTU and the Contemporary Macroeconomic Consensus
Survey
Document related concepts
Washington Consensus wikipedia , lookup
Nouriel Roubini wikipedia , lookup
Non-monetary economy wikipedia , lookup
Edmund Phelps wikipedia , lookup
Early 1980s recession wikipedia , lookup
Austrian business cycle theory wikipedia , lookup
Inflation targeting wikipedia , lookup
International monetary systems wikipedia , lookup
Helicopter money wikipedia , lookup
Money supply wikipedia , lookup
Fiscal multiplier wikipedia , lookup
Stagflation wikipedia , lookup
Keynesian economics wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
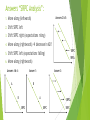
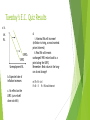
Answers “SRPC Analysis”: Answers 2 & 5: 1. Move along (leftwards) 2. Shift SRPC left 3. Shift SRPC right (expectations rising) 4. Move along (rightwards) decrease in AD! 5. Shift SRPC left (expectations falling) 6. SRPC SRPC2 Move along (rightwards) Answer 3: Answer 1: Answers 4 & 6: .A .B .B .A SRPC SRPC2 SRPC SRPC Tuesday’s E.C. Quiz Results a/b. d. Inf. Rt. SRPC2 SRPC Unemployment Rt. b. Expected rate of inflation increases c. No effect on the LRPC (curve itself does not shift) i. Nominal IRs will increase! (inflation is rising, so must nominal prices/interest) ii. Real IRs will remain unchanged! Will return back to a point along the LRPC) Remember: Real values in the longrun do not change! e. R = N ─ Inf. R=8─3 R = 5% real interest SOTU & the Modern Macroeconomic Consensus : Students will assess President Obama’s SOTU Address from opposing schools of economic thought in order to form conclusions about the contemporary macroeconomic consensus. 3 Leading Schools of Macroeconomic Thought: Keynesian (Policy Activism): The general Theory of Employment, Interest, and Money 1936. Roots founded during Great Depression Short-run bursts of AD to promote short-run growth & “animal spirits” “We’re all dead in the long-run”—balanced budget it not central focus Asserted expansionary monetary policy would be ineffective in the face of recession…liquidity trap 3 Leading Schools of Macroeconomic Thought: Monetarist A (Discretionary Monetary Policy): Monetary History of the United States, 1867-1970 Friedman & Schwartz showed business cycle fluctuations link to the money supply FED policy to steadily increase the money supply to steadily increase GDP regardless of business cycle Take all decision-making away from politicians & avoid the lag that comes with discretionary fiscal policy In fact, discretionary fiscal policy only prolongs recession Very little contemporary support—research has shows too much monetary policy can destabilize (inflation) 3 Leading Schools of Macroeconomic Thought: Classical (New Supply-Siders): A change in AD cannot have an impact on the aggregate output of an economy, only the price level Muth’s Rational Expectations: people and firms are Rationale and utilize all information available to them…essentially eliminating “sticky” inputs If you are going to negotiate a contract all past experiences and future predictions allow you to anticipate inflation Real Business Cycle Theory: changes in productivity are the sole determinants of business cycle fluctuations (AS is perfectly vertical) SOTU 2015: Economic Highlights https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tIafRj_p95M LISTEN CAREFULLY AND BE PREPARED TO DO SOME ANALYSIS OF PRESIDENT OBAMA’S PROPOSALS The Current Macroeconomic Perspective (as proposed by your textbook) Is expansionary monetary policy helpful in fighting recessions? Yes—except in special circumstances (liquidity trap) Is expansionary fiscal policy effective in fighting recessions? YES. Can monetary and/or fiscal policy reduce unemployment in the longrun? NO. Should fiscal policy be used in a discretionary way? No—except in special circumstances Should monetary policy be used in a discretionary way? Still in dispute… 2-Minute Paper: 1. Assume that the US decides, albeit misguidedly, to grant the President absolute control over fiscal and monetary policy. You are currently the President of the United States. What actions do you take given the current state of the economy? Give 3 supporting details. 2. Why is there a debate about the correct actions for a government to take in the face of economic fluctuations.