* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download - Fairview High School
Transitional fossil wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Group selection wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Dual inheritance theory wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive evolution in the human genome wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
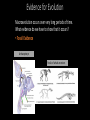
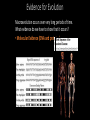
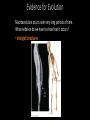
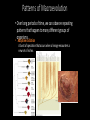
Evolution • Evolution refers to observable biological changes in a population (or larger group of related organisms) over time • A population is a group of organisms of the same species that interact and interbreed with each other. Important Evolution Vocabulary • Gene – a segment of DNA that holds the information for determining a trait. • Gene pool – all of the genes of all of the members of a population. • Population - a group of reproducing individuals of the same species in the same area (same gene pool). • Alleles are different forms of the same gene (for example, different colors of beetle shells) Microevolution vs. Macroevolution •Microevolution – changes to the gene pool of a single population. Changes can occur over a short period of time. • Example – differences between dog breeds Microevolution vs. Macroevolution •Macroevolution – changes and patterns over a long period of time that result in the origin of new species. Usually refers to a group larger than a single population (ex: birds) • Example – the evolution of birds from dinosaurs Both Microevolution and macroevolution are dependent upon genetic mutation and the exchange of genes. Microevolution • When allele frequencies (relative abundance of alleles of a given gene in a population) change in a population, microevolution occurs. • Natural populations are never in genetic equilibrium. (genetic equilibrium = no change) • Six processes of microevolution (smallscale changes in a population's allele frequencies) prevent genetic equilibrium: 1. Mutation A mutation is a permanent small-scale change in an organism's DNA. For Example: ACCGA -> AGCG Mutations are the primary source of new alleles 2. Gene Flow Gene flow is the migration of individuals and their genes among populations 3. Genetic Drift Genetic drift is the random change in allele frequencies over generations. Genetic Drift Continued: Small populations repopulating The Bottleneck Effect: The Founder Effect: 4. Natural Selection Natural selection: In a given environment, differential survival and reproduction among individuals of a population that vary in details of shared, inherited traits. Any trait that enhances an individual’s fitness (ability to survive and reproduce in a particular environment) is called an adaptive trait. Survival of the fittest? How do these organism’s traits increase their fitness? 5. Artificial selection In artificial selection humans choose which traits are passed on. 6. Sexual selection In sexual selection certain traits are preferentially chosen by mates. Microevolution Review Review Use your COLORED PENCILS to fill out the microevolution worksheet Movie time! Lets watch some super super cute animals get eaten! Short Evolution Discussion Are humans still evolving? Evidence for Evolution Macroevolution occurs over very long periods of time. What evidence do we have to show that it occurs? • Observations of microevolution • Light color is adaptive in areas of low pollution; dark color is adaptive in areas of high pollution. Evidence for Evolution Macroevolution occurs over very long periods of time. What evidence do we have to show that it occurs? • Fossil Evidence Archaeopteryx Fossils of whale ancestors Evidence for Evolution Macroevolution occurs over very long periods of time. What evidence do we have to show that it occurs? • Molecular Evidence (DNA and proteins) Evidence for Evolution Macroevolution occurs over very long periods of time. What evidence do we have to show that it occurs? • Vestigial Structures Patterns of Macroevolution • Over long periods of time, we can observe repeating patterns that happen to many different groups of organisms. • Coevolution Predator and prey Host and parasite Pollinator and flower Patterns of Macroevolution • Over long periods of time, we can observe repeating patterns that happen to many different groups of organisms. • Stasis A lineage exists for millions of years with little or no change (e.g. Bdelloid Rotifers and Coelacanths). Patterns of Macroevolution • Over long periods of time, we can observe repeating patterns that happen to many different groups of organisms. • Adaptive radiation A burst of speciation that occurs when a lineage encounters a new set of niches.