* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Structure Study Guide Answer Key
Survey
Document related concepts
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
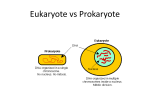
Cells Structure and Function Study Guide – Answer Key Lesson 1 OUTBREAK! 1. Think about the infectious disease you modeled and how it was spread in the community. What are some things that could be done to prevent the disease from spreading? You may suggest such actions as: Don’t swim in or even go near the lake. Post signs warning people to stay away. Be sure the lake is not used for drinking water or landscape watering. 2. Imagine that you are the director to the health department in the town where the disease is spreading. It is your job to help prevent people from getting sick. Explain what actions you would recommend to try to end the outbreak. SAMPLE ANSWER (2 recommendations): I would recommend that people stay away from the lake. I would put up warning signs around the lake. I would publicize this problem through the Internet, newspapers, and radio stations and suggest that anyone who has recently visited the lake seek medical attention if they become sick. 1 Lesson 3 1) Compare the onion cell, elodea leaf and human cheek cells you observed. a) What structures do they have in common? Explain. All of the cells observed have a cell membrane and a nucleus. However, what looks like a membrane around onion cell is a cell wall. The cell membrane inside the cell wall is probably not visible. All of the cells have cytoplasm as well. The cheek cell has cytoplasm that stains a pinkish purple color. The elodea and onion cells have cytoplasm – harder to see until you stain onion cell and the cytoplasm stains orange. b) How are the cells different? Explain. The cells have different shapes. Cheek cells are somewhat circular and the plant cells are both rectangular. The cheek cell appears to have tiny structures in cytoplasm. The onion cell looks empty (due to large vacuole that pushes cytoplasm to edge of cell.) The elodea cells has green structures called chloroplasts. 2 Lesson 4 This diagram shows the outline of a “typical cell.” The animal and plants cell models are below along with the list of organelles and their functions. Cell organelle Cell function Endoplasmic reticulum, vesicles Carry materials from one place to another Cytoskeleton, cell wall Provide support Nucleus Directs the activities of the organism or the cell Vesicles Excrete wastes Lysosomes Destroys wastes Cytoskeleton Movement Cell membrane Controls what enters the cell Cytoplasm, mitochondria Breaks down food for energy Golgi Apparatus Sorts and packages proteins 3 Plant cell only structures Cell wall chloroplast Plant cell functions Provides structure Where photosynthesis occurs and provides plant cells with food (sugars) Stores water in plant 1 Large vacuole (animal cell has several small) Lesson 5: Single Celled Microorganisms 1. Identify the protist on the line below each picture. Choose from this list of microorganisms: Euglena Amoeba Bacteria Paramecium Label structures A, B and C in each drawing beside the letter. pseudopod C A Cytoplasm Cell membrane Amoeba C B Cell membrane chloroplast flagella Euglena 4 B A B cytoplasm Cell membrane C A cilia Paramecium Lesson 6 Microbes Would you describe bacteria as being harmful or helpful to people? Explain. Bacteria may be helpful, such as the bacteria that live in our digestive system. Other bacteria can make us ill and cause disease. Why are viruses not considered to be microorganisms? Viruses are not cells. They don’t perform most cell functions. Viruses do not grow and reproduce by themselves. How do the sizes of protists, bacteria and viruses compare? Protists are a lot bigger than bacteria, and bacteria are a lot bigger than viruses. What are the advantages of using the highest power objective on a microscope? What are the advantages of using the lowest power objective on a microscope? Explain. The higher power of a microscope shows greater detail. The lower power shows a wider field of view (more area). 5