* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Types of Chemical Reactions
Cracking (chemistry) wikipedia , lookup
Coordination complex wikipedia , lookup
Rutherford backscattering spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Chemical equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
Inorganic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Rate equation wikipedia , lookup
Photoredox catalysis wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear fusion wikipedia , lookup
Process chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Asymmetric induction wikipedia , lookup
Acid–base reaction wikipedia , lookup
Enantioselective synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Multi-state modeling of biomolecules wikipedia , lookup
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Radical (chemistry) wikipedia , lookup
Electrolysis of water wikipedia , lookup
Ring-closing metathesis wikipedia , lookup
George S. Hammond wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Marcus theory wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Chemical thermodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Bioorthogonal chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Strychnine total synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Transition state theory wikipedia , lookup
Liquid-feed flame spray pyrolysis wikipedia , lookup
Click chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Stoichiometry wikipedia , lookup
Hydrogen-bond catalysis wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Chemical reaction wikipedia , lookup
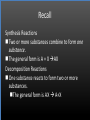
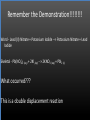
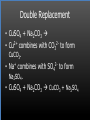
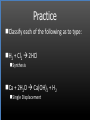
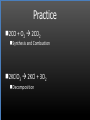
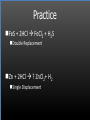
Types of Chemical Reactions Single Replacement Reactions Double Replacement Reactions Combustion Reactions Recall Synthesis Reactions Two or more substances combine to form one substance. The general form is A + X AX Decomposition Reactions One substance reacts to form two or more substances. The general form is AX A+X Single Replacement Reactions A metal will replace a metal ion in a compound. The general form is A + BX AX + B A nonmetal will replace a nonmetal ion in a compound. The general form is Y+BX BY + X Single Replacement Reactions • Examples: – Ni + AgNO3 NiNO3 + Ag • Nickel replaces the metallic ion Ag+ (metal replaces metal ion) • The silver becomes free silver and the nickel becomes the nickel (II) ion. • Ni + AgNO3 Ag + Ni(NO3)2 –Balance the equation: –Ni + 2AgNO3 2Ag + Ni(NO3)2 Thermite Reaction • Steve Spangler Video Thermite Thermite Reaction • Al + Fe2O3 • Aluminum will replace iron (III) as was seen in the video. • Iron (III) becomes Fe and aluminum metal becomes Al3+. • 2Al + Fe2O3 Al2O3 + 2Fe Double Replacement Reactions Ions of two compounds exchange places with each other. Reactants must be two ionic compounds, in aqueous solution The general form is AX+BY = AY + BX Remember the Demonstration!!!!!!!! Word - Lead (II) Nitrate + Potassium Iodide --> Potassium Nitrate + Lead Iodide Skeletal - Pb(NO3)2 (aq) + 2KI (aq) --> 2KNO3 (aq) + PbI2 (s) What occurred??? This is a double displacement reaction Double Replacement NaOH + CuSO4 The Na+ and Cu2+ switch places. Na+ combines with SO42- to form Na2SO4. Cu2+ combines with OH- to form Cu(OH)2 NaOH + CuSO4 Na2SO4 + Cu(OH)2 2NaOH + CuSO4 Na2SO4 + Cu(OH)2 Double Replacement • CuSO4 + Na2CO3 • Cu2+ combines with CO32- to form CuCO3. • Na+ combines with SO42- to form Na2SO4. • CuSO4 + Na2CO3 CuCO3 + Na2SO4 Double Replacement Reactions • Think about it like “foil”ing in algebra, first and last ions go together + inside ions go together • Example: AgNO3(aq) + NaCl(s) AgCl(s) + NaNO3(aq) • Another example: K2SO4(aq) + Ba(NO3)2(aq) 2 KNO3(aq) + BaSO4(s) Recognition You need to be able to recognize which reaction is taking place Practice Examples: • • • • • H2 + O2 H2O Zn + H2SO4 HgO KBr + Cl2 • AgNO3 + NaCl • Mg(OH)2 + H2SO3 Synthesis Decomposition Single Displacement Decomposition Single Displacement Double Replacement Double Replacement Combustion Reactions • Combustion means “add Oxygen” Normally, a compound composed of only C, H, (and maybe O) is reacted with oxygen – usually called “burning” • If the combustion is complete, the products will be CO2 and H2O. • If the combustion is incomplete, , the products will be CO (or possibly just C) and H2O. Combustion Reaction When a substance combines with oxygen, a combustion reaction results. The combustion reaction may also be an example of an earlier type such as 2Mg + O2 2MgO. The combustion reaction may be burning of a fuel. Combustion Reactions • Combustion reactions involve light and heat energy released. • Natural gas, propane, gasoline, etc. are burned to produce heat energy. • Most of these organic reactions produce water and carbon dioxide. Combustion Reaction When hydrocarbon compounds CxHx are burned in oxygen, the products are water and carbon dioxide. CH4 + O2 CO2 + H2O CH4 + 2O2 CO2 + 2H2O Demonstration Combustion Reactions Generally combustion reactions involve the burning of a Hydrocarbon (CxHx) in Oxygen. Other elements can also burn with Oxygen 2Mg + O2 2MgO+ Energy 2H2 + O2 2H2O+ Energy (basis behind fuel cell energy) P4 + 5O2 P4O10 + Energy (matches) Practice Classify each of the following as to type: H2 + Cl2 2HCl Synthesis Ca + 2H2O Ca(OH)2 + H2 Single Displacement Practice 2CO + O2 2CO2 Synthesis and Combustion 2KClO3 2KCl + 3O2 Decomposition Practice FeS + 2HCl FeCl2 + H2S Double Replacement Zn + 2HCl ? ZnCl2+ H2 Single Displacement