* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Networks Local area network
Survey
Document related concepts
Network tap wikipedia , lookup
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
Net neutrality law wikipedia , lookup
Wake-on-LAN wikipedia , lookup
Airborne Networking wikipedia , lookup
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
Internet protocol suite wikipedia , lookup
Deep packet inspection wikipedia , lookup
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
Zero-configuration networking wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
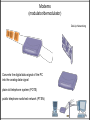
Networks Networks Topology Local area network (LAN( Wide-area network (WAN( Know the Definitions of Local Area Networks (LAN) and Wide Area Networks (WAN). • LAN – A LAN (Local Area Network) is a system whereby individual PCs are connected together within a company or organization • WAN – A WAN (Wide Area Network) as the name implies allows you to connect to other computers over a wider area (i.e. the whole world). Know the Definitions of Local Area Networks (LAN) and Wide Area Networks (WAN). • If ten people are working together within an office it makes sense for them all to be connected. • In this way the office can have a single printer and all ten people can print to it. • In a similar way other devices such as modems or scanners can be shared. • Even more useful is the ability to share information when connected to a network. Networks Architecture peer-to-peer all nodes on a network are equal and resources are shared equally client/server Networks Topology Bus Token Ring Star Networks Protocols Data packets TCP/IP : Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol HTTP : Hypertext Transfer Protocol PPP : Point-to-Point Protocol FTP : File Transfer Protocol Repeater A repeater is used to extend the signal distance of the cable by regenerating the signal . Hub if an 8-port hub receives a signal on port 4, the hub immediately passes the signal to ports 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 7, and 8 . Switch sends the message out only to the port on which the addressee workstation exists based on a MAC table that is created by listening to the nodes on the network . Bridge Bridges are used to connect two different LANs or two similar network segments Router This device sends data across networks using the logical or network address of a message to determine the path that the data should take to arrive at its destination . Modems (modulator/demodulator) Dial-Up Networking Converts the digital data signal of the PC into the analog data signal plain old telephone system (POTS) public telephone switched network (PTSN) Internet / Intranet Domains domain is a collection of hardware and software resources and the user accounts that have access to them . Internet Domains Internet domain : Domain Name Server/System (DNS). www.yahoo.com Top-Level Domains (TLDs) TLD Purpose .com Unrestricted, but intended for commercial entities .edu U.S. educational institutions .gov U.S. government agencies .info Unrestricted use .mil U.S. military .net Unrestricted use, but intended for network access providers .org Unrestricted use, but intended for nonprofit organizations and organizations that don't fit elsewhere A Little About the Technology • A message sent over the Internet is divided into uniformly sized packets – Each packet labeled with its destination address • Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) – TCP creates and reassembles packets – IP handles addressing • Ensures that packets are routed to their ultimate destination Return Copyright © 2003 by 14 The Internet Service Provider and the Browser • An Internet service provider (ISP) provides the server computer and software to connect to the Internet – Online service, such as America Online, includes Internet access, Internet service, and a browser • When you connect to the Internet, the browser displays a home page Return Copyright © 2003 by 15 Browser Functions • • • • • Menus and buttons Uniform Resource Locator (URL) Plug-ins Web page programs Wireless Internet access Return Copyright © 2003 by 16 File Transfer Protocol (FTP) • A protocol for transferring files among computers • FTP servers maintain collections of downloadable files – Downloading can often be done anonymously, without logging in • Many FTP servers can be accessed through Web browser Return Copyright © 2003 by 17 Mail Server • Collects and stores messages in mailbox • E-mail address consists of user name, followed by @ symbol, then domain name of mail server Return Copyright © 2003 by 18 E-Mail Client Software • Allows you to manage your e-mail messages • Features – Address books – The ability to attach files • Some e-mail servers block all attached files – Filters • • Direct incoming e-mail to specific folders Block spam Return Copyright © 2003 by 19