* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Pathogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Hybrid (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Essential gene wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
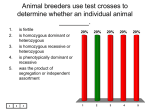
Name:______________________ Date:____________________ Period:_____ Genetics (6.3-6.5 and 7.1-7.4) 6.3 Mendel and Heredity (B.5.2 Describe how hereditary information passed from parents to offspring is encoded in regions called genes). 1. Genetics involve __________________ being passed from parent to offspring and is the study of biological _______________ patterns and __________________ in organisms. 2. Who was the first person to use clues to understand inheritance? 3. What plant did he study? 4. How did he control his experiment (prevent any self-fertlization)? 5. If any organism receives different genetic traits from both its parents, it is a _________________. If it receives the same genetic traits from both its parent is a ___________________. 6. Mendel crossed a pure yellow with pure green in the P generation (parental). He got all hybrids in the F1. He then let them fertilize each other and got 3 yellow and 1 green. Please show this experiment. P F1 F2 7. In the F1 generation, he realized that some “alleles” were ____________________. In the previous example, what is the “allele” that was hidden? 8. What are Mendel’s 7 traits of the pea that he studied? 1. 3. 2. 4. 5. 6. 7. 9. What is Mendel’s First Law of Segregation? (There are 2 parts). 1. 2. 6.4 Traits, Genes and Alleles (B.5.2 Describe how hereditary information passed from parents to offspring is encoded in regions called genes). 1. The vast amount of information encoded in _______ is organized into units called ________. 2. A _______ is a segment of DNA that codes for a protein. Proteins are your _____________. So, genes play an important role in determining how a person’s body develops and functions. 3. Draw a chromosome and label a gene. 4. How many alleles do you inherit for each trait? 5. If yellow is dominant to green, using the letters Y,y show the following genotypes and list the phenotypes. Genotype Phenotype Homozygous (pure) dominant Homozygous (pure) recessive Heterozygous (hybrid) dominant 6.5 Traits and Probablity (B.7.1 Distinguish between dominant and recessive alleles and determine the phenotype that would result from the different possible combinations of alleles in an offspring.) (B.7.3 Determine the likelihood of the appearance of a specific trait in an offspring given the genetic make-up of the parents). 1. Show a punnett square. Yellow is dominant to green. In box 1, cross a heterozygous yellow pea with a pure yellow pea. In box 2, cross a pure yellow with a green pea. Show the genotype and phenotype ratios. 1. 2. 2. We use a _______________________ to find an unknown genotype. 3. A __________________ cross is one where you only deal with one trait. (MM x mm) 4. A dihybrid cross examines the inheritance of _______ different traits.( MMYy x mmYy) 5.Mendel’s 2nd law is the law of ___________________ __________________. It states that ____________ pairs __________________ independently of each other during gamete formation of meiosis. In other words Traits are inherited ___________________. For example, hair color and widows peak are _________inherited together. 6. Punnett square do not give the ______________ outcomes of offspring, but just show the _______________ of each trait being inherited. 7.1 Chromosomes and Phenotype and 7.2 Complex Patterns of Inheritance (B.7.2 Describe dominant, recessive, co-dominant, sex-linked, incomplete dominant, multiple allele and polygenic traits and illustrate their inheritance patterns over multiple generations). 1. Sometimes 2 parents do not have a disorder, but have a child with it. These parents are known as ______________ and the disease would have to be _____________________. Show the punnet square for Cystic Fibrosis in question 1 using the letter C. 2. Complete the table. Inheritance pattern Mendelian Genetics Co-dominant Sex-Linked Involves sex chromosomes (___ and ____) Incomplete dominance Intermediate phenotype, one allele is not completely ___________________ over another. Multiple alleles Genes with 3 or more alleles (you still only inherit _____ from each parent) More than 1 gene influences a trait. Polygenic traits 3. Description Dominant and recessive traits expressed 2 _____________ alleles expressed at same time Example Give 2 examples of how the environment interacts with the genotype and affects phenotype. 1. 2. 7.3. Gene Linkage and Mapping (B.5.2 Describe how hereditary information passed from parents to offspring is encoded in regions called genes). 1. What is a gene map? 2. Genes located _______________ apart on a chromosome are _____________ likely to cross over. 3. Genes located closest together are said to be ______________. 7.4 Human Genetics and Pedigrees (B.7.3 Determine the likelihood of the appearance of a specific trait in an offspring given the genetic make-up of the parents). 1. Females can be ________________ of sex-linked disorders, and this gene could be passed on to her _______. Show this example for Colorblindness, which is a recessive sex-linked disorder. 2. The X chromosome carries about ____________ genes, where the Y carries about ________ known genes. 3. We use a ___________________ to trace the phenotypes and genotypes in a family. It can trace ________________ genes or ___________________ genes. (See page 215) 4. A ______________ is a picture of all of the chromosomes in a cell. What are some diseases we can diagnose using this tool?