* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PowerPoint
Survey
Document related concepts
Perturbation theory wikipedia , lookup
Computer simulation wikipedia , lookup
History of numerical weather prediction wikipedia , lookup
Computational fluid dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical computer science wikipedia , lookup
Computational electromagnetics wikipedia , lookup
Mathematical economics wikipedia , lookup
Linear algebra wikipedia , lookup
Multi-objective optimization wikipedia , lookup
Inverse problem wikipedia , lookup
Least squares wikipedia , lookup
Mathematical optimization wikipedia , lookup
Generalized linear model wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
Operations Research
Chapter one
1
Introduction
• Operations Research is an Art and Science
• World War 2
• George Dantzig [Linear Programming], First
Computer (Father of computer)
• It had its early roots in World War II and is flourishing in
business and industry with the aid of computer
• Primary applications areas of Operations Research include
forecasting, production scheduling, inventory control, capital
budgeting, and transportation.
2
What is Operations Research?
Operations
The activities carried out in an organization.
Research
The process of observation and testing characterized
by the scientific method. Situation, problem
statement, model construction, validation,
experimentation, candidate solutions.
Operations Research is a quantitative approach to decision
making based on the scientific method of problem solving.
3
What is Operations Research?
•
Operations Research is the scientific approach to execute
decision making, which consists of:
• The art of mathematical modeling of complex
situations
• The science of the development of solution
techniques used to solve these models
• The ability to effectively communicate the results
to the decision maker
4
Definition of OR
1. OR professionals aim to provide rational bases for
decision making by seeking to understand and
structure complex situations and to use this
understanding to predict system behavior and
improve system performance.
2. Much of this work is done using analytical and
numerical techniques to develop and manipulate
mathematical and computer models of organizational
systems composed of people, machines, and
procedures.
5
Terminology
• The British/Europeans refer to “Operational Research", the
Americans to “Operations Research" - but both are often
shortened to just "OR".
• Another term used for this field is “Management Science"
("MS"). In U.S. OR and MS are combined together to form
"OR/MS" or "ORMS".
• Yet other terms sometimes used are “Industrial Engineering"
("IE") and “Decision Science" ("DS").
6
Operations Research Models
• Linear Programming
• Nonlinear Programming
7
Chapter 2
Linear Programming: Model
Formulation and Graphical Solution
8
Linear Programming
Objectives of business firms frequently include maximizing profit or
minimizing costs.
Linear programming is an analysis technique in which linear
algebraic relationships represent a firm’s decisions given a
business objective and resource constraints.
Steps in application:
Identify problem as solvable by linear programming.
Formulate a mathematical model of the unstructured problem.
Solve the model.
9
Model Components and Formulation
• Decision variables - mathematical symbols that does not have a specific value
representing controllable inputs.
• Objective function - a linear mathematical relationship describing an goal of the
firm, in terms of decision variables, that is maximized or minimized Examples :
•
•
•
•
Maximize profit
Minimize cost
Minimize distance
Minimize time
• Constraints - restrictions placed on the firm by the operating environment stated
in linear relationships of the decision variables.
• Parameters - numerical coefficients and constants used in the objective function
and constraint equations.
• The objective and constraints must be definable by linear mathematical
10
functional relationships
Graphical Solution of Linear Programming Models
• Graphical solution is limited to linear programming models
containing only two decision variables (can be used with
three variables but only with great difficulty).
• Graphical methods provide visualization of how a solution
for a linear programming problem is obtained.
11
Step of Graphical method
• Drawing the two axis
• Plot the constraints as equations
• Determine the feasible solution points
• Optimal solution with objective function
12
13
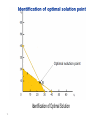
Identification of Optimal Solution
14
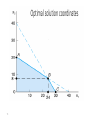
Optimal solution coordinates
15
solution at all corner pointe
16
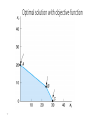
Optimal solution with objective function
17