* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 14--Part 3
Pacific Ocean wikipedia , lookup
History of research ships wikipedia , lookup
Abyssal plain wikipedia , lookup
Atlantic Ocean wikipedia , lookup
Deep sea fish wikipedia , lookup
Marine geology of the Cape Peninsula and False Bay wikipedia , lookup
Southern Ocean wikipedia , lookup
Indian Ocean wikipedia , lookup
Marine pollution wikipedia , lookup
Future sea level wikipedia , lookup
Marine biology wikipedia , lookup
Anoxic event wikipedia , lookup
Ocean acidification wikipedia , lookup
Marine habitats wikipedia , lookup
Arctic Ocean wikipedia , lookup
Physical oceanography wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on oceans wikipedia , lookup
Ecosystem of the North Pacific Subtropical Gyre wikipedia , lookup
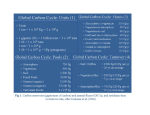
Chapter 14—Part 3 Younger Dryas Period/ CO2-climate feedbacks CO2 Variations Bubbles in ice cores provide samples of ancient air. These samples tell us that CO2 levels track the changes in temperature CO2 T CH4 http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/warming/stories/ Temperature and CO2 change together Temperature http://www.env.leeds.ac.uk/envi2150/lecture6/lecture6.html CO2 CO2 Variations Bubbles in ice cores provide samples of ancient air. These samples tell us that CO2 levels track the changes in temperature This suggests CO2 can amplify climate change that is initiated by orbital variations. How? The Weathering Cycle is TOO SLOW! The weathering cycle operates over millions of years Glacial climate changes take place over thousands of years CaSiO3 + CO2 CaCO3 + SiO2 The Biological Pump (marine organic carbon cycle) transfer of CO2 to the deep ocean: North Atlantic Pacific Ocean Transfer of carbon Deep water surface water Photosynthesis CO2 + H2O CH2O + O2 sinking particles Respiration CH2O + O2 CO2 + H2O deep water Changes in the Biological Pump: Atmospheric CO2 can decrease if more CO2 is stored in deep waters Changes in the Biological Pump: Atmospheric CO2 can decrease if more CO2 is stored in deep waters. This could be due to: 1) slower deep ocean circulation Changes in the Biological Pump: Atmospheric CO2 can decrease with more storage of CO2 in deep waters. This could be due to: 1) slower deep ocean circulation or 2) greater photosynthesis in surface waters Changes in the Biological Pump: Atmospheric CO2 can decrease with more storage of CO2 in deep waters. This could be due to: 1) slower deep ocean circulation or 2) greater photosynthesis in surface waters More nutrients to the ocean? Limiting nutrients: N, P, and Fe Redfield Ratios These are the ratios of different elements in living organisms Element C N P Fe Relative # of atoms 106 15 1 0.01-0.1 Nitrogen in organisms • Amino acids (shown at left) are the building blocks of proteins • Nitrogen is part of the amino (NH2) group Diagram from Wikipedia Phosphorus in organisms • Phosphorus is a key component of nucleic acids, i.e., DNA and RNA • Nucleic acids also contain nitrogen http://www.isof.cnr.it/ppage/capob/synth.html Iron in organisms • Iron is used as part of various catalysts • There evidently is some iron in chlorophyll, but not much (main metal atom is Mg) – But, iron is required for the synthesis of chlorophyll http://chaitanya1.wordpress.com/2007/07/09/strawberries/ Possible glacial-interglacial CO2/climate feedback loops • Broecker’s “shelf hypothesis” (P) • Martin’s “iron hypothesis” (Fe) • “Coral reef hypothesis” (carbonate saturation state) Broecker’s “Shelf” hypothesis Interglacial sea level -Weathering releases P from rocks -Some of this P accumulates in sediments on the shelves P-rich sediments Glacial sea level • When sea level falls, P-rich sediments on the continental shelves are washed into the deep ocean, raising productivity The Shelf Hypothesis Feedback Loop Start here Atm. CO2 Surf. Temp. Ts Continental Ice Sheets (+) Biological Pump P to ocean Shelf exposure Positive feedback loop! Sea Level Martin’s “Iron hypothesis” • Iron is a limiting nutrient in parts of the ocean, especially the southern oceans near Antarctica • Iron is supplied to the oceans by windblown dust from the continents • Wind strength increases when the climate becomes glacial because the poles cool more than does the equator Saharan dust plume Iron Fertilization Feedback Loop Start here Atm. CO2 Surf. Temp. Ts Equator to pole Temp. gradient (+) Biological Pump Iron in Dust to Ocean Positive feedback loop! Wind Speeds Coral Reef Hypothesis Interglacial sea level Coral reef (CaCO3) CaCO3 + CO2 + H2O Ca++ + 2 HCO3 Glacial sea level • Reefs form when sea level goes up CO2 goes up • Reefs weather and dissolve when sea level goes down CO2 goes down Coral reef feedback loop Start here Surf. temp Ts Continental glaciers Sea level (+) Atmospheric CO2 Surface ocean CO2 Positive feedback loop! Reef formation • So, there are several positive feedback loops that may cause atmospheric CO2 to go up and down in concert with the glacial-interglacial cycles • Some combination of these feedback loops, combined with changes in ocean circulation, is probably responsible for the CO2 fluctuations seen in the Vostok ice core Younger Dryas Period • Towards the end of the last Ice Age, climate warmed, then suddenly cooled again for almost 1000 yrs • The evidence comes from the reappearance of the Dryas flower in the Alps, which flourishes in glacial climates Image from Wikkipedia Younger Dryas Period • Temperatures come from O and H isotopes in ice cores • High 18O (or high D/H) warmer temperatures Younger Dryas The Atlantic Conveyor • Did the oceanic thermohaline circulation shut down during the Younger Dryas Period? Atlantic Conveyor Shutdown • As the Laurentide ice sheet retreated, melt water was diverted from the Mississippi River to the St. Lawrence River • North Atlantic ocean became capped with freshwater not dense enough to sink thermohaline circulation shut down for ~1000 yrs • Could this happen again as a result of global warming?