* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 5 Sparks Civil War North Vs South
Ulysses S. Grant and the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Stones River wikipedia , lookup
Baltimore riot of 1861 wikipedia , lookup
Fort Fisher wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Appomattox Station wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Island Number Ten wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Wilson's Creek wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Hampton Roads wikipedia , lookup
Texas in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Red River Campaign wikipedia , lookup
Confederate States of America wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Shiloh wikipedia , lookup
List of American Civil War generals wikipedia , lookup
United States presidential election, 1860 wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Gaines's Mill wikipedia , lookup
Lost Cause of the Confederacy wikipedia , lookup
Battle of New Bern wikipedia , lookup
East Tennessee bridge burnings wikipedia , lookup
South Carolina in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Fort Pillow wikipedia , lookup
Union blockade wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Cedar Creek wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Lewis's Farm wikipedia , lookup
Hampton Roads Conference wikipedia , lookup
Pacific Coast Theater of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Tennessee in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
First Battle of Bull Run wikipedia , lookup
Capture of New Orleans wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Namozine Church wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Seven Pines wikipedia , lookup
Blockade runners of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Opposition to the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Georgia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Alabama in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Conclusion of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Economy of the Confederate States of America wikipedia , lookup
Military history of African Americans in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Virginia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Confederate privateer wikipedia , lookup
Border states (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
Issues of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Commemoration of the American Civil War on postage stamps wikipedia , lookup
Anaconda Plan wikipedia , lookup
Union (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
Mississippi in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom and the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
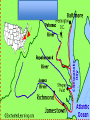
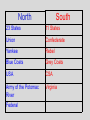
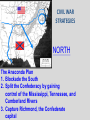
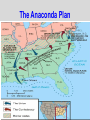
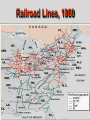
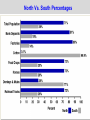
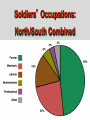
Mr. Sparks American Civil War Section III: Basic Facts & The Comparison of the Union and the Confederates States of America Basic Facts of Civil War • • • • • April 12, 1861 - April 9, 1865 Richmond – CSA Capital Washington D.C. – USA Capital Abraham Lincoln – USA President Jefferson Davis – CSA President Basic Facts of Civil War • • • • • • 3 million men and women fought 600,000 die (400,000 of sickness) Most of the fighting is in the south Union blockades south with ships Europe stays out of it, but favors south * The Europeans would love the CSA to win to “stick-it to the Americans”, but will NOT help a country with slavery. Civil War Casualty and Death Numbers • https://www.phil.muni.cz/~vndrzl/amstudies/civil war_stats.htm This site is one of many that breaks down the casualty and death rates of the Civil War North South 23 States 11 States Union Confederate Yankee Rebel Blue Coats Grey Coats USA CSA Army of the Potomac River Virginia Federal The Leaders Abraham Lincoln was the sixteenth President of the United States. He opposed the expansion of slavery. A Republican, Lincoln led the Union during the Civil War. John Wilkes Booth assassinated Lincoln in Washington, D.C., on April 14, 1865. Jefferson Davis was President of the Confederate States of America. During the Mexican War, he had been an officer in the United States Army. Davis also had served as the United States Secretary of War. When the South surrendered, he was charged with treason and prohibited from running for public office again. Abraham Lincoln (Before and After) Washington, D.C. • Capital of the Union The Leaders of the Confederacy Pres. Jefferson Davis VP Alexander Stevens The Confederate “White House” The Capital of the CSA is in Richmond, Virginia. The Confederate Seal C.S.A. MOTTO “With God As Our Vindicator” The Generals Ulysses S. Grant Robert E. Lee William T. Sherman Thomas Jackson George Meade James Longstreet George B. McClellan James E.B. Stuart (JEB) Goals of Each Country • Union – Get the South to Re-join the Union • Confederacy – Leave the Union Strategies Anaconda Plan Union General Winfield Scott suggested the Anaconda Plan to halt Southern trade. The plan would impose a blockade. This would eventually enable the North to control the Mississippi River. Meanwhile, the army would divide and isolate sections of the South and capture its vital cities and the capital in Richmond, Virginia. Under General Ulysses S. Grant, the North’s strategy kept pressure on General Robert E. Lee’s army and constantly weakened their numbers. The larger population of the North made this possible. King Cotton The Confederacy adopted a defensive strategy and attempted to secure alliances with more powerful countries such as Britain and France. To do that, the South needed to show it could win the war. As a result, the Confederate army attacked Union territory to draw Union troops away from the South and to impress potential allies. As the war continued, the Southern strategy became one of evading the Union army, prolonging the war, and inflicting casualties to demoralize the North. The “Anaconda” Plan CIVIL WAR STRATEGIES NORTH The Anaconda Plan 1. Blockade the South 2. Split the Confederacy by gaining control of the Mississippi, Tennessee, and Cumberland Rivers 3. Capture Richmond, the Confederate capital CIVIL WAR STRATEGIES SOUTH WIN RECOGNITION AS AN INDEPENDENT NATION 1. Capture Washington, D.C. 2. Seize central Pennsylvania 3. Defend homeland until the North tired of fighting 4. Get Britain to pressure North to end blockade to restore cotton supplies Strategy of South • Win enough major battles to make the Union quit. • Starve Europe of Cotton- Economic involvement. Is it possible to win a war, without winning all of the battles? Similarities: American Rev. War, Vietnam. Issues with these Strategies • Union • Confederate Slow and Steady…. Issues with King Cotton- by this time Britain and France were planting cotton in North Africa and other territories (so the demand for South Cotton began to diminish) -Britain & France DID NOT want to lose the Northern Market in textiles/industry/consumers!!!! Congress wanted the war to end quickly and couldn’t wait. Naval Blockade & Capturing the Mississippi would allow control of the Tennessee and Cumberland Rivers (heart of the South)…but you need a large Navy, which the Union didn’t have during the start of the war. -Plus they had abolished slavery years ago and morally didn’t want to support the South. The Anaconda Plan Railroad Lines, 1860 Resources: North & the South North Vs. South Percentages Men Present for Duty in the Civil War CIVIL WAR ADVANTAGES/DISADVANTAGES NORTH ADVANTAGES Larger population More industry More resources Better banking system More railroad mileage Abraham Lincoln More ships DISADVANTAGES Faced hostile people Southern territory unfamiliar CIVIL WAR ADVANTAGES/DISADVANTAGES SOUTH ADVANTAGES Strong popular support Familiar territory Superior military leadership DISADVANTAGES Smaller population Few factories Less food production Fewer railroad miles Fewer ships Jefferson Davis Belief in states’ rights South: Plantations Bad for War North, Factories Good For War Soldiers’ Occupations: North/South Combined Popular Pressure for a Fight Stanton…Secretary of War… Wants the fight…popular opinion is screaming for a fight Neither side is really ready Politicians have too much power in this war. • On paper . . . the Union should have a relatively easy time quelling this rebellion. • However the southern advantages coupled with the almost inept early leadership on the Union’s part help lead to one of the most extraordinary epics of American History. Comparison • Union – (24 states, 21 million pop.) – More Railroads – More Money – More Factories – More People • Confederacy – (11 states 10 million pop.) – Better Generals at start of War – Fighting on their home turf • Know terrain • Defend or Die Next Up…. Prepare for War: Military Concepts & Tactics