* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download True or False - St. Clair Schools
Survey
Document related concepts
Marketing strategy wikipedia , lookup
Product planning wikipedia , lookup
Market penetration wikipedia , lookup
Darknet market wikipedia , lookup
Gasoline and diesel usage and pricing wikipedia , lookup
Grey market wikipedia , lookup
Service parts pricing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing channel wikipedia , lookup
Pricing strategies wikipedia , lookup
Dumping (pricing policy) wikipedia , lookup
Price discrimination wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
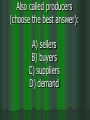
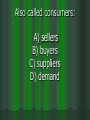
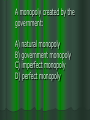
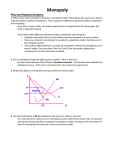
Chapter 6 & 7 Economics 12 First part of Jeopardy is on Chapter 6 This is an example of what--- when the red line and blue line intersect: (Market) Equilibrium A minimum price for a good or service: Price Floor A product that is popular for a short period of time: Fad The quantity of goods that a firm has on hand: Inventory A price ceiling placed on apartment rent: Rent Control A situation in which consumers want more of a good or service than producers are willing to make available at a particular price: Shortage A minimum price that an employer can pay a worker for an hour of labor: Minimum Wage Any price quantity not at equilibrium, when quantity supplied is not equal to quantity demanded in a market: Disequilibrium A maximum price that can legally be charged for a good or service: Price Ceiling A sudden shortage of a good: Supply Shock A system of allocating scarce goods and services using criteria other than price: Rationing A market in which goods and services are sold illegally without regard for government controls on price or quantity: Black Market True or False Many factors can shift a product’s demand or supply curve: True True or False The price system responds to surpluses and shortages by steering producers and consumers to market equilibrium: True True or False When either the demand or supply curve shifts, the equilibrium point remains constant: False—the equilibrium also shifts True or False Market equilibrium is reached when surpluses and shortages are avoided: True Price ceilings tend to lead to: A) Shortages B) Surpluses C) Black markets D) Rationing programs A) Shortages The minimum wage is an example of a: A) Price floor B) Rationing program C) Price ceiling D) Black market A) Price Floor Rationing is thought to be an unwise economic policy because it is: A) expensive, time-consuming, and creates black markets B) expensive, unfair, and time-consuming C) unfair, time-consuming, and creates black markets D) unfair, expensive, and creates black markets D) unfair, expensive, and creates black markets Governments sometimes set prices to: A) Increase demand for a particular product B) protect producers and consumers from dramatic price swings C) ensure that there will be an adequate supply of goods for consumers to purchase D) decrease the demand for a particular product B) protect producers and consumers from dramatic price swings Prices coordinate the decisions of producers and consumers by: A) Decreasing variability in supply and demand B) Increasing variability in supply and demand C) Limiting the impact of supply and demand D) Balancing the forces of supply and demand D) Balancing the forces of supply and demand The benefits provided by the price system include: A) incentives, flexibility, and externality B) incentives, choice, and flexibility C) choice and the availability of public goods D) information, efficiency, and positive externality B) incentives, choice, and flexibility One of the limitations of the price system: A) It’s a failure to assign the cost of public goods to all consumers B) the availability of a variety of goods and services C) that it encourages the wise use of resources D) its ability to deal with change A) It’s a failure to assign the cost of public goods to all consumers Second part of Jeopardy is on Chapter 7 Also called producers (choose the best answer): A) sellers B) buyers C) suppliers D) demand A) Sellers Gives a business exclusive rights to produce an invention: Patent Two to Five businesses dominating the marketplace is known as a (an) _______. Oligopoly Also called consumers: A) sellers B) buyers C) suppliers D) demand B) Buyers This happens when sellers start undercutting their competitor’s price: Price War An ideal market condition that includes a large number of sellers of identical goods and services and in which no one seller controls supply or prices: Perfect Competition Laws that encourage competition in the marketplace: Antitrust Laws A product such as petroleum or milk that is considered the same no matter who produces or sells it: Commodity A government issued right to operate a business: License True or False Non-Price competition is competition on a basis other than price. True True or False The main goal of price differentiation and Non-Price competition is to increase profits. True A monopoly created by the government: A) natural monopoly B) government monopoly C) imperfect monopoly D) perfect monopoly B) government monopoly A market structure in which one seller controls all production of a good or service: Monopoly Give me an example of a monopoly---you can’t say Microsoft: Answers may vary…….. What sets the price in a perfectly competitive market: Supply and Demand Yes or No Can the Federal Trade Commission order a shut down of a company that uses unfair methods of competition: No They may only force them to change their methods The effort by sellers to secretly set production levels or prices is called: Collusion A market that runs most efficiently when one large firm supplies all the output: A) Natural monopoly B) Technological monopoly C) Geographical monopoly D) Government monopoly A. Natural Monopoly True or False Factors that cause a products average cost per unit to fall as output rises is called economies of scale. True True or False When the Civil War ended in 1865, many small companies were forced out of business or were taken over by larger companies: True An organized system of price fixing and market sharing is known as a ______________. Cartel Non-Price competition is competition on a basis other than _________ . Price The most common type of noncompetitive market in the United States is a(n): A) Monopoly B) Oligopoly C) Perfect Competition D) Collusion B. Oligopoly Which of the following is an illegal form of determining prices: A) Collusion B) Price war C) Substitution D) Price Leadership A. Collusion The expenses a new business must pay before it can begin to produce and sell goods: Start-up Costs Last Question: When a surplus exists in a market, what tends to fall: Prices Last Question: When two or more companies join to form a single firm: Merger