* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Forces Notes - watertown.k12.wi.us
Survey
Document related concepts
Artificial gravity wikipedia , lookup
Mechanics of planar particle motion wikipedia , lookup
N-body problem wikipedia , lookup
Roche limit wikipedia , lookup
Potential energy wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Woodward effect wikipedia , lookup
Coriolis force wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
Negative mass wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic angular momentum wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Modified Newtonian dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Newton's law of universal gravitation wikipedia , lookup
Centrifugal force wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
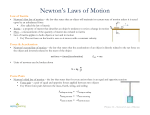
Forces Notes “Any influence that can cause a body to be It is measured in accelerated . .” Newtons A Newton is the force needed to accelerate one kg one meter per second per second A Push or Pull exerted by an object to/on another object Always occurs in It can alter the Pairs (Sometimes referred to as Agent & Receiver) Shape It is represented by or Arrows Motion that show Demos of an object Direction and size What it demonstrates Rolling Ball Shows Acceleration Pushing a closed door All show that forces occur in pairs Standing on the floor All show that forces occur in pairs Clay ball Shows how force is required to change shape Tennis ball Change of shape- Elasticity Pushing on a table Forces occur in pairs; Net Force Newton’s Laws of Motion Law #1: “Every body continues in its state of rest , or of uniform motion in a straight line, unless it is compelled to by forces impressed upon it.” Sometimes called the Law of Change that state Inertia Who is this? Sir Isaac Newton What is Inertia? “The sluggishness or apparent Resistance a body offers to changes in its state of motion” The larger the Mass A body with less , the larger its Mass A body with more mass is Inertia is easier to get moving harder to get moving Demos What it demonstrates Ping pong ball Small inertia; easy to move & stop Bowling ball Larger inertia; hard to move & stop Granny Small inertia; easy to move & stop Mack Truck driven by Granny Larger inertia; hard to move & stop Mass Defined as “The quantity of Matter It is the measurement of Inertia in a body” m = mass; F = force; a = acceleration m = F/a F = m(a) a Why should Eeyore ALWAYS wear a seatbelt? = F/m Momentum The product of It is Mass Inertia and in motion Demos Car on a ramp Velocity What it demonstrates A small mass accelerated at high velocity can be produce a lot of force Eeyore on a car on a ramp Momentum Conservation of Momentum All energy stored in a moving object is not lost Stated by: Albert Einstein , but only changes Phillip Morrison Demos form Mr. Watts What it demonstrates Newton’s Cradle Conservation of Momentum Swinging Rock Potential and Kinetic energies; Conservation of Momentum Mass in a Circular Motion When an object moves in circular path, it has a property called AKA: Gyroscopic Rotational Inertia Inertia “An object rotating about an axis tends to remain rotating about that same axis unless it is interfered with by some external force.” This definition is similar to Newton’s First Law of Motion Demos What it demonstrates Bicycle tire Gyroscope Top Frisbee Football Moment of Inertia Angular Momentum It is a measure of an object’s rotation about a particular Axis For an object small compared to the radial distance, it is the product of mass, velocity and radius (m x v x r) It is the measure of the rotational property of motion It is perpendicular the centripetal force Describe what’s happening in this diagram: to Demos What it demonstrates Rolling objects Washer on a string Slingshot (old-fashioned!) Bucket with water spun in vertical circles Q: What holds the water in the bucket? Spin cycle of washing machine “Whizzer” Brendan on the Scrambler Carnival Ride Know-How It’s better to take the outside of the car if you’re riding alone If you’re riding with someone else, take the inside seat seat The following formula is similar to those for Newton’s First Law , but deals with mass in motion in a circular path: mvr = mvr m= Mass v= Velocity r= radius What was demonstrated to show what happened here? What happens in this situation? mv r = mvr … The mass is not affected by a smaller radius, while is. Centripetal Force A center-seeking Force that causes an object to follow a circular path. “Any force that is directed at produces circular motion.” right angles to the path of the moving body and Name the centripetal force that keeps the moon revolving around the earth: Centrifugal Force A fictitious due to rotation outward force It is a Reaction to centripetal force but there is no agent, therefore it is experienced relative to position What we are really experiencing is ANGULAR MOMENTUM ! Newton’s Second Law The acceleration of a body is and inversely NET FORCE Formulas: a = F/m F = m (a) m = F/a directly proportional to the net force acting on the body proportional to the mass of the body and is in the direction of the 5N 5N 5N Acceleration = 6 kph Acceleration = _____ Acceleration = _____ N Newton’s Third Law Whenever one body exerts a force on a second body, the second body exerts an equal and opposite force on the first For every action , there is an equal and opposite reaction You cannot touch without being touched Common Forces Gravitational – non contact 5 Every object exerts an N Buoyancy - contact The tendency to Acceler ation = ? attractive force on every other object float in a fluid Friction - contact The resistance to motion where two objects touch Magnetic – non contact The repelling or Attraction of a magnet and ferromagnetic material Elastic - contact Ability to spring back to its original size, shape, or position after being stretched, squeezed, flexed, expanded, etc. Electrical – non contact Flow or gathering of a negative charge by Other Physics concepts of interest: Energy The quality of an object that enables it to do electrons K P K work Power Work/ Time Potential Energy The stored energy that a body possesses because of its position with respect to other bodies Kinetic Energy The energy of motion Kinetic Energy = 1/2 mv2 P At which point is potential and kinetic energy equal?