* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Feeding Time - Waterford Public Schools
Survey
Document related concepts
Brownian motion wikipedia , lookup
Hunting oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Modified Newtonian dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Classical mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Seismometer wikipedia , lookup
Rigid body dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Centrifugal force wikipedia , lookup
Equations of motion wikipedia , lookup
Mass versus weight wikipedia , lookup
Newton's theorem of revolving orbits wikipedia , lookup
Centripetal force wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
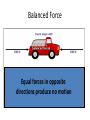
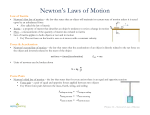
Feeding Time Find the 6 differences between the two pictures. Source: http://www.slylockfox.com/arcade/6diff/index.html The answers are … Answers: Feed, boy’s hair, bird’s legs, bucket, dog’s collar, duck’s wing Source: http://www.slylockfox.com/arcade/6diff/index.html CAR CRASH VIDEO Scrambled Words T. Trimpe 2006 http://sciencespot.net/ Unscramble each set of letters to reveal a forensic science term. 1. ginainvetosti 2. munilol 3. mitciv 4. curot 5. netdal corerd HINT: The underlined letters are the first letters of the words. The answers are ... 1. ginainvetosti INVESTIGATION 2. munilol LUMINOL 3. mitciv VICTIM 4. curot COURT 5. netdal corerd DENTAL RECORD Newton’s First Law (Law of Inertia) • An object at rest tends to stay at rest and an object in motion tends to stay in motion unless acted upon by an unbalanced force Well What is Force? Force is a push or a pull on an object Balanced Force Equal forces in opposite directions produce no motion Unbalanced Forces Unequal opposing forces produce an unbalanced force causing motion What does this mean? • A object will “keep doing what it was doing” unless acted on by an unbalanced force • If the object was sitting still, it will remain stationary • If it was moving at a constant velocity, it will keep moving • It takes force to change the motion of an object Forces Change Motion! Newton’s First Law of Motion Newton’s First Law and Mass • MASS is the measure of the amount of matter in an object • It is typically measured in kilograms Newton’s First Law • Newton’s First Law is also known as the Law of Inertia • INERTIA is the tendency of an object to resist changes in its state of motion • Newton’s First Law states that all objects have inertia • The more mass an object has, the more inertia it has (and the harder it is to change its motion) Examples from Real Life A powerful locomotive begins to pull a long line of boxcars that were sitting at rest. Since the boxcars are so massive, they have a great deal of inertia and it takes a large force to change their motion. Once they are moving, it takes a large force to stop them. On your way to school, a bug flies into your windshield. Since the bug is so small, it has very little inertia and exerts a very small force on your car (so small that you don’t even feel it). If objects in motion tend to stay in motion, why don’t moving objects keep moving forever? Things don’t keep moving forever because there’s almost always an unbalanced force acting upon them A book sliding across a table slows down and stops because of the force of friction If you throw a ball upwards it will eventually slow down and fall because of the force of gravity Inertia Video