* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download fourth nine weeks
Magnetochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Multiferroics wikipedia , lookup
High voltage wikipedia , lookup
Static electricity wikipedia , lookup
Electromotive force wikipedia , lookup
Scanning SQUID microscope wikipedia , lookup
Magnetohydrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Electrostatics wikipedia , lookup
Superconductivity wikipedia , lookup
Photoelectric effect wikipedia , lookup
Eddy current wikipedia , lookup
Force between magnets wikipedia , lookup
Electric current wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetic radiation wikipedia , lookup
Electric machine wikipedia , lookup
History of electromagnetic theory wikipedia , lookup
Superconducting magnet wikipedia , lookup
Electrical injury wikipedia , lookup
Electrification wikipedia , lookup
Electricity wikipedia , lookup
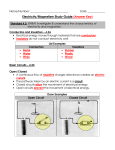
Fourth nine weeks unit plan 8th grade science Layman and Hedrick Sound and Light Standards: Waves 1. Understand how light and radio waves carry energy through vacuum or matter by: • straight-line travel unless an object is encountered • reflection by a mirror, refraction by a lens, absorption by a dark object • separation of white light into different wavelengths by prisms • visibility of objects due to light emission or scattering. 2 Understand that vibrations of matter (e.g., sound, earthquakes, water waves) carry wave energy, including: • sound transmission through solids, liquids, and gases • relationship of pitch and loudness of sound to rate and distance (amplitude) of vibration Activities Introduce vocabulary (light, reflection, refraction, absorption, transparent, translucent, opaque, convex, concave, rods, cones, lens, focal point, optical illusions, sound, sound wave, Doppler effect, vibration, medium, wavelength, frequency, pitch, amplitude, interference, resonance, echo, reverberation, echo location, sonar) pre-assessment to determine student’s readiness to learn. Agree/disagree statements Chapter 13, lesson 1 and Chapter 14, lesson 1 Students will demonstrate their understanding of sound and light waves through various lab and center stations, including but not limited to practicing with mirrors, prisms, tuning forks, optical illusions, lights, color, musical instruments, common household items to demonstrate sound and light qualities. Post assessment – quiz Electricity and Magnetism Standards: 1. Know that electrical energy is the flow of electrons through electrical conductors that connect sources of electrical energy to points of use, including: • electrical current paths through parallel and series circuits • production of electricity by fossil-fueled and nuclear power plants, wind generators, geothermal plants, and solar cells • use of electricity by appliances and equipment (e.g., calculators, hair dryers, light bulbs, motors). 2. Know that electric charge produces electrical fields and magnets produce magnetic fields. * Know how a moving magnetic field can produce an electric current (generator) and how an electric current can produce a magnetic field (electromagnet). *know that Earth has a magnetic field. Activities: Introduction of vocabulary: (electrically charged, electric discharge, insulator, conductor, force, field, current, circuit, generator, series vs parallel circuits, ac vs. dc, voltage, amps, electromagnet, poles) Chapters 15 Students will complete several lab activities and centers demonstrating their knowledge of electricity and magnets; including, but not limited to using different types/shapes of magnets, creating series and parallel circuits, testing conductivity and magnetism of different objects, create and electromagnet and a temporary magnet. Students will determine how we use electricity and magnets in day to day life. Post assessment - quiz