* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
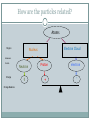
Gathering Atomic Information ALMOST ALL OF THE INFORMATION YOU NEED TO KNOW ABOUT A PARTICULAR ELEMENT CAN BE FOUND BY LOOKING AT THE PERIODIC TABLE. THE PERIODIC TABLE WILL TYPICALLY HAVE ONE OF THE FOLLOWING FORMATS: If this stadium were the size of an atom’s electron cloud, the nucleus would be the size of a marble setting on the 50 yard line. Electrons occupy the VOLUME, protons and neutrons constitute the MASS of an atom. Subatomic Particles Protons and electrons are the only particles that have a charge. Protons and neutrons have essentially the same mass. The mass of an electron is so small (2000 time smaller than the proton), we ignore it. 0.0005486 is the way to write this number! 3 What do all atoms of the same element have in common? ***Atoms of the same element always contain the same number of protons!*** What is the name of the two numbers on an element’s square of the periodic table? Carbon 12.011 C 6 Atomic Number: Smallest of the two numbers Always a whole number Indicates number of protons Average Mass Average number of protons (p+) and neutrons Usually a decimal Mass Number # of protons and neutrons added together round the average atomic weight to the nearest whole number to find the most common combination of p+ and n (isotope) 6 C Carbon 12.011 What information can be obtained from the two numbers on a square of the periodic table? Subatomic Particle & symbol Charge Mass (amu) Location (region) How to find number in an atom Founder and Date Proton (p+) Positive (+) 1 Nucleus Same as atomic number E. Rutherford 1914 Neutron (n) or (0) Neutral 1 Nucleus Mass # -Atomic # # Neutrons J Chadwick 1932 Electron (e-) Negative (-) 0 Electron cloud Same as JJ Thomson atomic 1897 number in a neutral atom How are the particles related? Atoms Electron Cloud Nucleus Region Subatomic Particle Charge Charge Balance Neutron 0 Proton + electron - Isotope ATOMS OF THE SAME ELEMENT THAT HAVE DIFFERENT NUMBER OF NEUTRONS Models of Carbon Isotopes Carbon-12 6p+ 6n Carbon-13 6p+ 7n Carbon-14 6p+ 8n How are isotopes of the same element identified? Isotopes are identified by the name of the element and by the atom’s mass number (written like Li-6 or Li-7) It’s called ISOTOPE NOTATION Lithium Isotope Examples Isotope Name Symbol # protons # neutrons # electrons Lithium-6 Li-6 3 3 3 Lithium-7 Li-7 3 4 3 Chlorine-35 Cl-35 17 18 17 Chlorine-37 Cl-37 17 20 17 How to find Mass Number Number of protons AND neutrons (added together) of a specific isotope of an element. Mass Number = #p + #n Found one of two ways (prioritized) Given to you after the element symbol (isotope notation) C-14 or Na-23 100% accuracy Most common isotope method (mci). Round the average atomic mass value from the periodic table to the nearest whole number Carbon’s Atomic mass is 12.011 = round to 12 Manganese’s Atomic mass is 54.95 = round to 55 50% accuracy