* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download World War II
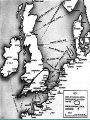
Swedish iron-ore mining during World War II wikipedia , lookup
British propaganda during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Allied plans for German industry after World War II wikipedia , lookup
Technology during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Mediterranean and Middle East theatre of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of the attack on Pearl Harbor wikipedia , lookup
Battle of the Mediterranean wikipedia , lookup
Naval history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
World War II by country wikipedia , lookup
Home front during World War II wikipedia , lookup
End of World War II in Europe wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
Causes of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
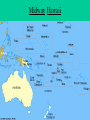
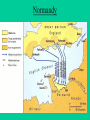
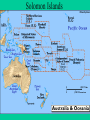
World War II Major Battles Battle of Britain 1940 Skies above England….London German(Luftwaffe) vs Britain Continuous air raids and bombing of industrial areas, railroads, bridges, cities Really no winner. Britain never surrendered and Germany stopped the bombing and cuts the loses. Cost them planes, bombs, men and money. North Africa • • • • Summer 1942 –Summer 1943 Northern coast of Africa Allies vs mostly Germans Attempt to drive out all Axis powers to keep away from oil/trade routes • Allies successful • Would now be able to invade Italy from the south Balkan Invasion • • • • Early 1941 Balkan Region German drive British forces from Greece Take control of Caspian Sea (oil) and Suez Canal trade. • Be able to attack Soviet Union from the south Battle of Leningrad • Sept 1941-first part of 1942 • Now called St. Petersburg • Germany surrounds Leningrad and over million civilians starve and die • Soviets never gave up • German losses near 500,000 Pearl Harbor • • • • • • • December 7th, 1941 Surprise attack on main naval base in Pacific 2300 soldiers, 150 planes and 18 ships lost Crushing American defeat FDR “This day will live in infamy” Tojo “I feel we have woke a sleeping giant!” Brings US into war on both fronts-Pacific and European Midway Hawaii Battle of Midway • June 1942 • Japan send 100 ships to Midway to take the base to continue towards Hawaii • US intercepted and decoded message, ready for the attack • War fought mostly by planes, shot down 38 Zero’s • US sank 4 Japanese aircraft carriers in a period of minutes to send Japan retreating. • Turning point of war with Japan Iwo Jima • March-June 1945 • Small island in the Pacific • Part of Island hopping technique in Pacific to closer and closer to Japan to launch invasion. Attack and take over islands not well defended. • Japan dug in, literally into side of mountain and ground. Held off til June. One of the bloodiest battles of war. • US victory took control of airbase Iwo Jima (Memorial in DC) Iwo Jima (Memorial in DC) Map of Iwo Jima Battle at Coral Sea • May 1942 • Eastern coast of Australia • American Navy despite being half the size of Japans stop Japan’s movement towards Australia • Battle fought by Warplanes • Beginning of Japanese aviation decline Hiroshima • • • • • • August 6th, 1945 A city of military and industrial significance in Japan 7th Largest city in Japan First A-bomb was dropped Name of the airplane was the “Anola Gay” Tibbets mother Instantly killed 80,00 people, Japan claimed 200,000 Nagasaki •August 9th, 1945 •Nagasaki was picked as a result of Military and Industrial importance also • It was the largest port in south Japan • Instantly killed 70,000 people •Force Japanese to surrender Paul Tibbets and the Anola Gay Little Boy After Little Boy Fat Man After Fat Man Battle of Stalingrad • • • • • 1942-1943 Stalingrad, Soviet Union Soviets vs Germans Bloodiest standoff on the war Over one million casualties. Turning point in war, Germans retreat, Soviets begin offensive • Allies decided to let Russia fight on their own THIS DECISION WILL COST THE U.S. FUTURE RELATIONS WITH SOVIETS. D-Day Invasion • • • • • June 6th, 1944 Normandy (North Shore of France) Code Name “Operation Overlord” British and US forces vs German Had to invade France to be able to invade/attack Germany • Largest single invasion in military history • Now able to liberate France and attack Germany Higgins Boats Normandy Invasion Battle of Bulge December 16, 1944 Border areas near Luxembourg, France and Germany Germany last ditch effort to take back France and regain some power. Germany made some ground but not enough. This is were the phrase “Bend but not Break” was used Impact – Germans begin retreat signaling their defeat. First time allies will enter Germany since war started First time allies will see concentration camps Battle of the Bulge Battle of Alamein • • • • Oct-Nov 1942 North coast of Africa in Egypt Allies vs Axis Italy and Germany have control of Northern Africa and are headed towards Cairo/Suez Canal • US decides to start here because the Axis forces are less powerful. • The Battle of Alamein begins to push Germany out Northern Africa Guadalcanal • Aug 1942-Feb 43 • Solomon Islands controlled by Japan • First US offensive. Marine stormed the shores to root out Japan and cut supply lines. • Many causalities but finally succeeded Solomon Islands Okinawa • Apr-July 1945 • Another major Island hopping victory in the Pacific • US Victory • Now able to safely bomb Japan/Tokyo Map of Southeast Asia Invasion of Italy • • • • July 1943- June 1944 Southern part of Italy Allies vs Axis mostly Italians Allies trying to get rid of Mussolini and attack Germany from south • Victorious..April 44 he is killed • Able to launch bombings on Germany European Front April 29, 1945 Mussolini and 15 other fascist leaders are executed and hanged in the Piazzale Loreto in Milan. Leyte Gulf • • • • Oct 1944 Off coast of Philippines Largest Naval engagement in History US wiped out Japan’s Navy for good and supplies routes. • 1st time Japan uses Kamikazes Map of Leyte Gulf (in Philippians) WW II Fatalities Country Military Civilian Total Soviet Union* 8,668,000 16,900,000 25,568,000 China Germany Poland Japan Yugoslavia Rumania* France* Hungary* Austria Greece* Italy 1,324,000 3,250,000 850,000 1,506,000 300,000 520,000 340,000 10,000,000 3,810,000 6,000,000 300,000 1,400,000 465,000 470,000 11,324,000 7,060,000 6,850,000 1,806,000 1,700,000 985,000 810,000 750,000 525,000 520,000 410,000 380,000 145,000 330,000 80,000 Czechoslovakia 400,000 Great Britain USA Holland Belgium Finland Canada India Australia Spain** Bulgaria 326,000 295,000 14,000 10,000 79,000 42,000 36,000 39,000 12,000 19,000 62,000 New Zealand 12,000 12,000 South Africa Norway Denmark 9,000 5,000 4,000 9,000 5,000 4,000 236,000 75,000 *** 10,000 2,000 388,000 295,000 250,000 85,000 79,000 42,000 36,000 39,000 22,000 21,000 The End