* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Different Jobs of Cells
Survey
Document related concepts
Embryonic stem cell wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Artificial cell wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Stem-cell therapy wikipedia , lookup
Chimera (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Dictyostelium discoideum wikipedia , lookup
Induced pluripotent stem cell wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal lineage marker wikipedia , lookup
Hematopoietic stem cell wikipedia , lookup
Human embryogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Microbial cooperation wikipedia , lookup
State switching wikipedia , lookup
Cell theory wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
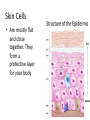
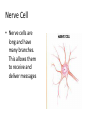
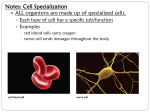
The Different Jobs of Cells 2.2 I. Special Cells for Special Jobs • Cells that make up many-celled organisms are specialized • Bacteria cells are single celled, all other cells are “many celled” organisms A. Types of Human cells • A cell’s shape and size can be related to its function • FAT CELLS – can store so much fat that the nucleus gets pushed against the cell membrane Skin Cells • Are mostly flat and close together. They form a protective layer for your body Bone Cells • Bone cell is surrounded by a hard substance made of calcium and phosphorus Muscle Cell • Muscle cells are usually long and have many fibers that can contract and relax Nerve Cell • Nerve cells are long and have many branches. This allows them to receive and deliver messages B. Types of Plant Cells • Plants have different type of cells in their leaves, roots, and stems • Root Cells are block shaped and do not contain chloroplasts Plant Stem Cells • Stem Cells - Many of the cells in stems are long and tubshaped. They move water and other materials through the plant II. Cell Organization • Cells are organized into systems that perform functions that keep the organism healthy and alive A. Tissues and Organs • Cells that are alike are organized into tissues – Tissues are groups of similar cells that all do the same sort of work • Different types of tissues working together can form an organ B. Organ Systems • A group of organs that work together to do a certain job is an organ system • Organ systems in the human body include: – Digestive system, respiratory system, circulatory system, reproductive system and nervous system