* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download KaryoNIM Postnatal EN
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Birth defect wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Saethre–Chotzen syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Segmental Duplication on the Human Y Chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of autism wikipedia , lookup
Comparative genomic hybridization wikipedia , lookup
Skewed X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
Williams syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Turner syndrome wikipedia , lookup
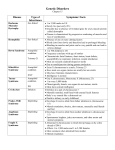
Leading genetic diagnosis What is array-CGH? Array CGH (Comparative Genomic Hybridization) is the newest and most powerful genomic technique for the diagnosis of genetic disorders. Array CGH allows to analyze the complete genome of a person to search for possible variations due to the gain or loss of genetic material. In addition, it is a quick and reliable test, requiring less than 20 days for whole genome analysis. How Array CGH works The sample DNA is compared to control DNA. Both samples are marked with different coloured uorophores and hybridized to the KaryoNIM®Postnatal platform. After being read by a specic scanner, the obtained data are analyzed. Control DNA (without variations) Fluorescent marking Patient DNA Hybridize and scan using KaryoNIM® Postnatal Array CGH are first-tier tests in genetic diagnosis Reasons: Microarrays are recommended to assess DNA copy number variations in patients being studied due to: • Presence of dismorphologic features • Non-syndromic developmental delays/intellectual disabilities • Autism spectrum disorders ACMG PRACTICE GUIDELINES. Array-based technology and recommendations for utilization in medical genetics practice for detection of chromosomal abnormalities. Melanie Manning,MD,MS FACMG and Louanne Hudgins,MD,FACMG. For the Practice and Guidelines Committee “Array-CGH offers a much higher diagnostic yield than a G-banded karyotype (15-20% vs. 2-3%, excluding Down syndrome and other recognizable chromosomal syndromes) for individuals with developmental delay/intellectual disability, autistic spectrum disorders and multiple congenital anomalies, primarily because of its higher sensitivity for submicroscopic deletions and duplications” “Available evidence strongly supports the use of arrays instead of karyotyping as the first-tier genetic diagnostic test for patients with developmental delay/intellectual disability, autistic spectrum disorders and congenital polymalformative syndromes” Consensus Statement: Chromosomal Microarray is a first-tier clinical diagnostic test for individuals with developmental disabilities or congenital anomalies. D.T. Miller, et all., The American Journal of Human Genetics 86, 749-764, May 14, 2010. The most reliable test for genetic diagnosis CGH Arrays are cost-effective tests Conclusions and recommendations Systematic review of literature on array-CGH reveals the cost effectiveness of the technique for diagnosing language, developmental and intellectual disabilities. This is possible because its greater resolution and sensitivity. Backed by reviews and meta-analyses, array CGH allows a larger number of diagnoses, which translates into cost savings. This is due to a decrease in the number of additional conventional genetic tests that are usually required to achieve a diagnosis. Although intellectual disabilities or developmental delays are not curable, a diagnosis that conrms the disease, syndrome or disorder is essential to: (1) Define its prognosis, (2) Shape the family's expectations and (3) Enable the appropriate planning required to manage each case separately, at both clinical and social level. In addition, it also enables genetic counseling and provides important information to cover the present and future educational needs of these individuals. Consenso para la Implementación de los Arrays (CGH y SNP-Arrays) en la genética clínica. Instituto Roche 2012. Duplication in a child of the MECP2 gene in Xq28 (chrX:153059079-153877929, 820 kb). Syndromic autism. Array-CGH platforms designed to improve genetic diagnosis KaryoNIM® 60K Developed and designed by NIMGenetics, this array CGH platform simultaneously detects the presence or absence of genetic and chromosomal variations (duplications or deletions) responsible for 160 genetic syndromes with a minimum resolution of approximately 275 kilobases (resolution at least 20 times higher than conventional G-banded karyotyping). It is primerily used for intellectual disabilities and poly-malformative syndromes. Technical description Total number of probes in the selected syndromic regions: 7500 probes Average detection capacity in syndromic regions: 165 kb Number of probes in critical genes: 655 probes Minimum coverage of critical genes in syndromic regions: 5 probes/gene Number of probes in the rest of the genome: 48000 probes Average detection capacity in the rest of the genome: 275 kb KaryoNIM® Autism 180K This array CGH platform was also developed and designed by NIMGenetics, and is aimed at detecting copy number variations linked with susceptibility to autism. The autism chip covers two regions: 1. Critical regions affected by microdeletions or microduplications associated with susceptibility to autism (syndromic or non- syndromic). A total of 45 syndromes related to autism are covered. 2. Regions that include individual genes whose duplication or deletion is directly linked to susceptibility to autism, sporadic or family-related. Some of these genes that are also included in critical regions, due mainly to their key role in the development of autism, have been specically considered in this design. It covers a total of 115 related genes. This design provides in these regions a minimum resolution 50 times higher than conventional G-banded karyotype. Technical description Number of probes in critical autism genes: 15887 probes Average detection capacity in critical autism genes: 15 kb Coverage of critical genes in syndromic regions: 1 probe for each 3 kb Number of probes in the genome: 150000 Average detection capacity in the genome: 80 kb. KaryoNIM® UPD 180k This array CGH platform is designed to enable the simultaneous detection of the presence or absence of genetic and chromosomal variations, including the 500 regions of the genome described and accepted by the ISCA consortium. Furthermore, this microarray also includes the possibility of detecting regions with loss of heterozygosity due to uniparental disomy (UPD). This platform is especially indicated for detecting genetic disorders caused by this type of mutation, which are not detectable with the array CGH methodology. Technical description Number of probes for detecting CNVs: 110700 probes Average capacity to detect CNVs in the whole genome: 120 kb Number of probes for detecting UPD regions: 59650 probes Average capacity to detect UPD regions: 10 Mb KaryoNIM® 400K This is a very high-density array-CGH platform, developed and designed by NIMGenetics. With a minimum resolution of approximately 25 kilobases (at least 200 times greater than the conventional karyotype), it simultaneously detects the presence or absence of genetic and chromosomal variations (amplications or deletions) responsible for genetic syndromes. This array is used for studies that require a high resolution in the analysis of the complete genome, and is capable of simultaneously detecting deletions that affect fragments of a single gene (for example, in neurological disorders). Technical description Number of probes in the genome: 411000 probes Average detection capacity in the whole genome: 25 kb Syndromes included in KaryoNIM® 60k OMIM 607872 613735 274000 612474 612475 612530 612337 164280 606407 157170 612513 613564 605274 609583 256100 235730 186000 606708 612345 612313 193500 605934 600430 211750 110100 220200 206900 605289 609425 611936 194190 613509 180500 123450 608098 122470 613174 612881 613443 169500 168500 117550 612582 119600 613544 176270 612863 101400 175700 194050 609757 606382 220600 183600 142945 222400 228250 214800 600257 600383 166780 608156 150230 190350 179613 154230 158170 610828 161200 610253 146255 601362 612242 600095 609625 130650 606528 612469 194072 SYNDROME Chromosome 1p36 monosomy syndrome Chromosome 1p32-p31 deletion syndrome Thrombocytopenia-absent radius syndrome (TAR) Chromosome 1q21.1 deletion syndrome, region 1.35Mb Chromosome 1q21.1 duplication syndrome Chromosome 1q41-q42 deletion syndrome Chromosome 1q43-q44 deletion syndrome Feingold syndrome Hypotonia-cystinuria syndrome Holoprosencephaly 2 Chromosome 2p16.1-p15 deletion syndrome Chromosome 2p11-p11.2 deletion syndrome Mesomelic Dysplasia Savariayan type Joubert syndrome 4 Nephronophthisis 1 Mowat-Wilson syndrome Synpolydatyly Split/hand foot malformation 5 Chromosome 2q31 deletion syndrome Chromosome 2q32-q33 deletion syndrome Waardenburg syndrome 1 Holoprosencephaly 6 Brachydactyly-mental retardation syndrome C Syndrome Blepharophimosis, ptosis and epicanthus inversus Dandy-Walker syndrome Syndromic Microphthalmia 3 Split/hand foot malformation 4 Chromosome 3q29 deletion syndrome Chromosome 3q29 duplication syndrome Wolf-Hirschhorn syndrome Chromosome 4q31 deletion syndrome Axenfeld Rieger Syndrome Cri-du-chat syndrome (includes distal region) Heterotopia periventricular associated with chromosome 5p anomalies Cornelia de Lange Syndrome Chromosome 5p13 duplication syndrome Periventricular Heterotopia associated with chromosome 5q deletion Chromosome 5q14.3 deletion syndrome Demyelinating, adult-onset, autosomal dominant leukodystrophy Parietal Foramina 1 Sotos syndrome Chromosome 6pter-p24 deletion syndrome Cleidocraneal dysplasia Chromosome 6q11-q14 deletion syndrome Syndrome similar to the Prader-Willi syndrorme in chromosome 6 Chromosome 6q24-q25 deletion syndrome Saethre-Chotzen syndrome Greig Cephalopolysyndactyly syndrome Williams-Beuren Syndrome Williams-Beuren region duplication syndrome Williams-Beuren syndrome associated to infantile spasms Split-hand/foot malformation with sensorineural hearing loss Split-hand/foot malformation 1 Holoprosencephaly 3 Diaphragmatic Hernia 2 Unilateral bifid Femur with monodactylus ectrodactyly CHARGE syndrome Chromosome 8q12.1-q21.2 deletion syndrome Mesomelia-Synostoses Syndrome Otofaciocervical Syndrome Nablus mask-like facial syndrome Langer Giedion Syndrome Trichorhinophalangeal syndrome type I Recombinant chromosome 8 syndrome Chromosome 9p24.3 deletion associated to XY sex reversal 46, partial or complete Chromosome 9p deletion syndrome Holoprosencephaly 7 Nail-patella syndrome Kleefstra syndrome Hypoparathyroidism, sensorineural deafness and renal disease Digeorge Syndrome 2 (includes region of the Nebulette gene) Chromosome 10q23 deletion syndrome Split-hand/foot malformation 3 Chromosome 10q26 deletion syndrome Beckwith-Wiedemann Syndrome Homozygous 11p15-p14 deletion syndrome Chromosome 11p13-12 deletion syndrome WAGR Syndrome OMIM 601224 166750 147791 601803 163950 181450 609637 613457 607932 176270 105830 608636 612001 611102 613406 613406 142340 612626 613458 610543 141750 600273 180849 613604 136570 613444 611913 611913 247200 613215 219800 118220 162500 182290 610883 613675 137920 610443 613533 613618 613355 114290 146390 142946 610954 601808 607842 609334 613638 613638 613026 118450 190685 236100 115470 608363 188400 192430 145410 611867 606232 312865 308100 300679 310200 300578 300801 300706 300123 300475 300260 300815 400044 -- SYNDROME Potocki-Shaffer syndrome Otodental dysplasia Jacobsen Syndrome Pallister-Killian Syndrome Noonan Syndrome Ulnar-mamary Syndrome Patau Syndrome Holoprosencephalia 5 14q11-q22deletion syndrome Syndromic Microphthalmia 6 Prader-Willi syndrome Angelman syndrome Chromosome 15q11-q13 duplication syndrome Chromosome 15q13.3deletion syndrome Sensorineural deafness and male infertility associated to 15q15.3 Chromosome 15q24 duplication syndrome Chromosome 15q24 deletion syndrome Congenital diaphragmatic hernia Chromosome 15q26-qter deletion syndrome Chromosome 16p13.3 duplication syndrome Chromosome 16p13.3 deletion syndrome Chromosome 16-related Alpha-thalassemia and mental retardation syndrome Infantile severe polycystic kidney disease with tuberous sclerosis Rubinstein-Taybi Syndrome Chromosome 16p12.2-p11.2 deletion syndrome Chromosome 16p12.1deletion syndrome Chromosome 16p11.2 deletion syndrome, 220kb region Chromosome 16p11.2 deletion syndrome, 593kb region Chromosome 16p11.2 duplication syndrome Miller-Dieker Lissencephaly syndrome Chromosome 17p13.3 duplication syndrome Cystinosis Carchot-Marie-Tooth disease, demyelinating, type1A Hereditary neuropathy with liability to pressure palsies Smith-Magenis Syndrome Potocki-Lupski Syndrome Chromosome 17q11.2 deletion syndrome Renal cysts and diabetes syndrome Chromosome 17q21.31 deletion syndrome Chromosome 17q21.31 duplication syndrome Chromosome 17q23.1-q23.2 duplication syndrome Chromosome 17q23.1-q23.2 deletion syndrome Campomelic dysplasia Chromosome 18p deletion syndrome Edwards syndrome Holoprosencephelia 4 Pitt-Hopkins syndrome 18q Deletion syndrome Congenital aural atresia Pericentri inversion chromosome 18 Chromosome 19p13.13 deletion syndrome Chromosome 19p13.13 duplication syndrome Chromosome 19q13.1 deletion syndrome Alagille 1 syndrome Down syndrome Holoprosencephalia 1 Cat-Eye syndrome Chromosome 22q11.2 duplication syndrome Digeorge syndrome Velocardiofacial syndrome Opitz-GBBB Chromosome 22q11.2 deletion syndrome, distal Chromosome 22q13.3 deletion syndrome Short Stature homeobox linked to X (SHOX) Turner syndrome Triple X syndrome Klinefelter syndrome Ichthyosis X-linked, complicated Chromosome Xp21 deletion syndrome Duchenne muscular dystrophy (deletion of DMD gene) Chromosome Xp11.3 deletion syndrome Chromosome Xp11.23-p11.22 duplication syndrome Syndromic Mental retardation, X-linked, Turner type Mental retardation, X-linked, with panhypopituitarism Chromosome Xq28 deletion syndrome MECP2 duplication syndrome Chromosome Xq28 duplication syndrome 46, XY sex reversal 1 XYY syndrome Syndromes included in KaryoNIM® Autism 180k OMIM 613025 612474 612475 610836 612513 156200 606053 600430 613792 609425 613670 613603 609757 194050 214800 153480 106210 613454 608636 612001 614294 610543 613458 613604 136570 613444 611913 613215 610883 614527 613533 608363 611584 606232 192430 302350 300380 300143 300263 300260 309840 300495 300425 300496 608049 SYNDROME Susceptibility to schizophrenia 13 Chromosome 1q21.1 deletion syndrome Chromosome 1q21.1 duplication syndrome Susceptibility to autism 11 Chromosome 2p16.1-p15 deletion syndrome Mental retardation autosomal dominant 1 Susceptibility to autism 5 Brachidactyly-Mental retardation syndrome Chromosome 3pter-p25 deletion syndrome Chromosome 3q29 deletion syndrome Mental Retardation with language impairment and autistic features Chromosome 4q32.1-q32.2 triplication syndrome Williams-Beuren region duplication syndrome Williams-Beuren syndrome CHARGE Syndrome Bannayan-Riley-Ruvalcaba syndrome Aniridia Rett syndrome, congenital variant Chromosome 15q11-q13 duplication syndrome Chromosome 15q13.3 deletion syndrome 15q25 deletion syndrome Chromosome.3 deletion syndrome Chromosome 16p13.3 duplication syndrome Chromosome 16p12.2-p11.2 deletion syndrome Chromosome 16p12.1 deletion syndrome Chromosome 16p11.2de220kb deletion syndrome Chromosome 16p11.2 de 593kb Chromosome 17p13.3 duplication syndrome Potocki-Lupski syndrome Chromosome 17q12 deletion syndrome Chromosome 17q21.31 duplication syndrome Chromosome 22q11.2 duplication syndrome Waardenburg syndrome type 2E Chromosome 22q13.3 deletion syndrome Velocardiofacial syndrome Nance-Horan syndrome Chromosome Xp22 deletion syndrome X linked 21 mental retardation Siderius-X linked mental retardation Lubbs-X linked mental retardation X-Linked modifier for neurofunctional defects Suceptibility to autism linked to X2 Suceptibility to autism linked to X1 Suceptibility to autism linked to X3 Suceptibility to autism 3 Sample Delivery Samples will be collected by NIMGenetics, subject to prior notice. Samples must be kept at 4ºC until they are collected (except frozen samples, which must be kept at least at -20ºC). Sample Requirements Peripheral blood: 5ml in heparin tube or EDTA (green, brown or purple top). Saliva swabs: Oral brushing as per instructions. It is advisable to send two swabs per patient (NB: delivery must be made within a maximum of 48 hours from sample collection). Cito-genetic Sacrifice Samples: We recommend sending the visible cell pellet at 4ºC to be able to apply the technique. Frozen-dry cells (“dry pellet”): Conservation at -20ºC and delivery on dry ice. Tissue biopsies: A 2-cubic-millimeter fragment collected in a sterile tube (such as Falcon) within 10-15 ml of sterile solution (such as PBS). Detectables genes in KaryoNIM® Autism 180K GEN AFF2 AGMO ANKRD11 APC AR ASMT ASTN2 ATP10A BAIAP2 BTAF1 BZRAP1 C3orf58 CA6 CADPS2 CAMTA1 CASC4 CCDC64 CDH10 CDH8 CDH9 CDKL5 CHD7 CHRNA7 CNTN4 CNTNAP2 CNTNAP5 CREBBP CTNNA3 DCX DISC1 DLGAP2 DMD DPP10 DPP6 DPYD EIF4E FBXO40 FGFBP3 FHIT FOXG1 FOXP1 FOXP2 GABRA4 GALNT13 GLRA2 GNB1L GPX1 GRIP1 GRM5 GRM8 GRPR HDAC4 HOXB1 HTR3A ICA1 IL1RAPL1 IMMP2L KCNMA1 OMIM 300806 613738 611192 611731 313700 300015 612856 605855 605475 605191 610764 612200 114780 609978 611501 NO OMIM NO OMIM 604555 603008 609974 300203 608892 118511 607280 604569 610519 600140 607667 300121 605210 605438 300377 608209 126141 612779 133440 609107 NO OMIM 601153 164874 605515 605317 137141 608369 305990 610778 138320 604597 604102 601116 305670 605314 142968 182139 147625 300206 605977 600150 GEN KHDRBS2 KIAA0442 MAP2 MBD3 MBD5 MCPH1 MDGA2 MECP2 MEF2C NBEA NDNL2 NFIA NIPBL NLGN1 NLGN3 NLGN4 NLGN4Y NRXN1 NRXN2 NRXN3 NSD1 NXPH1 OPHN1 OXTR PARK2 PAX6 PCDH10 PCDH9 PLN PRKCB1 PTCHD1 PTEN PTPN11 PTPRD RAI1 RB1CC1 RBFOX1 RELN RFWD2 RIMS3 SCN2A SEMA5A SEZ6L2 SHANK2 SHANK3 SLC1A1 SLC4A10 STK39 SYN1 SYNGAP1 TBL1X TBX1 TMLHE TNIP2 TSC2 UBE3A UBL7 OMIM 610487 607270 157130 603573 611472 607117 611128 300005 600662 604889 608243 600727 608667 600568 300336 300427 400028 600565 600566 600567 606681 604639 300127 167055 602544 607108 608286 603581 172405 176970 300828 601728 176876 601598 607642 606837 605104 600514 608067 NO OMIM 182390 609297 NO OMIM 603290 606230 133550 605556 607648 313440 603384 300196 602054 300777 610669 191092 601623 609748 Detectable syndromes in KaryoNIM® UPD 180K caused by uniparental disomy (UPD) OMIM 176270 105830 130650 180860 601410 608149 SYNDROME Prader-Willi syndrome Angelman syndrome Beckwith-Wiedemman syndrome Silver-Russelss syndrome Neonatal diabetes mellitus Chromosome 14 uniparental disomy ISCA regions: information about the genes and regions included in the ISCA consortium is available through the following website: www.iscaconsortium.org 1 Test of choice in postnatal diagnosis 2 Cost-effective test 3 Results in 20 days 4 Array CGH platforms designed to improve genetic diagnosis 5 Written report for clinical use with a clear information on the presence or absence of genomic variations NIMGenetics' Team is committed to provide all necessary scientific and technical support for an accurate, reliable and well-defined genetic diagnosis. Parque Científico de Madrid Faraday, 7 (Campus de Cantoblanco) 28049 Madrid Tel.+34 91 804 7760 M. +34 647 426 518 www. nimgenetics.com [email protected] NIMGenetics is a Genetics Diagnosis centre authorized by the Health and Consumer Department for the Community of Madrid, being duly registered under Nº CS10673.