* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Notes on Chromosomal Mutations
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Copy-number variation wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Segmental Duplication on the Human Y Chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Oncogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Saethre–Chotzen syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Frameshift mutation wikipedia , lookup
Skewed X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
DiGeorge syndrome wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
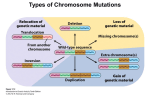
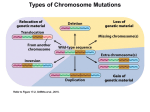
CHAPTER 10Chromosome Mutations REMEMBER THIS FROM CH. 12? What is a mutation? __________________________________________ There are two types of mutations that can occur in gamete cells: 1. Gene mutation: affect only one gene. Examples: point and frameshift. 2. Chromosomal mutation: affect the number or structure of chromosomes. Usually involves many, many genes. 5 TYPES OF CHROMOSOMAL MUTATIONS 1. Deletion 2. Duplication 3. Inversion 4. Translocation 5. Non-disjunction DELETION: INVOLVES THE LOSS OF ALL OR PART OF A CHROMOSOME. Examples: Cri du Chat syndrome, Angelman’s syndrome, Prader-Willi syndrome, Miller-Dieker syndrome DUPLICATION Involves the production of extra copies of parts of the chromosome Examples: Fragile X syndrome, Beckwith-Wiedeman syndrome Inversion: Reverses the direction of parts of a chromosome. Translocation: When one part of a chromosome breaks off and attaches to another chromosome. Example: Edward’s syndrome NON-DISJUNCTION: Means “not coming apart”. When homologous chromosomes fail to separate properly during meiosis. Results in abnormal numbers of chromosomes. Normal is two of each type of chromosome. Trisomy means a person has an extra copy of a chromosome. Monosomy means a person is missing a copy of a chromosome. Examples of Trisomy: Down syndrome, Trisomy 13, Cat eye syndrome (tetrasomy), Klineflelter’s syndrome (XXY) Example of Monosomy: Turner’s syndrome