* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Volcanoes!
Mono–Inyo Craters wikipedia , lookup
Axial Seamount wikipedia , lookup
Mount Pinatubo wikipedia , lookup
Mount Garibaldi wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Mount Meager massif wikipedia , lookup
Itcha Range wikipedia , lookup
Llullaillaco wikipedia , lookup
Mount St. Helens wikipedia , lookup
Level Mountain wikipedia , lookup
Cerro Blanco (volcano) wikipedia , lookup
Mount Pleasant Caldera wikipedia , lookup
Cascade Volcanoes wikipedia , lookup
Lascar (volcano) wikipedia , lookup
Potrillo volcanic field wikipedia , lookup
Nevado del Ruiz wikipedia , lookup
Craters of the Moon National Monument and Preserve wikipedia , lookup
Mount Pelée wikipedia , lookup
Olympus Mons wikipedia , lookup
Mount Edziza volcanic complex wikipedia , lookup
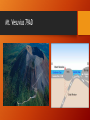
Mount Vesuvius wikipedia , lookup
Shield volcano wikipedia , lookup
Wells Gray-Clearwater volcanic field wikipedia , lookup
Cerro Azul (Chile volcano) wikipedia , lookup
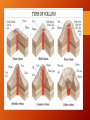
Volcanoes! Pg222-235 Quick Review • magma-? • lava-? • Can be explosive • Can be nonexplosive • lava flows • lava fountains • • • • Molten rock explodes into air Hardens Circle the globe for years Larger pieces fall closer Cross-section of a volcano What makes a volcano more explosive? Water • Dissolves in the magma (turns into gas because of high temps.) • Gases need more room • Pressure builds up • (like shaking a can of pop) Silica • Is thick, flows slowly • Plugs the vent • Build-up of pressure/gases Mt. Vesuvius 79AD People of Pompeii Types of Lava Aa Pahoehoe Flows slowly, like wax dripping on a candle Glassy surface with wrinkles Stiffer lava Pours out quickly with brittle crust, jagged surface Lava underneath keeps moving Pillow Lava Forms underwater Blocky Lava Cool, stiff, can’t travel far, oozes Pyroclastic Material Magma explodes and cools in the air Existing rock is shattered by eruptions Volcanic Blocks Volcanic Bombs Large blobs of magma, harden in the air Largest pieces, solid rock Lapilli “little stones” Pebble-like bits of magma Volcanic Ash Gases and stiff magma expand, walls of gas bubbles explode into tiny slivers Too much Ash • Can block the sun for days= lower Earth’s temperature • Mix with water= like wet cement • Collapse buildings, dam rivers • Can be a good fertilizer (in moderation) Types of Volcanoes Composite Volcano Cinder Cone Volcano Moderately explosive Pyroclastic materials Steeper, form in clusters (on sides of shield/composite) Most common Are both explosive and nonexplosive Shield Volcano Nonexplosive Runny lava= sloping sides Crater • Central vent in a volcano • Funnel shaped Caldera • Larger than craters • Magma chamber empties, roof collapses (ground sinks) Fissures Long cracks in the Earth Runny lava oozes out Makes lava plateaus Forming Magma • Solid in the earth= pressure keeps the atoms of mantle rock packed tight, keeping it solid • Magma forms= • Temperature increases • Pressure decreases • Becomes less dense, floats to surface Hot Spots • Places directly above columns of rising magma (mantle plumes) • As the plate moves, new volcanoes form in a chain How to Predict Eruptions • Measure earthquakes • Measure the slope (bulges) • Measure volcanic gases • Measure temperature from orbit