* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Heart - Parma City School District
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Heart arrhythmia wikipedia , lookup
Atrial septal defect wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
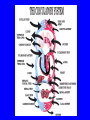
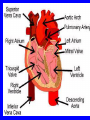
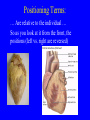
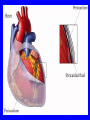
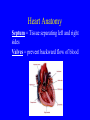
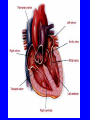
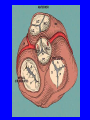
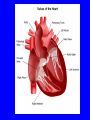
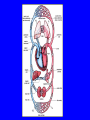
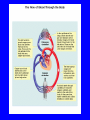
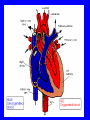
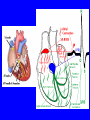
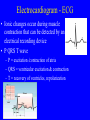
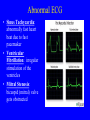
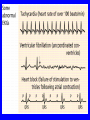
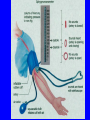
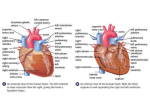
Heart = 4 chambers • Two Atria: Right and Left Atrium - The thin walled UPPER chambers of the heart – receive blood, pump it down into ventricles • Two Ventricles: Right and Left - The thick walled LOWER chambers of the heart – pump blood out of heart, more muscular Correct Position of heart in your body RIGHT SIDE LEFT SIDE Positioning Terms: … Are relative to the individual … So as you look at it from the front, the positions (left vs. right are reversed) Heart Anatomy MYOCARDIUM: major portion of the heart = Cardiac Muscle Tissue Endocardium = inner surface lining of heart Pericardium = membrane covering the heart, forms a sac, filled with small amount of fluid for lubrication Heart Anatomy Septum = Tissue separating left and right sides Valves = prevent backward flow of blood Valves • Atrioventricular Valve: lie between the atria and the ventricles; supported by strong fibrous strings called Chordae tendineae – Right Side = Tricuspid (3 flaps) – Left Side = Bicuspid or Mitral (2 flaps) • Semilunar Valves: resemble “half moons”; separate the ventricles Flow of Blood Through the Body • Arteries & Arterioles: carry oxygenated blood away from the heart - brings oxygen, nutrients, amino acids, glucose to tissues • Veins & Venules: carry deoxygenated blood back to the heart, removes wastes • Capillaries: Exchange material at the tissues Blood Circuits • Pulmonary = Heart ---> Lungs ---> Heart • Systemic = Heart ---> Rest of Body ---> Heart Left ventricle has the harder job of pumping blood to the entire body so its walls are thicker than the right ventricle which pumps blood only to the lungs The Path of Blood in the Heart 1. Superior and Inferior Vena Cava return deoxygenated blood to the RIGHT ATRIUM 2. Right Atrium ---> atrioventricular valve (Tricuspid) ---> RIGHT VENTRICLE 3. Right Ventricle ---> pulmonary semilunar valve --> Pulmonary Arteries ---> Lungs The Path of Blood in the Heart 4. Pulmonary Vein carries Oxygenated blood from lungs to left atrium 5. Left Atrium ---> atrioventricular valve (bicuspid valve) ---> left ventricle 6. Left Ventricle ---> Aortic Semilunar Valve ---> rest of body The Heartbeat • The 2 atria contract at the same time; 2 ventricles contract at the same time • Systole: contraction of heart muscle • Diastole: relaxation of heart muscle Heart beats about 70 times / minute; each beat lasts 0.85 seconds The Cardiac Conduction System • The heart can beat without any nervous stimulation! • Nodal Tissue = has both muscular and nervous characteristics – SA Node (Sinoatrial): “The Pacemaker” upper wall of right atrium, initiates heartbeat, causes the atria to contract – AV Node (atrioventricular): receives signal via Purkinje fibers, causes ventricles to contract Electrocardiogram - ECG • Ionic changes occur during muscle contraction that can be detected by an electrical recording device • P QRS T wave – P = excitation /contraction of atria – QRS = ventricular excitation & contraction – T = recovery of ventricles, repolarization Abnormal ECG • Sinus Tachycardia: abnormally fast heart beat due to fast pacemaker • Ventricular Fibrillation: irregular stimulation of the ventricles • Mitral Stenosis: bicuspid (mitral) valve gets obstructed Blood Pressure • Pulse = expansion & recoil of arterial wall due to surge of blood flow • Blood Pressure = pressure of blood flow against the wall of a blood vessel; normal is 120/80 taken at the brachial artery in the arm (systolic / diastolic) Sphygmomanometer • Systolic = highest arterial pressure when cuff is tight (Normal 120) • Diastolic = lowest arterial pressure when cuff is loose (Normal 80) Fetal Circulation • 1. Pulmonary circulation bypasses the lungs (Foramen Ovale - one way opening in the septum between atria) • 2. Fetal blood flows through the placenta; Ductus Arteriosus leads blood away from lungs and into systemic route