* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
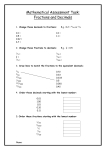
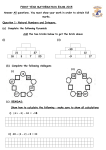
Download NUMBER, NUMBER SYSTEMS, AND NUMBER RELATIONSHIPS
Survey
Document related concepts
History of logarithms wikipedia , lookup
Ethnomathematics wikipedia , lookup
Foundations of mathematics wikipedia , lookup
Law of large numbers wikipedia , lookup
Infinitesimal wikipedia , lookup
Georg Cantor's first set theory article wikipedia , lookup
Approximations of π wikipedia , lookup
Mathematics of radio engineering wikipedia , lookup
Surreal number wikipedia , lookup
Real number wikipedia , lookup
Large numbers wikipedia , lookup
Location arithmetic wikipedia , lookup
Elementary arithmetic wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
NUMBER, NUMBER SYSTEMS, AND NUMBER RELATIONSHIPS Kindergarten: •Count by 1’s and 10’s to 100. •Count on from a given number (other than 1) within the known sequence to 100. •Count up to 20 objects with 1-1 correspondence. •Identify whether the number of objects in one group is greater than, less than, or equal to the number of objects in another group with quantities up to 20. •Compare two numbers between 1 and 20 presented as written numerals. •Represent equivalent forms of the same number up to 20 with objects or pictures. •Write numerals from 0 to 20 without a model and out of sequence. •Represent a number of objects with a written numeral 0-20 (with 0 representing a count of no objects). •Identify and state the value of a penny, nickel, and dime. •Show various combinations of a given amount up to 10¢ using pennies, nickels, and dimes. •Count and group objects into sets of 10 using diagrams, drawings and models. •Divide whole objects into equal parts. •Read and write numerals from 0 to 20 without a model and out of sequence. •Break apart numbers from 11 to 19 into groups of tens and ones using objects or drawings with assistance. •Identify 2, 4, 6, 8, 10 as even numbers and 1, 3, 5, 7, as odd numbers. •Solve simple story problems through 10. •Use manipulatives to solve addition and subtraction equations horizontally through 10. Grade 1: •Count to 200 starting at any number less than 200. In this range, read and write numerals and represent a number of objects with a written numeral. •Count by 1’s, 2’s, 5’s and 10’s up to 200. •Compare two 2-digit numbers using the terms equal to (=), great than (>), and less than (<). •Represent equivalent forms of the same number up to 100 with objects or pictures. •Represent a number of objects with a written numeral with numbers from 0-100. •Identify and state the value of a quarter, dime, nickel, and penny. •Show various combinations of a given amount up to 25¢. •Divide circles and rectangles into two and four equal shares. •Describe shares using the vocabulary: halves, fourths. •Use the phrases: half of, fourth of, and quarter of. •Write the corresponding fraction given a shaded figure (halves and fourths). •Read and write whole numbers from 0-100 without a model and out of sequence. •Identify the place value (tens and ones) for digits up to 99. •Include counting and grouping objects by tens and ones. •Understand that the two digits of a two-digit number represent amounts of tens and ones. Grade 1 continued . . . •Identify odd and even numbers on the 100’s chart up to 100. •Use addition and subtraction within 20 to solve word problems involving situations of adding to, taking from, putting together, taking apart, and comparing with unknowns in all positions. •Use both horizontal and vertical notation. Grade 2: •Count by 1’s, 2’s, 5’s and 10’s to 1,000. •Compare 2- and 3-digit whole numbers using >, =, < symbols up through 999. •Read and write whole numbers to 999 by dictation, using pictures and number names. •Represent a given amount of money in 3 or more ways (up to 1 dollar) using quarters, dimes, nickels, and pennies. •Identify and state the value of the quarter, dime, nickel, and penny. •Count combinations of coins up to $1.00. •Show various combinations of a given amount up to $1.00 using a quarter, dime, nickel, and penny. •Make change using coins up to $1.00 •Divide whole objects into 2, 3, or 4 equal shares. Describe the shares using the words halves, thirds, half of, a third of, fourth, a fourth of. Describe the whole as two halves, three thirds, four fourths. •Given a shaded figure (halves, thirds, or fourths) write its corresponding fraction. •Given a fraction (halves, thirds, or fourths) shade a figure that represents that fractional part. •Read and write whole numbers to 999 by dictation, using base-ten numerals or from expanded form. •Identify 1, 2, and 3-digit odd or even numbers. •Use repeated addition to find the total number of objects arranged in rectangular arrays with up to 5 rows and up to 5 columns (using manipulatives or picture representations). •Use manipulatives and write multiplication equations for a given group of equal sets to products of 25 (factors 0-5). •Use addition and subtraction within 100 to solve one- and two-step word problems with unknowns in all positions. Grade 3: •Compare two whole numbers using greater than (>), less than (<), and equal to (=); up through 9,999. (M3.A.1.1.3) •Count a collection of bills and coins less than $5.00 (penny, nickel, dime, quarter, dollar). Money may be represented as 15 cents, 15¢, or $0.15. (M3.A.1.3.1) •Compare total values of combinations of coins less than $5 (penny, nickel, dime, quarter, dollar). (M3.A.1.3.2) •Make change for an amount up to $5.00 with no more than $2.00 change (penny, nickel, dime, quarter, dollar). (M3.A.1.3.3) •Identify and read decimals through hundredths. •Match the word name with the appropriate whole number up through 9,999. (M3.A.1.1.1) •Match a symbolic representation of numbers to appropriate whole numbers (e.g., base 10 blocks; 7 hundreds, 4 tens and 8 ones). (M3.A.1.1.5) •Create a drawing or set that represents a given fraction (numerators 1-9, denominators 210; no equivalent or improper fractions, or mixed numbers). (M3.A.1.2.2) •Recognize equivalent fractions (e.g., halves/fourths and fourths/eighths). •Write a fraction that corresponds to a drawing or a part of a set (numerators 1-9, denominators 2-10; no equivalent or improper fractions, or mixed numbers). (M3.A.1.2.1). •Compare fractions with like denominators using greater than (>), less than (<), and equal to (=). •Read and write whole numbers in expanded, standard, and/or word form through 4 digits. •Order a set of whole numbers from least to greatest or greatest to least (up through 9,999 (limit sets to no more than 4 numbers). (M3.A.1.1.4) •Identify and use the symbols >, <, and =. •Differentiate between and/or give examples of even and odd numbers (limit to 3 digits). (M3.A.1.1.2) •Identify the first five multiples of numbers through 10. •Identify factors of numbers to 50. •Use drawings and/or concrete objects to show the relationship between multiplication and division. •Demonstrate the inverse relationship between addition and subtraction using fact families and/or factors. (M3.A.2.1.2) Grade 4: •Compare and/or order whole numbers through 6 digits and amounts of money to $100. (M4.A.1.2.2) •Compare two multi-digit numbers based on meanings of the digits in each place, using >, =, and < through six digits. •Locate/identify fractions or decimals on a number line (decimals and fractions through the hundredths-do not mix fractions and decimals). (M4.A.1.2.1) - *fractions through twelfths. •Compare fractions and decimals using greater than (>), less than (<), and equal to (=). •Compare two fractions with different numerators and different denominators by using strategies such as comparing to a benchmark fraction (1/2), using a visual model, or creating common denominators. •Match the standard number form to the word form of decimal numbers through the hundredths place. (M4.A.1.1.3) •Write the fractional decimal including mixed numbers, which corresponds to a drawing or set-no simplification. (M4.A.1.1.1) •Create a drawing or set that represents a given fraction or decimal, including mixed numbers through the tenths place. (M4.A.1.1.2) •Explain why a fraction is equivalent to another fraction using pictures, manipulatives or words •Demonstrate fractional parts using drawings, diagrams, or models (e.g., using number lines, manipulatives, and simple drawings). •Use drawings, diagrams, and models to represent fractions as division of a whole number by a whole number. •Write * whole numbers in expanded, standard, and /or word form through 6 digits. (M4.A.1.1.4) *(and read) •Order a set of whole numbers from least to greatest or greatest to least up through 6 digits. •Find/list/identify all factors through 10 of any given number. (M4.A.1.3.1) •Identify factors of numbers to 100. •Find/list/identify multiples of a number, where the multiples do not exceed 100. (M4.A.1.3.2) •Recognize that a whole number is a multiple of each of its factors. •Determine whether a given whole number in the range 1-50 is prime or composite. •Solve problems involving all operations with whole numbers and/or explain the solution (limit to two-step problems, e.g., multiply then add, single digit multipliers and divisors). (M4.A.2.1.1) •Solve problems involving addition and subtraction with decimals through the hundredths, or money to the cent and/or explain the solutions. Limit to two-step problems. (M4.A.2.1.2) •Demonstrate the inverse relationship between addition and subtraction and multiplication and division using fact families. Grade 5: •Compare whole numbers through 9 digits using the words more, less, equal, least, most, greater than, less than, or the symbols >, < =. (M5.A.1.3.1) •Compare and/or order decimals through the hundredths (limit to 4 numbers). (M5.A.1.3.2) •Compare proper fractions through sixteenths with like and unlike denominators. (M5.A.1.3.3) *Using the appropriate symbol >, <, or =. •Compare and/or order decimals through the thousandths using the appropriate symbol >, <, or =. •Match the standard form to the word form of decimal numbers through hundredths. (M5.A.1.2.1) *and thousandths •Use appropriate sign to indicate the relationship between decimals (greater than or less than). •Use or develop regions and/or sets to model fractions and mixed numbers through hundredths (may include reducing the fractions). (M5.A.1.5.1 ) •Represent decimals through the thousandths using grids. •Recognize common equivalents for percents, fractions, and decimals (e.g.10%, 25%, 50%, 75%, and 100%. •Locate/identify integers on a number line (greater than or equal to -20). (M5.A.1.4.1) •Identify negative temperatures on a thermometer (through -20 degrees C). (M5.A.1.4.2) Convert between common fractions, decimals and percents. •Use expanded notation to represent whole number (less than 10,000,000) or decimals (through hundredths). (M5.A.1.1.1) *and thousandths •Identify the place value of a digit (millions through hundredths). (M5.A.1.2.2) •Understand basic exponential notation using powers of 10. •Define/list/identify prime and composite numbers less than or equal to 100. (M5.A.1.6.1) •Define/list/identify factors and/or multiples of a given whole number less than or equal to 50. (M5.A.1.6.2) *or to 100. •Define 0 and 1 as neither prime nor composite. •Define and identify Greatest Common Factor (GCF) and Least Common Multiple (LCM) when listing factors and multiples. •Write an equation to solve problems involving multiplication and division of whole numbers. •Use multiplication to solve a division problem and relate to fact families, such as: 36 divided by _____ = 4 is the same as 4 x ____ = 36 or vice versa.