* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 3
Survey
Document related concepts
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
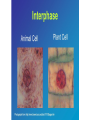
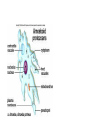
Chapter 3 From a Cell to an Organism Cell Cycle - Most cells in an organism go through a cycle of growth, development, and division. Phases of the Cell Cycle Interphase - part of the cell cycle that includes the cell’s growth and development A cell spends most of the time in Interphase Interphase has 3 stages 1. rapid growth and replication of the organelles 2. copying of DNA 3. preparation for cell division During interphase DNA of the cell is copied. Sister chromatids - two identical chromosomes, that make up a duplicated chromosome Centromere - the center structure that holds the sister chromatids together Mitotic Phase - cell reproduces during this stage ● mitosis - nucleus divides ● cytokinesis - cytoplasm divides At the end of this stage, 2 new identical cells called Daughter Cells Phases of Mitosis Prophase - DNA forms chromosomes Metaphase - chromosomes line up Anaphase - chromatids separate Telophase - two nuclei form Cytokinesis - last phase of mitosis the cell’s cytoplasm divides Results of Cell Division Reproduction - cell division is a form of reproduction in some unicellular organisms Growth - organisms grow from one cell to many Replacement - organisms replace any cells that wear out or are damaged. Repair - Cell division is important for repairing damage. Lesson 2 Levels of Organization Unicellular Organisms Prokaryotes - organisms without a membrane bound nucleus, smaller than eukaryotic cells, and fewer cell structures Found at the bottom of the 7.800 ft. deep Homestake ‘gold Mine in S.D. Deinococcus peraridilitoris in the soil of Chili’s Atacoma Desert Maybe extreme bacteria living under Europa’s ice Stromatolites Eukaryotes - specialized organelles membrane bound nucleus Multicellular Organisms many eukaryotic cells working together Cell Differentiation - the process by which cells become different types of cells Stem Cells - unspecialized cells that are able to develop into many different cell types Plants have unspecialized cells located in meristems - tips of roots and stems Tissues - groups of similar types of cells that work together to carry out specific tasks. Four main types of tissue in animal cells 1. 2. 3. 4. Muscle - cause movement Connective - provides structure, support Nervous - carries messages to/from the brain Epithelial - protective outer layer of skin, lining of organs Plants have 3 main types of tissues 1. Dermal - protection, reduces water loss 2. Vascular - transports water, nutrients 3. Ground - storage, support, location of photosynthesis Organs - groups of different tissues working together to perform a particular job. Plants also have organs Organ Systems - groups of different organs that work together to complete a series of tasks. Plants have 2 major organ systems 1. Shoot system includes leaves, stems, & flowers Job - transports food and water Plant organ system: 2. Root System which anchors the plant and takes in food and nutrients Cells - Tissues - Organs - Organ Systems Organisms Organisms are made up of many organ systems that work together.