* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download industry
Propaganda in Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
World War II by country wikipedia , lookup
Historiography of the Battle of France wikipedia , lookup
Collaboration with the Axis Powers wikipedia , lookup
Role of music in World War II wikipedia , lookup
World War II casualties wikipedia , lookup
Appeasement wikipedia , lookup
British propaganda during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Allied Control Council wikipedia , lookup
Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Technology during World War II wikipedia , lookup
New Order (Nazism) wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Allied plans for German industry after World War II wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
Home front during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
End of World War II in Europe wikipedia , lookup
Economy of Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
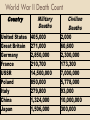
: Economic Crisis and Political Turmoil Economic Crisis • Germany owed the Allies 132 billion marks ($33 billion) in war reparations (Treaty of Versailles) • Germany could not make payments so France occupied the Ruhr Valley (Germany’s chief industrial and mining center) and collected reparations directly from the German mines and factories • Germany tried printing more paper money but this only generated inflation – 1914: 4.2 German marks equaled 1 U.S. dollar – 1923: 4.2 trillion German marks equaled 1 U.S. dollar Worldwide Economic Depression Increase in oil and hydroelectricity severely damaged the coal industry European prosperity depended on American loans American investors withdrew their European loans so they could invest in booming U.S. stock market U.S. stock market crash of 1929 persuaded more investors to withdraw their European loans The Great Depression begins worldwide (late 1929) Unemployment rises 25% of British workforce unemployed 40% of German workforce unemployed Production falls Industrial productivity fell 50% in the U.S. Industrial productivity fell 40% in Germany Results of the Great Depression Social discontent Increased government involvement Lower wages Foreign goods unaffordable (tariffs) Unemployment Feeling of hopelessness More government regulation of economic systems Communism endorsed by more political scientists and workers Totalitarianism in, democracy out Democracy/Capitalism had failed and people sought strong totalitarians (dictators) to seize power and “quick fix” the crisis Soviet Russia • • • • • • • Socialism: public ownership of the means of production Communism: system of ownership of all property by the community – Supports a classless society Socialism exists when people receive according to their deeds (work) while communism exists when people receive according to their needs Politburo: leading institution of the Soviet Communist Party After Lenin’s death, two Politburo members, Leon Trotsky (Commissar of War) and Joseph Stalin (Party General Secretary), engaged in a power struggle Stalin seized control of the Politburo in 1929 and established a Communist dictatorship Stalin collectivized the agricultural industry – Russia’s 26 million private farms were joined into 250,000 units – Resistant farmers hoarded food and slaughtered livestock – Stalin intensified the process – 10 million peasants died from famine “The Boss” in Soviet Russia • Stalin transformed Russia from an agricultural nation into an industrial nation – Steel production increased from 4 to 18 million tons, coal from 36 to 128 million tons – Produced oil, armaments (weapons), and machinery • Stalin purged (removed) all political, intellectual, or military leaders that opposed his policies – Between 1936 and 1938, 8 million Russians were arrested…million of which were shipped to Siberian labor camps never to return • Women encouraged to work outside the home and received equal rights as men • Stalin’s message: “Sacrifice for the good of the new socialist state.” Fascism in Italy fascism: political philosophy in which the ruling government exercises total control over the state and holds the interests of the state or race above individual rights/interests Benito Mussolini: fascist dictator of Italy that promised the rebirth of a new grand Roman Empire Mussolini’s acts of fascism Arrested opposition without due process of law Exercised total control over mass media Created youth fascist organizations Eliminated women from the workforce Named Catholicism the only religion of the state Japan Mobilizes For War Dictator: Emperor Hirohito Platform: Create a self-sufficient and secure Japan by gaining territory and providing land for agriculture and raw materials Political philosophy…militarism: military leaders independent from civilian government; embrace very aggressive military policies Extended borders and made Japan a great empire Hitler 101 • • • • • • • • • • Struggling artist (understood power of propaganda) Anti-Semitic: strong racial intolerance of Jews WWI veteran Organized National Socialist German Workers’ Party (Nazis) in 1921 and developed the party into a mass political movement with party flags, banners, badges, uniforms, newspapers, and its own police force known as the SA (Storm Troopers) Beer Hall Putsch: failed Nazi uprising in 1923 to seize power over the state Imprisoned for a short time for involvement in a failed uprising in 1923 Wrote Mein Kampf (My Struggle) while in prison for political beliefs; book provided earlier indications of anger, rage, plans for revenge, and racism (Aryan superiority) Motivational orator: inspirational speaker full of conviction, energy, confidence, and power Brawler not a debater (appealed to young men) Propaganda master: brainwashed German masses – Poor leadership kept Germans from winning WWI – Germany treated unfairly by Treaty of Versailles – Aryans are dominant race Hitler Seizes Power Hitler and the Nazis murdered political opponents Hitler appointed German Chancellor in 1933 (given power to make laws) Reichstag (German legislature) grants Hitler emergency powers during time of crisis Hitler abolishes office of president in 1934 and declares himself Fuhrer or supreme ruler of Third Reich totalitarian dictator: controlled all aspects of life including industry, economics, foreign policy, mass media, religion, etc. Hitler’s Economic Reform: mobilize nation for war; concentrate all efforts on building war supplies Ignore Treaty of Versailles restrictions Stimulate industrial growth Reduce unemployment (1931: 6 million; 1934: 2.6 million; 1937: 500,000) Diminish poverty Revive German spirits The Terror of Nazism Women encouraged to stay at home and bear more Aryan children Hitler Youth: youth organization created to educate and indoctrinate young Aryan children with Nazi ideologies SS (Schutzstaffel or “defense squadron): Nazi terror organization led by Heinrich Himmler that controlled the regular police force, secret police force (Gestapo), and managed the concentration camps Terror of Nazism Nuremberg Laws (September 1935): Nazi laws created to oppress the Jewish race Excluded Jews from German citizenship Forbade marriage between Jews and German citizens Separated Jews from Germans politically, legally, and socially Forced Jews into ghettos Kristallnacht (“night of broken glass”): destructive rampage led by the Nazis in November of 1938 during which synagogues were burned, Jewish businesses destroyed, about 100 Jews killed, and 30,000 Jewish males rounded up and sent to concentration camps Axis Advances: Events Leading to World War II Japan invades Manchuria (September 1931) to take possession of natural resources and territory Italy invades Ethiopia (October 1935) to strengthen its empire Japan invades China (1937) to extend empire Rape of Nanking: Japanese soldiers seized China’s capital city Germany annexes Austria (March 1938) Anschluss: The belief that all German speaking people should be unified Hitler sends troops to Austria to unify it with German Germany occupies Sudetenland of Czechoslovakia (September 1938) Britain and France exercise appeasement: give in to demands in order to maintain peace; believed Munich Pact achieved “Peace for our time.” Hitler signs nonaggression pact with Soviet Union (August 1939): neither Germany nor Soviet Union will attack each other Thousands of people were killed…between 20,000 to 80,000 women raped by soldiers Pact contained secret deal to divide Poland between them Germany invades Poland (September 1939) using blitzkrieg warfare tactics: “lightning war;” swift offensive combining ground and air forces in attempt to make a quick, devastating blow to the enemy Britain and France declare war on Germany Causes of World War II Axis Powers on quest for world domination Revenge for World War I results and reparations Post-World War I economic depression: war production promises jobs Allied Appeasement: gave in to German demands in exchange for peace Nationalism: love and pride for nation Fascism: for the good of the nation Racism: rule over inferior races Militarism: nations desiring to flex military might AXIS POWER: THE WAR BEGINS Nazis Take Western Europe Just months after Poland falls, Nazis conquer Norway, Denmark, Belgium, and Luxembourg Fall of France: Nazis avoid the Maginot Line and draw the enemy away from the Ardennes Mountains Defeat French in one month; Nazis take Paris without a fight (May 1940) Dunkirk: French seacoast town where 338,000 defeated French and British troops evacuate across English Channel to avoid total annihilation Battle of Britain: series of German bombing raids intended to demoralize and weaken Great Britain; 20,000 London civilians die American Neutrality? America divided: interventionism (America should fully support Britain) vs. isolationism (America should not get involved) Nye Committee: Documented the huge profits that arms factories had made during WWI Neutrality Act of 1935: Made it illegal for Americans to sell arms to any country at war Britain needs supplies but has no money Destroyers -for-Bases Deal: In exchange for the right to build American bases in British territory, Roosevelt sent 50 old American destroyers to Britain Lend-Lease: FDR’S policy allowing the U.S. to lend or lease military supplies to Britain if considered vital to national defense Allowed Britain to receive arms without paying cash for them War on the Atlantic: undeclared war between German submarine wolf packs and American or British merchant convoys Atlantic Charter: Britain and the US agreed to a postwar world of democracy, non-aggression and free trade Nazi Advances in the East Operation Barbarossa: Germany invades Russia in June of 1941 and betrays non-aggression pact German Blitzkrieg (lightening war) routes Red Army (Russian army) Luftwaffe (German air force) dominates air Nazis starved or executed almost a million Russian citizens Battle of Stalingrad begins: last hope for Soviets to make a stand Soviets win – for the rest of the war, Germans will be on the defensive Bloodiest battle in history over 1,225,000 deaths America and Japan Japan fights to extend empire into China, Southeast Asia, and the western Pacific Axis Powers Created: Japan recognizes formal alliance with Germany and Italy (1940) FDR imposes trade embargo on Japan, denying it any materials that could be used for war Pearl Harbor Encouraged by Hitler and in retaliation for trade embargo, Japan orders sneak attack on American naval base of Pearl Harbor in an effort to destroy the entire Pacific Fleet Attack occurs on December 7, 1941 Japanese achieves total surprise (Tora! Tora!) Japanese bombers and fighters destroy 19 ships (including 5 battleships), 188 planes, and kill more than 2,400 Americans in less than 3 hours “A day that will live in infamy” December 8, 1941 U.S. declares war on Japan THE ALLIES FIGHT BACK America Fights Back 15 million GI’s (government issued) go to war Battle of the Atlantic: U.S. and Britain battles against the German U-boat Led to the use of a Convoy System General Dwight D. Eisenhower named the Supreme Allied Commander North African Campaign (Winter 1942 – Spring 1943): first major Allied offensive; first German defeat Battle of El Alamein British General Bernard Montgomery defeats the Germany’s Erwin Rommel Turned the tide of war in North Africa Operation Torch: American/British invasion of North Africa Battle of Kasserine Pass Americans defeated (7,000 casualties) Eisenhower promotes George Patton to commander Patton forced the Germans to surrender Italian Campaign (1943-1944): General Patton and Allied troops defeat Italians and kick Germans out of Italy; Mussolini overthrown Soviets turn the tide at Stalingrad and defeat the Nazis (February 1943) without Allied help; Soviets suffer more casualties at Stalingrad than the U.S. suffers the entire war D-Day: Operation Overlord Invasion Planning: Allies must invade Germany’s new empire and liberate Western Europe; Allies deceive Nazis and choose beaches of Normandy, France as landing site D-Day: June 6, 1944, massive Allied forces cross English Channel and defeat German forces at Normandy; set up base from which to launch western offensive Allies suffer about 4,000 casualties while taking the beaches and winning one of the war’s most significant battles Western Theater Allies advance from Normandy Paris liberated (August 1944) Battle of the Bulge: major German counterattack; US airborne soldiers (101st) surrounded in Bastogne; Germany calls for surrender, troops reply “NUTS”; Allied counter-offensive kills 100,000 German troops; Allies win biggest land battle in American history Allies advance on Berlin (Russians from east, Americans/British from west) Hitler commits suicide VE Day: victory in Europe; Germany surrenders on May 8, 1945 Pacific Theater General Douglas MacArthur commanded American forces in Pacific Philippines fall; thousands of American prisoners killed by Japanese during Bataan Death March Battle of Coral Sea: code breakers discovered Japan’s plan for two attacks America attacks forced Japan to call of their invasion on New Guinea Battle of Midway: turning point in Pacific; American planes sank four Japanese aircraft carriers 65 mile march Devastating blow to Japanese naval power and crippled the Japanese carrier fleet Island hopping: American marines gain key victories at Guadalcanal, Iwo Jima, and Okinawa The Atomic Bomb Manhattan Project: secret project responsible for developing the first atomic bomb; led by scientist Robert Oppenheimer Roosevelt dies of stroke; Vice-President Truman takes office and learns of project; believes bombs will prevent U.S. from having to invade Japan with ground forces, thus saving thousands of American soldier lives American B-29 bomber, the Enola Gay, drops worlds first A-bomb on Hiroshima on August 6, 1945, instantly killing 100,000 and another 100,000 died later from burns or radiation Second bomb dropped on Nagasaki on August 9, 1945, killing 40,000 Japanese World War II Ends VJ Day: Japan surrenders on August 14, 1945 CIVILIAN EXPERIENCES OF WORLD WAR II American Home Front Volunteer Efforts Bomb raid wardens Victory Gardens Red Cross Collected materials that could be converted to war armaments such as paper, rubber, scrap metal, aluminum pots Rationing Coupons needed to purchase goods like sugar, meat, butter, gasoline, and shoes Blue points – process foods, Red points – meats, fats and oils Media Propaganda Film industry “Double V” campaign Used to supplement rations African-Americans should join the war effort in order to achieve a double victory – a victory over Hitler’s racism abroad and a victory over racism at home War Bonds Money loaned to government is later paid back with interest American Wartime Industry Deficit spending: government uses borrowed money to counteract economic depression Liberty ship: welded ships that were very hard to sink compared to riveted ships – mass produced cargo ship War Production Board (WPB): created to help American industry convert to war production; regulate economy Industrial capacity: amount of goods/products a nation has the potential of mass producing Gross National Product (GNP): dollar value of all goods and services produced annually In 1941, the production time for 1 merchant ship was 105 days By 1945, 1 merchant ship could be produced in 4 ½ days GNP 1939: $90 billion GNP 1945: $211.9 billion New workers: “Rosy the Riveter”: 6 million women join the labor force as welders, riveters, and mechanics African-Americans granted jobs once reserved for whites Minorities and Women During the War Tuskegee Airmen African-American fighter pilots Trained in Tuskegee, AL Fought bravely and performed well Women’s Army Auxiliary Corps (WAAC) Women’s Army Corps (WAC) First organization that allowed women to serve in the military Replaced WAAC “Rosie the Riveter” A character who worked in the factory while her boyfriend served in the military Female symbol of manufacturing Injustice on the Home Front Japanese Internment Japanese Americans stripped of their civil liberties More than 100,000 moved from their homes to relocation camps Lost farms, houses, and businesses ($500 million worth of losses) Reasons: Racial fear and prejudice Guard against espionage Protection against hate crimes Holocaust 1930’s 1939-1942 European Jews in Germany and other territories occupied by the Nazis forced to wear yellow stars, close businesses, leave homes, and move into Jewish ghettos European Jews, Slavs, Gypsies, Communists, homosexuals, and other social outcasts exiled to concentration camps for slave labor Camps: Auschwitz 1942-1945 Hitler begins “final solution” plan for “Jewish problem” involving the total extermination of Jews and other “inferior” races 6 million Jews killed (two-thirds of all European Jews) Holocaust atrocities: Starvation Beaten to death Shot Medical experiments Gas chambers Buried in mass graves or burned in crematoriums World War II Death Count Country United States Great Britain Germany France USSR Poland Italy China Japan Military Deaths Civilian Deaths 405,000 271,000 2,850,000 210,700 14,500,000 850,000 279,800 1,324,000 1,506,000 2,000 60,600 2,300,000 173,300 7,000,000 5,778,000 93,000 10,000,000 300,000