* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Objective bits
Spark-gap transmitter wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Electrification wikipedia , lookup
Commutator (electric) wikipedia , lookup
Skin effect wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Electric motor wikipedia , lookup
Mercury-arc valve wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Transformer wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Distribution management system wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Transformer types wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Electric machine wikipedia , lookup
Brushed DC electric motor wikipedia , lookup
Resonant inductive coupling wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Semiconductor device wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Stepper motor wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Induction motor wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
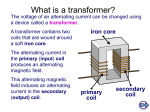
OBJECTIVE QUESTIONS Course Name : Electrical and Electronics Engineering Course Code : A30203 Class : II B. Tech I Semester Branch : Mechanical Engineering Year : 2015 – 2016 Course Faculty : Mr.M Sreenivasa Reddy, Associate Professor UNIT-1: 1. Which of the following are the units of the Resistance? (A) Amperes (B) Volts (C) Watts (D)Ohms 2. Kirchhoff’s Voltage Law is Based on Law of Conservation of (A) Energy (B) charge (C) Voltage (D) None 3. What are the Factors of effecting on Resistance? (A) Temperature (B) Length of conductor (C) A&B (D) Voltage 4. Which of the following is an Active Elements? (A) Inductance (B) Capacitance (C) Voltage source (D) Resistance 5. Which of the following is Passive Elements? (A) Voltage source (B) Current Source (C) Power (D) Resistance 6. Inductance in a Circuit (A) Prevents the Current from changing (C)Causes power loss (B) delays the change in Current (D) causes the Voltage 7. In Parallel Circuit all components must (A) Have same potential difference a cross them (C)Carry equal currents (D) carry same currents (B) have same value 8. Delta – Star Transformation if equal resistances are given (A) 3times Increases (B) 3 times reduces (C) same value (D) None 9. Star – Delta Transformation if equal resistances are given its value is (A) 3times Increases (B) 3 times reduces (C) same value (D) None 10. Voltage Division rule is applied for which of the following (A) Series Circuits (B) Parallel Circuits (C) both A&B (D) None 11. Kirchhoff’s Current Law is based on Law of Conservation of (A) Energy (B) charge (C) Voltage (D) None 12. Current Division rule is applied for which of the following (A) Series Circuits (B) Parallel Circuits (C) both A&B (D) None 13. Physical conditions being unchanged In a conductor the flow of current is directly proportional to (A) Voltage (B) Current (C) Power (D) None 14. Positive Temperature co-efficient of conductor (A) R increases, T decreases (C) R&T are Constant (B) R increases, T increases (D) R decreases T decreases 15. The difference in the potentials of two charged bodies is called (A) Current (B) potential difference (C) work done (D) None 16. which of the following is an acceptable classification of measuring instruments? a. absolute b.digital c. secondary d.all of these 17. which of the following is an absolute measuring instrument? a. moving coil b.tangent galvanometer c. permanent magnet d. moving iron 18.which of the following measuring measuring instruments are not categorized as secondary instruments? a. absolute c. digital b.analog d.all of these 19.which of the following can be categorized as ammeter and voltmeter? a. hot wire type b. moving iron type c. moving coil dynamometer type d. all of these 20. which of the following can be used for measuring alternating quantities only? a.moving coil dynamometer type b. induction typeProportional to Cosθ c. moving iron type d.all of these 21.which of the following cannot be used to measure both alternating and direct quantities? a. moving coil permanent magnet type c. moving iron type b.moving coil dynamometer type d. hot wire type 22. which of the following is not an advantage of movin coil instruments? a. uniform scale b. high sensitivity c. immune to stray magnetic fields d.none of these 23.which of the following is an advantage of moving coil dynamometer instruments? a. high cost b.low sensitivity c. measure both alternating and direct quantities d.none of these 24.which of the following applies to a wattmeter? a. it has a voltage coil b.it has current coil c. the voltage coil has a high resistance d. all of these 25.wattmeters are available with a. single current and voltage ratings b.multiple current rating and single voltage rating c. single current rating and multiple voltage rating d.multiple current and voltage ratings UNIT-2 1. Mechanical Energy Converted to Electrical energy which of the following (A)Generator (B) Motor (C) Both A&B (D) None 2.The direction of induced e.m.f and hence current in a conductor can be determined by (A)Lenz’s Law (B) Fleming’s Right hand rule (C) Both A&B (D) Fleming’s Left hand rule 3.In DC Machine which Induced e.m.f is suitable (A)Statically induced e.m.f (B) dynamically induced e.m.f (C) there is no e.m.f (D) None 4. The function of the commutator (A)Ac to dc (B) dc to ac (C) both A&B (D) None 5. Brushs are made up of (A)Carbon (B) Silicon (C) copper (D) Mild steel 6. Armature Reaction is related to (A)Main flux &Armature flux (B) only Main flux (C) only Armature flux None 7. Which is suitable for Electric Traction? (A)Series Motor (B) Shunt Motor (C) Compound Motor (D) Dc Generator 8. Which of the following are Iron Losses? (A)Copper losses (B) Mechanical losses (C) friction loss (D) Eddy current losses 9. The Basic Principle in dc generator is (A)Electro Magnetic Induction (B) Flemings Left hand rule (C) Law of conservation Energy 10. DC Motors in Starters are used to (A)To limit starting current (B) to start the motor (C) to increase starting current 11. Swinburne’s test conduct on DC Shunt Machine is (A) No load (B) Full load (C) Both A&B (D) None (D) to increase line voltage 12. Armature windings are made up on (A)Copper (B) Mild wire (C) Aluminum (D) None 13. Which of the following is unit of Torque is (A)Newton-meter (B) watts (C) Length (D) None 14.the starting resistance of a D.C. motor is generally (A)Low (B) around 500 ohm (C) 100 ohm (D) infinitely large 15. Small DC motors up to 5 H.P. Usually (A) 2 poles (B) 4poles (C) 6poles (D) 8poles UNIT-3 1). Induced e.m.f in a coil is directly proportional to (a) Rate of change of flux linkage (b) Rate of change of charge (c) Depends on the material used(d) Rate of change of current 2). The transformer rating is (a) KW (b) KVA (c) KV (d) WATT 3). The transformer transforms (a) Frequency (b) Voltage (c) Current (d) Voltage & Current 4). The main purpose of using Core in transformer is to (a) Decrease Iron losses (b) Prevent Eddy current losses (c) Eliminate Magnetic hysteresis (d) Decrease Reluctance of the Common magnetic circuit 5). The transformer cores are laminated in order to (a) Simplify its constructions (c) Reduce cost (b) Minimize Eddy current losses (d) Reduce Hysteresis losses 6). The Primary and Secondary induced E.M.Fs E1 & E2 in a Two winding transformer are always (a) Equal in magnitude (b) Anti-Phase with each other (c) In-Phase with each other (d) Determined by load on transformer Secondary 7). The Step-up transformer increases (a) Voltage (b) Current (c) Power (d) Frequency (c) Power (d) Frequency 8). The Step-down transformer decreases (a) Voltage (b) Current 9). The main purpose of performing open circuit test on a transformer is to measure Its (a) Copper losses (b) Iron losses (c) Total losses (d) Insulation resistance 10). The main purpose of performing short circuit test on a transformer is to measure Its (a) Copper losses (b) Iron losses (c) Total losses (d) Insulation resistance 11). In a transformer the load is connected to (a) Primary (b) Secondary (c) Both (a) & (b)(d) None 12). The efficiency of the transformer depends on (a) Input power (b) Losses in transformer (c) Power factor (d) All the above 13). The transformation ratio is (a) E2/E1 (b) N2/N1 (c) I1/I2 (d) All the above 14). The Cosine angle between the Voltage and Current (a) Power factor (b) Voltage (c) Load of the transformer 15) When the transformer is more efficiency (a) Constant load current (b) Load power factor is unity (c) Both A&B (d) None O.C test: field current = 12.5 A, Voltage between lines =420V SC test: field current = 12.5 A, line current = rated value. (d) Current Calculate the voltage regulation of alternator at 0.8 power factor lagging 16). Induction motor works on the principle of a. Mutual induction b. Ampere's law c. Lenz's law d. Ohm's law 17). The rotor speed of induction motor is always slightly a. Less than synchronous speed b. More than synchronous speed c. Less than slip speed d. More than slip speed 18). The operating speed of induction motor never be equal to a. Synchronous speed b. Slip speed c. Stator speed d. Speed of magnetic field 19). An Induction motor is a. Self-starting with low torque b. Self-starting with zero torque c. Self-starting with high torque d. Non- Self starting 20). In case of induction motor the torque is a). Directly proportional to slip b). inversely proportional to slip c). Directly proportional to square of the slip d). inversely proportional to square of the slip 21). Induced e.m.f in an alternator is (a) Dynamical induced e.m.f (b) neither statically nor dynamical (c) Statically induced e.m.f (d) Both statically and dynamical 22). the torque is zero, when a). Slip is zero b). Slip is unity c). Slip is infinity d). Slip is 0.5 23). The condition for the maximum torque occurs when the slip is equal to a). ratio of rotor resistance and leakage reactance b). ratio of leakage reactance to rotor c). rotor resistance d). leakage reactance 24)In an induction motor the core losses occur mainly in a). Stator core b). Armature core c). Slip rings d). Brushes 25). The maximum torque is also called a). Pull-out torque b). Starting torque c). Running torque d). Stator torque 26).In induction motor, the maximum efficiency occurs, when a. Variable losses equal to constant losses b. Variable losses are equal to zero c. Constant losses are equal to zero d. The total losses equal to zero 27). The induction motor is a a. Self starting motor b. Not self starting motor c. Coupled to other drive d. Coupled to other drive 28). The salient type rotor is also called a. Projected type b. cylindrical type c. Conical type d. Spherical UNIT-IV 1). Valence electronics are the (a) Loosely packed electronics (b) Mobile electronics (c) Electronics present in the outermost orbit (d) All the above 2). the element having four valence electronics is (a) Silicon (b) Germanium (c) Both (a) and (b) (d) None of the above 3). the donor impurity element is (a) Aluminium (b) Boron (c) Phosphorus (d) Indium 4). the acceptor impurity element is (a) Antimony (b) Gallium (c) Arsenic (d) Phosphorus 5). the element which does not have five valence electronics is (a) Antimony (b) Arsenic (c) Gallium 6). A PN-junction diode (a) Has high resistance in both forward and reverse directions (d) Phosphorus (b) Has low resistance in the forward direction (c) Has high resistance in the forward direction (d) Has low resistance in the reverse direction 7). In a PN-junction, the region containing the uncompensated acceptor and donor ions is called (a) Transition zone (b) Depletion region (c) Neutral region (d) Active region 8). In a forward biased PN-junction diode the (a) Positive terminal of the battery is connected to the P side and the negative side to the N side (b) Positive terminal of the battery is connected to the N side and the negative side to the P side (c) N side is connected directly to the P side (d) Junction is earthed 9).Zener diode is usually operated (a) In forward bias (c) Near cut-in voltage (b) In reverse bias (d) In forward –linear region 10). which of the following diodes is used for voltage stabilization (a) PN-junction (b) Tunnel (c) Zener (d) Varactor 11). Majority carries are in p-type semiconductors. (a). Protons (b). Electrons (c). Holes (d). Neutrons 12). Majority carries are in N-type semiconductors. (a). Holes (b). Protons (c). Electrons (d). Neutrons 13). A PNP transistor is made of (a). Silicon (b).Germanium (c) both (d). None 14). Conventional biasing of a bipolar transistor has (a). EB forward biased and CB forward biased (b). EB reversed biased and CB forward biased (c). EB forward biased and CB reverse biased (d). EB reversed biased and CB reversed biased 15). In an NPN transistor, if both the emitter junction and collector junction are reverse biased, the transistor will operate in (a). Active region (b). Saturation region (c). Cut-off region (d). Inverted region 16). In an normally biased NPN transistor, the main current crossing the collector junction is (a). A drift current (c). A Diffusion current (b). A hole current (d). Same as the base current 17). In a transistor, the region that is very lightly doped and very thin is the (a). Emitter (b). Base (c). Collector (d). None of the above 18). In an NPN transistor, the emitter (a). Emits or injects holes into the collector (b). Emits or injects electrons into the collector (c). Emits or injects electrons into the base (d). Emits or injects holes into the base 19). In an NPN transistor, when the emitter junction is forward biased and the collector junction is reverse biased, the transistor will operate in the (a). Active region (b). Saturation region (c). Cut-off region (d). Inverted region 20). Which of the following statements is true? (a). FET and BJT, both are unipolar (b). FET and BJT, both are bipolar (c). FET is a bipolar and BJT is unipolar (d). FET is a unipolar and BJT is bipolar UNIT-V 1). Vertical amplifier in CRO is also known as Y-amplifier 2). The shape of a waveform used as the time base is saw tooth waveform 3). The order of voltage required for accelerating the electron beam deflect and sweep is of the order of kv 4). Triggering of the signal in CRO is done to get true representation of input signal 5). The type of electron emission that takes place in a CRT is thermionic emission 6). Scale markings provided on the front side of the CRT screen are called graticules 7). The control knob level in a CRO is used to DC offset voltage adjustment 8). The two types of storage techniques used in analog CROs are Mesh storage,phosphor storage 9). In a cathode ray tube ,the focusing anode is located between pre accelerating and accelerating anodes 10).The source of an electron emission in a cathode ray tube isAverage value barium and strontium oxide coated cathode. 11).An aquadag is used in a CRO to collect a)primary electrons b)secondary electrons c) both primary and secondary d)none. 12).Lissajious patterns are used to measure ---------------- and ------------ with CRO 13).The expression for electrostatic deflection sensitivity SE = ---------------14).In CRT ,the vertical deflection plates are placed a)horizontally b)vertically c)uniformly d)none 15).In CRT,the horizontal deflection plates are placed a)horizontally b)vertically c)uniformly d)none 16).In CRT, the fluorescent screen is coated with a)zinc or the silicate b)zinc tungstate c)zinc sulphate d) zinc. cadmium sulphide. 17). Delay line is used to delay the signal for some time in the horizontal sections. a)True b)False. 18).If a positive potential is applied to the vertical deflection plates, then the beam on the screen moves upwards.a) True b)False. 19)The voltage which varies linearly with respect to time is appled to a vertical amplifier. a)True b)False 20).The time base of an oscilloscope is developed by sawtooth waveform a)True b)False. 21).Display is possible ina CRO, because of a)CRO b)CRT C)power supply d)accelerating mode