* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lesson 5.2 - Townview Education and Social Services
Market penetration wikipedia , lookup
Target audience wikipedia , lookup
Digital marketing wikipedia , lookup
Guerrilla marketing wikipedia , lookup
Neuromarketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing plan wikipedia , lookup
Youth marketing wikipedia , lookup
Multi-level marketing wikipedia , lookup
Integrated marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Marketing mix modeling wikipedia , lookup
Direct marketing wikipedia , lookup
Supermarket wikipedia , lookup
Product planning wikipedia , lookup
Multicultural marketing wikipedia , lookup
Target market wikipedia , lookup
Advertising campaign wikipedia , lookup
Street marketing wikipedia , lookup
Sensory branding wikipedia , lookup
Green marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing strategy wikipedia , lookup
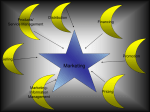
Lesson 5.2: Marketing in a Global Environment Lesson Purpose: Marketing is more than just advertising. Marketing is the creation and maintenance of satisfying relationship. In other words, it’s a specialized form of communication in which companies work together to provide both necessary and convenient products and services. Marketing begins with the planning of a product or service and continues through the production, distribution, promotion, and sale. Lesson Objectives: Research international consumer activity and prepare a feature and benefit analysis for a variety of consumer products and services Select international, consumer product, transportation, service and presentation options Select procurement procedures to accommodate the manufacturing and distribution plan, for example: maquiladoras (twin plant operation) Outline an effective foreign advertising campaign Document the return on international marketing activities by providing a cost-benefit analysis Identify the issues affecting marketing in international trade Identify advertising media used in foreign markets, for example: newspaper, radio, television, Internet and magazine Lesson Content: (1)Marketing is more than just advertising. Marketing is the creation and maintenance of satisfying relationship. In other words, it’s a specialized form of communication in which companies work together to provide both necessary and convenient products and services. Marketing begins with planning a product or service and continues through the production, distribution, sale, and feedback. When marketing in an international environment, procedures and methods might change but the marketing principles stay the same. (2)What is marketing? According to Marketing by Burrow, marketing can be grouped into seven functions: Product/Service Management, Distribution, Selling, MarketingInformation Management, Financing, Pricing, and Promotion. (3)Product/service management is assisting in the design and development of precuts and services that meet the needs of prospective customers. Sony used this function to create the Video Walkman. Distribution is determining the best methods and procedures to use so prospective customers can locate, obtain, and use the organization’s products and services. Hertz is known for its unique distribution in the car rental service: It parks a car at the exit of an airport terminal with the engine running, heated in the winter and cooled in the summer, with all the paperwork ready for a customer’s signature inside. This greatly expedites the customer’s departure from the airport in their rental vehicle. 1 (4)The third function of marketing is selling, which is the direct, personal communications with prospective customers to assess needs and satisfy those needs with appropriate precuts and services. Many professional services firms like law and accounting firms recognize the benefits of training its employees on personal selling in hopes of developing new client bases. Following selling, marketing-information management is obtaining, managing, and using market information to improve decision making and the performance of marketing activities. Electronic scanners used at checkouts at many retail and grocery establishments provide information on purchases so managers can instantly determine what is purchased in order to keep the best assortment of products available for customers. (5)The next marketing function is financing, which is budgeting for marketing activities, obtaining the necessary funding, and providing financial assistance to customers to assist them with purchasing the organization’s products and services. An example of financing in action is the automobile industry, in which manufacturers like General Motors maintain their own financing organization (GMAC) to make loans to consumers available at automobile dealerships. Pricing is establishing and communicating the value of products and services to prospective customers. For example, a bakery manager notices that customers aren’t purchasing certain pastries; as part of the pricing function, she lowers the prices of these pastries and places a sign in the front window advertising them. (6)The final function of marketing is promotion. Promotion is communicating information to prospective customers through advertising and other promotional methods to encourage them to purchase the organization’s products and services. Businesses that sell expensive products like oceanfront condominiums prepare high-quality videotapes that provide information and promote products using audio and video messages. To promote efficiently, the videotapes are sent to carefully selected customers to interest them in purchasing a condominium through a unique type of promotion. Television, radio, billboards, and the Internet can all be effective in promoting different products and services. (7)So how does marketing fit in the global economy? Businesses go into international trade for several reasons. Some do it out of necessity, because competition in their current markets is very intense and sales and profits are decreasing. Others enter the international market because they see foreign firms marketing within their domestic market. The last common reason for global marketing is the increasing demand for products on a worldwide scale. (8)As discussed in earlier lessons, companies can become involved in global marketing in many different ways. From indirect exporting to direct exporting to direct foreign investment to wholly owned subsidiaries, there are many ways to become involved in global trade. But there are several kinds of market information a company must get before jumping into the competitive waters of trade, including, Economic Environment, Consumer Characteristics, Culture and Customs, Technology, and Political and Legal Structures. 2 (9) An economic system is loosely defined as country’s plan for its services, goods produced, and the exact way in which its economic plan is carried out. In general, there are three major types of economic systems prevailing around the world. There are 4 types of economic systems: Market economy, Command economy, Traditional economy, and Mixed economy. (10) A market economy (free enterprise, capitalism) is an economic system in which individuals own and operate the factors of production. The unfettered interaction of individuals and companies in the marketplace determines how resources are allocated and goods are distributed. Individuals choose how to invest their personal resources—what training to pursue, what jobs to take, what goods or services to produce. And individuals decide what to consume. Market economies aim to reduce or eliminate entirely subsidies for a particular industry, the predetermination of prices for different commodities, and the amount of regulation controlling different industrial sectors. The absence of central planning is one of the major features of this economic system. Market decisions are mainly dominated by supply and demand. The role of the government in a market economy is to simply make sure that the market is stable enough to carry out its economic activities properly. (11) A command economy (socialism, communism) is an economic system in which the government owns and operates the factors of production. The state decides how to use and distribute resources. The government regulates prices and wages; it may even determine what sorts of work individuals do. Socialism is a type of command economic system. Historically, the government has assumed varying degrees of control over the economy in socialist countries. In some, only major industries have been subjected to government management; in others, the government has exercised far more extensive control over the economy. (12) A traditional economy (Non-Industrialized, Agrarian societies) is an economic system based upon customs and traditions. Economy is based upon agriculture and hunting. Example of countries that practice this kind of economy are Chad, Haiti, and Rwanda. (13) A mixed economy is an economic system that has features of both market and command economies. Many economic decisions are made in the market by individuals. But the government also plays a role in the allocation and distribution of resources. This system prevails in many countries where neither the government nor the business entities control the economic activities of that country - both sectors play an important role in the economic decision-making of the country. In a mixed economy there is flexibility in some areas and government control in others. Mixed economies include both capitalist and socialist economic policies and often arise in societies that seek to balance a wide range of political and economic views. (14)There are three stages of economic development: preindustrial, industrial, and postindustrial. A preindustrial economy is based on agriculture and raw material development through activities like mining, oil production and cutting timber. The standard of living of its citizens is low, and manufacturing, distribution, and retail systems are in their beginning stage. Leaders in a country at the preindustrial stage must recognize the importance of moving to the next stage. (15)At the next stage, the industrial economy, the primary business activity is manufacturing products. The standard of living of its citizens is higher than in a preindustrial economy, but unlike the preindustrial stage, raw materials remain within the country itself and are converted into products; sometimes more raw materials are imported to keep up with 3 expanding manufacturing plants. Sometimes the finished products are sold within the country itself, other times they are returned to their original country’s market. An example of this is maquiladoras, which are assembly plants in Mexico set up by foreign companies. At Ford Motor Company’s maquiladoras, many of the raw materials not already found in Mexico are imported into the plants, where Mexican workers convert the materials into automobile parts and then assemble parts together to produce a finished product. These finished products, automobiles, are then shipped back to the United States for retail sales. (16)The last type of economy is the postindustrial economy, which is based on a mix of industrial and consumer products and services produced and marketed using high-tech equipment and methods and purchased and sold in the global economy. Most countries with this type of economy have a high standard of living and have many international business opportunities. Its citizens are very aware of products and services available from other countries, and expect businesses in their own country to produce similar goods and services of comparable quality at competitive prices. If domestic businesses cannot satisfy those needs and wants, customers purchase them from companies in other countries. This is best illustrated in the automobile and electronics industries, where consumers force companies to truly compete in a global market. (17)After locating a country with an economy appropriate for its needs, a company must then gather market information. Included in this information gathering are consumer characteristics, like demographic information. Demographic information includes age, income, employment, and education. Businesses need to know where potential customers are located, where they buy products, etc. to best market their products to those customers. After the get this demographic information they take culture and customs into account. This is where communication is crucial, because certain words have very different meanings in some cultures. Another example is punctuality; in some countries being on time for an appointment is a sign of respect; in other countries, being on time is unimportant. (18)The final two market information needs are technology and political and legal structure. Businesses cannot assume that the technology used in their home country is available or used in other countries. Even basic technologies that have existed for many years might be utilized differently in other countries. The best example is the metric system. Because it is used throughout the world, the United States tried to convert to the metric system years ago. Though the conversion was unsuccessful, more people in the U.S. now use the metric system, which plays a significant part in measurement of parts, packages, containers, etc. traded on a global scale. (19)Perhaps the most significant factor effecting the success of international marketing is the political and legal structure in a country. In the recent past, one of the major political structures, communism, was rejected in many central European countries that were formerly part of the Soviet Union. Those countries chose to reorganize their political structures into systems employing more market driven principles. Political stability is important to businesses, because without it ownership and operating procedures can be threatened. There are numerous examples throughout the world of governments being overthrown and businesses owned by foreign companies being destroyed or taken over by the new government. Countries develop laws to regulate businesses, and many of these laws effect international businesses. As discussed in 4 previous lessons, some of these laws protect domestic businesses from foreign competition with tariffs and import quotas. Some countries provide subsidies, which are monies the government give businesses to assist in the development and sale of its products. (20)To develop the right marketing mix when expanding into international markets, businesses need to consider the seven main functions of marketing: product/service management, distribution, selling, marketing-information management, financing, pricing, and promotion. When used in conjunction with the four major marketing information needs, these functions can change significantly from country to country. However, to be successful marketing products and services in a global economy, a company must properly research and correctly implement all these things. 5