* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Section 5.2 – Cells: The Basic Unit of Life Cell Theory: 1. All Living
Survey
Document related concepts
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
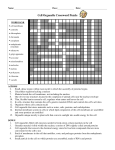
Section 5.2 – Cells: The Basic Unit of Life Cell Theory: 1. All Living things are composed of one or more cells. 2. The cell is the functional unit of life. 3. All cells come from pre-existing cells. Cell: The basic unit of life Organism: An individual living thing Gene: A unit of genetic information that determines a specific characteristic of an individual Organelle: A specialized structure inside plant and animal cells ANIMAL Cell Structures Nucleus: The main organelle of the cell which directs the cell’s activities Cell Membrane: A covering around a cell that controls the movement of materials into and out of the cell Chromosome: A threadlike structure that contains genetic information Cytoplasm: The area of a cell where nutrients are absorbed, transported, and processed Nucleolus: A spherical structure within the nucleus of some cells, probably involved in the making of proteins Mitochondrion: Tiny, oval-shaped organelle that provides cells with energy Centriole: Small protein structure crucial to cell division, found only in animal cells Lysosome: A saclike structure, formed by the Golgi Apparatus, that contains proteins that can break down large molecules and other cell parts Golgi Apparatus: A structure that stores proteins until needed for use inside or outside the cell Endoplasmic Reticulum: A series of “canals” that carry materials throughout the cell Ribosome: Organelle that builds proteins essential for cell growth and reproduction PLANT Cell Structures • • • • • • • • Nucleus Chromosomes Cell Membrane Cytoplasm Mitochondrion Endoplasmic Reticulum Nucleolus Ribosome Cell Wall: The non-living outermost covering of a plant cell Vacuole: An organelle filled with water, sugar, minerals, and proteins Chloroplast: The organelle in a plant cell that contains chlorophyll Structures for Movement: Flagellum: A whiplike tail on the outside of the cell membrane that helps the cell to move Cilia: Tiny, small hairs on an animal cell