* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 1 Slides
Survey
Document related concepts
Social network analysis wikipedia , lookup
Differentiation (sociology) wikipedia , lookup
Social contract wikipedia , lookup
Structuration theory wikipedia , lookup
Social rule system theory wikipedia , lookup
History of sociology wikipedia , lookup
Social Darwinism wikipedia , lookup
Social network wikipedia , lookup
Social exclusion wikipedia , lookup
Sociology of terrorism wikipedia , lookup
Social constructionism wikipedia , lookup
Symbolic interactionism wikipedia , lookup
Structural functionalism wikipedia , lookup
Postdevelopment theory wikipedia , lookup
Social group wikipedia , lookup
Sociology of knowledge wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
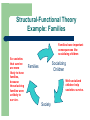
INTRODUCTION Introductory Sociology Edward Brent Copyright © 2016 Edward Brent Sociology l l l l Sociology is the scientific study of social life Sociology studies the relationship between individuals and social structures Sociology includes micro-level analyses focusing on individuals, such as studies of small groups and attitude change Sociology includes macro-level analyses focusing on social structures, such as studies of political and economic systems August Comte (1798-1857) l Born in France and heavily influenced by the French Revolution (1789) l Comte coined the term sociology l Comte proposed applying the scientific methods used in the natural sciences to the social sciences l He called this approach Positivism C. Wright Mills l The sociological imagination is the capacity for individuals to understand the relationship between their individual lives and broad social forces that influence them. The Sociological Imagination l The intersection of history and biography l The relationship between private troubles and public issues l Our lives are not purely personal, but are lived out in the context of social circumstances that affect us all Q1: The relationship between private troubles and public issues is associated with 1. 2. 3. 4. Social control Social structure Conflict theory The sociological imagination RECURRING THEMES l l l l l l Social Control The Social Construction of Reality Inequality Social Structure Knowledge Social Change Q2: Recurring Themes Which of the following is not one of the recurring themes covered in this course? 1. Social change 2. Inequality 3. The mind-body dualism 4. The social construction of reality SOCIAL THEORY Sociology has several theories that we use to explain these recurrent themes Structural-Functional Theory Conflict Theory Interactionist Theory CLASSIC SOCIOLOGISTS Marx Weber Durkheim Mead THEME: SOCIAL CONTROL l l How is social control maintained in a society? How powerful is social control? HOW FAR WOULD YOU GO IN RESPONSE TO SOCIAL CONTROL? SOCIAL CONTROL (Continued) l For example… l Would you let someone take pictures of you naked? l No…not when you were a child, but today? Posture Photos Have you had your posture photos yet? POSTURE PHOTOS Not Just the Few Thousands of students at some of the nation’s most prestigious universities had these posture photos taken, including George Bush, Sr., Hillary Rodham Clinton, and many others. Q3: They serve as their own policemen Which theoretical perspective or concept is most associated with the above phrase? 1. Verstehen 2. Conflict theory 3. Structural functional theory 4. Internalized social control How Can Social Control Be So Powerful? The great majority of social control is internalized social control in which people do things because they believe it is the right thing to do, not because they are forced to do so. - Emile Durkheim INTERACTIONIST THEORY l l l Individuals, though constrained by social circumstances, can make decisions and take actions that influence their own lives and those of others. Symbols are used to communicate meaning between people Emergent properties are important characteristics of groups that cannot be reduced to some simple combination of characteristics of individuals. THEME: THE SOCIAL CONSTRUCTION OF REALITY l People offer a “definition of the situation”--a statement or action that explicitly or implicitly suggests the meaning the actor would like others to attribute to their actions. l Competing definitions of the situation are reconciled to produce a “negotiated order”--a shared meaning of the situation agreed upon by all participants. l Since the meaning of social life is negotiated in a social process among participants, reality is not directly experienced by individuals so much as it is socially constructed. Definition of the Situation Michelangelo’s David She’s cute, but kind of 2dimensional for a senior, and has funny hair Amedeo Modigliani’s Head and Bust in Profile Competing Definitions of the Situation Michelangelo’s David He’s kind of immodest, but nice chest She’s cute, but kind of 2dimensional for a senior, and has funny hair Amedeo Modigliani’s Head and Bust in Profile Negotiated Order After all, it is a toga party Carpe Diem Michelangelo’s David Amedeo Modigliani’s Head and Bust in Profile Is This A Crime? l Is taking this picture a crime? l On November 2, 1995 Cambridge, MA police arrested Toni Marie Angeli for taking photographs of her nude 4-year old son after they were called by photo shop employees who developed the film. l Yet many families have nude photographs of young children taken in bathtubs, playing outside, and so on. l Mrs. Angeli claimed she was taking the photographs for a photography class at Harvard University. l What do you think? l How does this relate to defining the situation and negotiated order? Defining Crime Posters like this appeared on trains and subways early in the 20th Century as part of efforts to criminalize marijuana. - Howard Becker George Herbert Mead(1863-1931) l l l l Son of a New England minister Taught at the University of Chicago Developed Symbolic Interactionist Perspective Believed people can interact by taking the role of the other THEME: SOCIAL STRUCTURE l l l Social structures are enduring, relatively stable patterns of social behavior Social structures constrain social behavior, even behaviors we might think are solely individual For example, consider suicide. Suicide is not just a highly personal individual act, but is influenced by social factors Q4: Studied social statistics related to suicide Which sociologist conducted the first study of social statistics related to suicide? 1. Max Weber 2. Emile Durkheim 3. W. E. B. Dubois 4. Karl Marx SUICIDE Suicide Rates per 100,000 by Country, 2001 United States Switzerland Sweden Females Italy Males Germany France Canada Australia 0 5 10 15 20 Source: World Health Organization 25 30 Suicide rates differ systematically by country and Gender SUICIDE Suicide I. Russell Sorgi, 1942 The woman was described as a despondent divorcee. Sorgi’s camera caught her as she plunged to her death. SUICIDE A Bhuddist monk burns himself to death to protest the Diem government in South Vietnam Malcolm Browne, Associated Press, 1963. Emile Durkheim (1858-1917) l l l Social facts are regular patterns of behavior that exist independently of individuals and constrain individual behavior Conducted a classic study in which he found suicide to be related to social integration of individuals in the larger society (e.g., egoistic suicide and altruistic suicide) Developed the structural-functional perspective STRUCTURAL-FUNCTIONAL THEORY Some social structures lead to important consequences So societies that survive are more likely to have these structures Structures Social Consequences The consequences, in turn, help societies survive Society Structural-Functional Theory Example: Families Families have important consequences like socializing children So societies that survive are more likely to have families, because those lacking families were unlikely to survive. Socializing Children Families Well-socialized children help societies survive. Society THEME: SOCIAL INEQUALITY There is great inequality both within societies and between societies. POVERTY Death vigil in Sudan Kevin Carter, 1993 After taking this picture, the photographer chased away the vulture. Child Labor in the U.S. in early 20th Century EXAMPLES OF SOCIAL INEQUALITY l Top 10% of U.S. population owns 91% percent of all securities l The average income in the United States is hundreds, even thousands of times, larger than the average income in some developing countries. l The per capita energy consumption in developed countries is more than ten times the per capita consumption in developing countries. Q5: Marx Which theoretical perspective is Karl Marx associated with? 1. Symbolic interactionism 2. Conflict theory 3. Structural functional theory 4. The sociological imagination Karl Marx (1818-1883) l l l l Born in Germany, spent most of his life in Britain Influenced by the Industrial Revolution Believed that human history was the history of class conflict Father of the conflict perspective CONFLICT THEORY l l l Society consists of groups competing for scarce resources. What appears on the surface to be cooperation merely masks the struggle for power. Social structures persist in society because they serve the interests of those who have wealth and power. CONFLICT THEORY bourgeoisie proletariat THEME: KNOWLEDGE l How do we KNOW something? l How do we distinguish scientific knowledge from beliefs? So, is this some vast cosmic intergenerational conspiracy? Or could it be due to chance? THEME: SOCIAL CHANGE l l Social change is a pervasive aspect of social life Social change occurs more quickly in some societies than in others…Why? This statue of Lenin was torn down after the fall of the Soviet Union in 1989 This statue of Saddam Hussein met a similar fate in 2003 Max Weber (1864-1920) l l l l l German son of a successful Protestant entrepreneur Argued modern life was experiencing increasing rationality Traditional organizations were being superceded by bureaucracies The Protestant Work Ethic encouraged the rise of capitalism Social life is based on rational action guided by subjective understanding (verstehen) anchored in shared cultural ideas An Example: College Life Question Concept Illustrated Who’s not here? Inequality (race, gender, class) CLASSROOM BEHAVIOR Social structures (norms,etc.), socialization • what is a classroom? social construction of reality • how should we act? • talking and other disruptions deviance, social control, crowd behavior An Example: College Life (Continued) Question Concept Illustrated What is a university? Roles, Social statuses, organizations, social change Grading knowledge Grading on a curve latent functions, inequality Student subcultures Culture, distinction RECAP l What is Sociology? l Recurrent Themes l Theoretical Perspectives l Founding Sociologists